Genes, Alleles & Other Key Terms in Genetics (WJEC GCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 3400
Key Terms in Genetics
Genes and Alleles
A gene is a short length of DNA found on a chromosome that codes for a particular characteristic (expressed by the formation of different proteins)
Alleles are variations of the same gene
As we have two copies of each chromosome, we have two copies of each gene and therefore two alleles for each gene
One of the alleles is inherited from the mother and the other from the father
This means that the alleles do not have to ‘say’ the same thing
For example, an individual has two copies of the gene for eye colour but one allele could code for brown eyes and one allele could code for blue eyes
Genotype and Phenotype
The phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an organism (seen just by looking - like eye colour, or found – like blood type)
Phenotype occurs as the result of both genotype and environmental influences
Genotype is the combination of alleles that control each characteristic
Alleles can be dominant or recessive
A dominant allele only needs to be inherited from one parent in order for the characteristic to show up in the phenotype
A recessive allele needs to be inherited from both parents in order for the characteristic to show up in the phenotype
If there is only one recessive allele, it will remain hidden and the dominant characteristic will show
Homozygous and Heterozygous
Homozygous is used to refer to genotypes where two alleles of a gene are the same (homo = same)
An individual could be homozygous dominant (having two copies of the dominant allele), or homozygous recessive (having two copies of the recessive allele)
Heterozygous is used to refer to genotypes where the two alleles of a gene are different (hetero = different)
Alleles are often given a lettered code such as Bb or BB or bb to easily represent the genotype
When completing genetic diagrams, alleles are abbreviated to single letters
The dominant allele is given a capital letter and the recessive allele is given the same letter, but lower case
Genotype key terms diagram
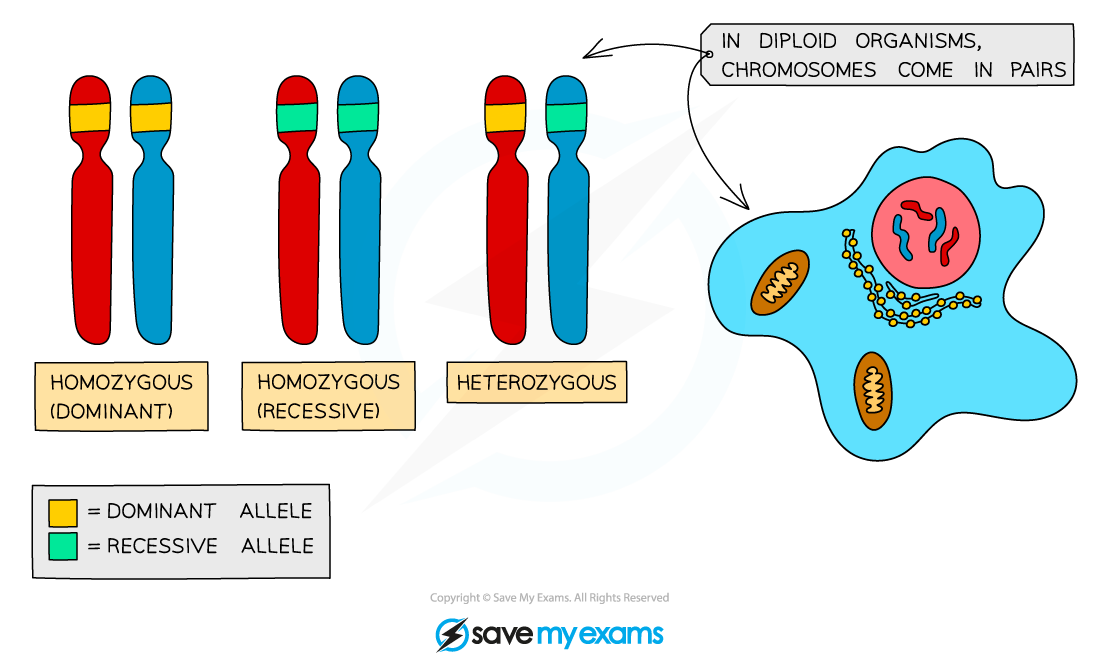
Alleles are different forms of the same gene. You can only inherit two alleles for each gene, and they can be the same (homozygous) or different (heterozygous)
F1 and F2 Generations
The F1 generation is the first generation of offspring produced from two parent organisms
The F2 generation is the offspring produced when two individuals from the F1 generation are crossed
We cannot always tell the genotype of an individual for a particular characteristic just by looking at the phenotype – a phenotype associated with a dominant allele will be seen in both a dominant homozygous and a dominant heterozygous genotype
If two individuals who are both identically homozygous for a particular characteristic are bred together
All of the F1 generations will have exactly the same genotype and phenotype as the parents
We describe them as being ‘pure breeding’
A heterozygous individual can pass on different alleles for the same characteristic each time it is bred with any other individual
It can therefore produce an F1 generation with a different genotype and phenotype to the parents
Heterozygous individuals are not pure-breeding
If a homozygous dominant individual is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual
All of the F1 generations are heterozygous
Key Terms & Definitions for Genetic Inheritance Table
Key term | Definition |
|---|---|
Gamete | Sex cells e.g. egg and sperm cells in animals or pollen and ovum in plants |
Chromosome | Thread-like structures of DNA carrying genetic information in the form of genes. Found in the nucleus of cells |
Gene | Short lengths of DNA are found on chromosomes. They code for specific proteins |
Allele | Different versions of a gene |
Dominant | An allele that is always expressed even if only one copy is present |
Recessive | An allele that is only expressed if two copies (and no dominant alleles) are present |
Homozygous | A genotype with two of the same alleles for a particular gene |
Heterozygous | A genotype with two different alleles for a particular gene |
Genotype | The combination of alleles that control a characteristic |
Phenotype | The observable characteristics of an organism that result from genotype and environmental influences |
F1 & F2 generation | F1 is the first generation of offspring from a cross. F2 is the generation of offspring from a cross between two of the F1 generation |
Self-fertilisation or selfing | When the male and female gametes of the same organism fuse to make a zygote e.g. in plants |

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?