Practical - Sampling Techniques - Quadrats (OCR GCSE Biology A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J247
Ecological Sampling with Quadrats
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies the distribution and abundance of species, the interactions between species, and the interactions between species and their abiotic environment
Ecologists are biologists that study these interactions by investigating ecosystems
One piece of equipment that is routinely used to investigate population size is a quadrat
Quadrats
Quadrats are square frames made of wood or wire
They can be a variety of sizes eg. 0.25m2 or 1m2
They are placed on the ground and the organisms within them are recorded
Plants species are commonly studied using quadrats to estimate the abundance
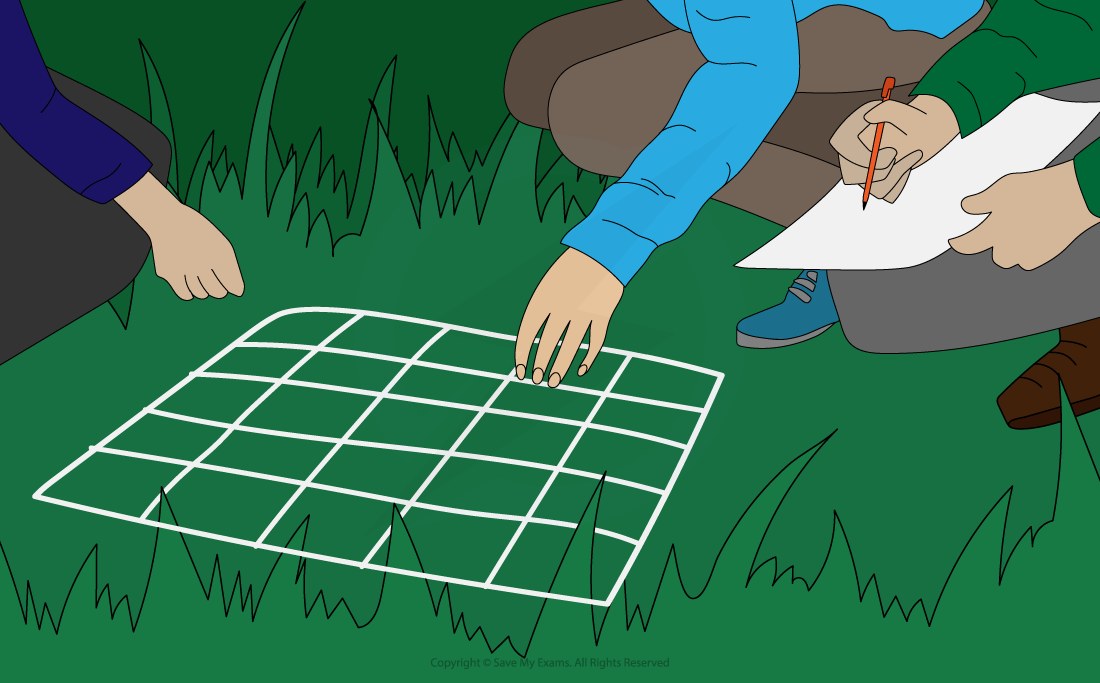
Using a quadrat to investigate population size or distribution
Quadrats can be used to measure abundance by recording:
The number of an individual species: the total number of individuals of a single species (eg. buttercups) is recorded
Species richness: the total number of different species (but not the number of individuals of each species) is recorded
Percentage cover: the approximate percentage of the quadrat area in which an individual species is found is recorded (this method is used when it is difficult to count individuals of the plant species being recorded eg. grass or moss

How to estimate percentage cover of one or more species using a quadrat
Investigating population size in 2 different areas using quadrats
Apparatus
2 tape measures
Quadrat
Random number generator
Species identification key
Method


How to estimate the population size of a plant species in a survey area. You must repeat steps 1-5 in the second study area.
Results
Once the results have been collected and the averages calculated, we can compare the abundance of the study species in each survey area
Species abundance is likely to be influenced by biotic factors such as:
Competition
Predator-prey relationships
Interactions with other organisms within the food chain or food web
The abundance will also be influenced by abiotic factors such as:
Light intensity
Mineral availability
Water availability
pH
Temperature
Salinity
Limitations
It can be easy to miss individual organisms when counting in a quadrat, especially if they are covered by a different species
Solution: Use a pencil or stick to move leaves carefully out of the way to check if there is anything else underneath
Identifying species may be tricky
Solution: Use a species identification key to identify the species
Sometimes, certain species of plants are too numerous to count
Such as grass plants in a quadrat
Solution: Use notation such as >100 or >>100
Which mean 'greater than 100' or 'much greater than 100'
If an approximate number is needed, use ∼
eg. ∼30 means 'approximately 30'

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?