Conditions Needed for Photosynthesis (WJEC GCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 3400
Conditions Needed for Photosynthesis
The rate at which photosynthesis occurs is affected by several factors in the environment:
Temperature
Carbon dioxide
Light intensity
Optimal levels of these environmental factors allow photosynthesis to occur at its maximum rate, but any factor that is less-than-optimum can limit the rate of photosynthesis
Temperature
As the temperature of the environment increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases
At low temperatures the kinetic energy of the molecules inside plant cells is limited, so there are few successful collisions between the photosynthesis reactants per unit of time
Increasing temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules, increasing the likelihood of successful collisions, and so allowing the reaction to occur faster
At very high temperatures the enzymes that catalyse photosynthesis can denature, meaning that the complementary shape of the active sites is lost; this causes a steep decline in the rate of photosynthesis
Temperature & photosynthesis graph

As temperature increases, so too does the rate of photosynthesis; this continues until the temperature becomes too high and plant enzymes begin to denature
Light
The higher the light intensity, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
This is because chlorophyll is able to absorb more light energy to power the reactions of photosynthesis
This trend will continue until another factor prevents the rate from increasing further; such a factor could be:
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
Light intensity & photosynthesis graph
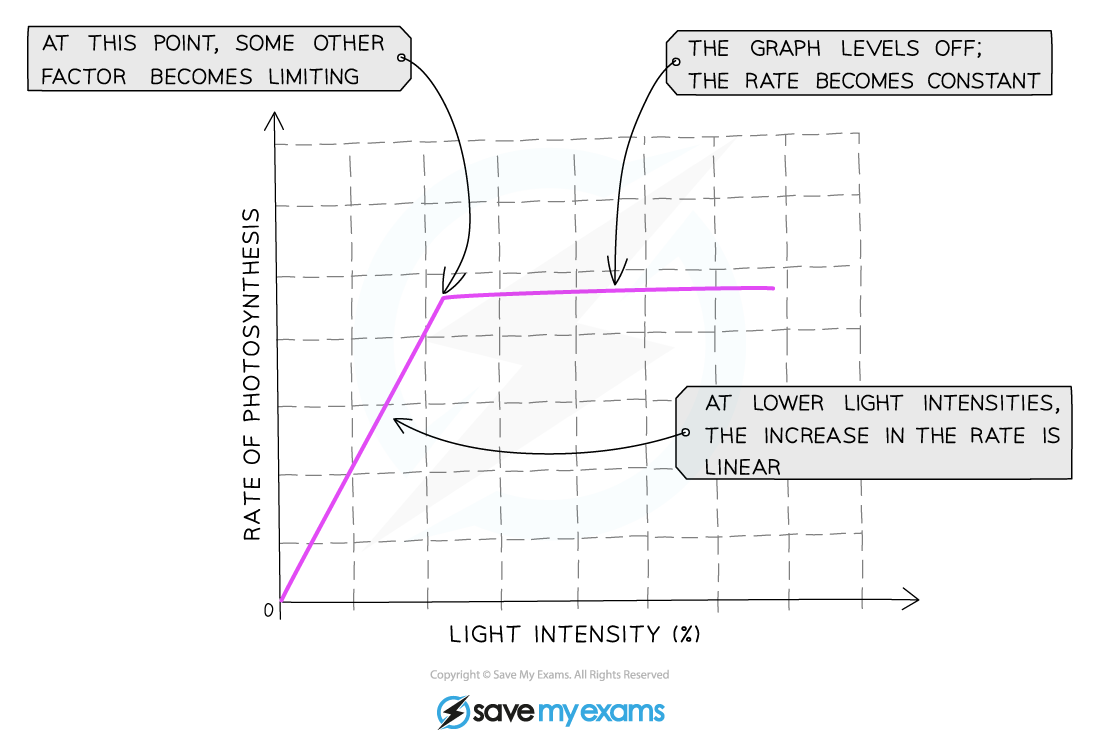
As light intensity increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis; this continues until another factor prevents the reaction from occurring any faster
Carbon dioxide
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, so too does the rate of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials required for photosynthesis
This trend will continue until another factor prevents the rate from increasing further; such a factor could be:
Temperature
Light intensity
Carbon dioxide concentration & photosynthesis graph
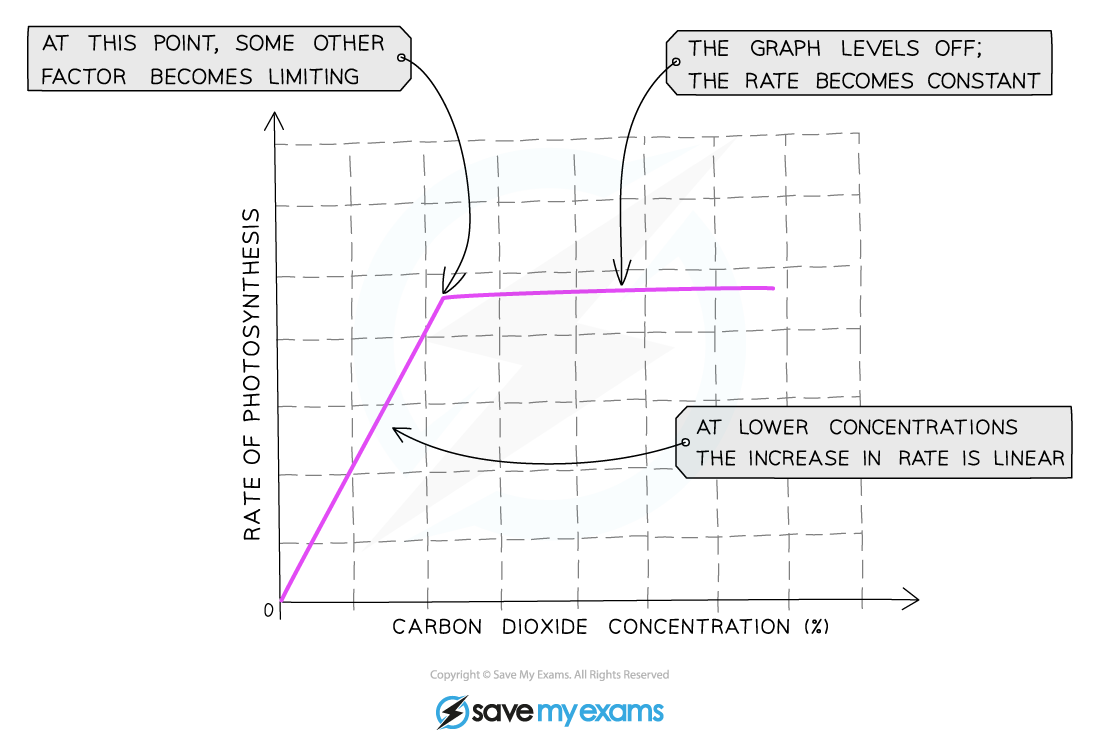
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis; this continues until another factor prevents the reaction from occurring any faster
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
Higher Tier Only
A perfect set of environmental conditions is very rare, meaning that the rate of photosynthesis is usually limited by factors in the environment
These factors are known as limiting factors
A limiting factor can be defined as:
An environmental factor that limits the rate of reaction when it is in short supply
The limiting factors for photosynthesis are:
Temperature
Light intensity
Carbon dioxide concentration
Note that although water is necessary for photosynthesis, it is not considered a limiting factor
If water availability is low enough to limit the rate of photosynthesis then the plant is likely to have closed its stomata, slowing photosynthesis due to carbon dioxide intake
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that when studying a graph of an environmental factor against rate of photosynthesis, any point on the graph at which the line is sloping upwards is a point at which the factor on the x axis is the limiting factor. Once the line levels off we would say that another factor has become limiting.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?