Evolution Through Natural Selection (OCR GCSE Biology A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Evolution Through Natural Selection
In any environment, the individuals that have the best adaptive features are the ones most likely to survive and reproduce
This results in natural selection, the process is as follows:
Individuals in a species show a range of variation caused by a variety of alleles formed by mutation
When organisms reproduce, they produce more offspring than the environment is able to support
This leads to competition for food and other resources which results in a ‘struggle for survival’
Individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment have a higher chance of survival and more chances to reproduce
Therefore, the alleles resulting in these characteristics are passed to their offspring at a higher rate than those with characteristics less suited to survival
This means that in the next generation, there will be a greater number of individuals with the better adapted variations in characteristics
This theory of natural selection was put forward by Charles Darwin and became known as ‘survival of the fittest’

The peppered moth is a good example of natural selection
Evolution
Natural selection results in a process of adaptation, which means that, over generations, those features that are better adapted to the environment become more common
If the environment does not change, selection does not change which favour individuals with the same characteristics as their parents
However, if the environment changes, or a chance mutation produces a new allele, selection might now favour individuals with different characteristics or with the new allele
So the individuals that survive and reproduce will have a different set of alleles that they pass on to their offspring
Over time, this will bring about a change in the characteristics of the species – it will produce evolution
Evolution is defined as the change in adaptive features of a population over time as a result of natural selection
If two populations of one species evolve to become so different in phenotype that they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring, they have formed two new species
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There are many examples of natural selection but they ALL follow the same sequence described above:
Within a species there is always variation and chance mutation
Some individuals will develop a phenotype (characteristic) that gives them a survival advantage and this allows them to:
live longer
breed more
be more likely to pass their alleles on
Evidence for Evolution
Fossil evidence for the theory of evolution by natural selection
Fossils are preserved remains of organisms or other features left by organisms, such as footprints, burrows and faeces
We can tell from fossils that environments (and the organisms living in these environments) have changed significantly over millions of years
Fossils, as well as the rocks they are found in, can be chemically dated, allowing us to accurately put fossil organisms into a sequence from oldest to youngest (i.e. to see how the organisms changed through evolutionary time)
Fossils also allow us to show similarities between extinct species (i.e. how related they are) and even between now-extinct, ancestral species and present-day species
All this has provided evidence for the gradual change from simple life forms, to more complex life forms and the evolutionary relationships between organisms
Fossil evidence of human evolution
Whilst you do not need to know this example as a specific example for the evidence of evolution through natural selection, it provides a really clear image of how humans have evolved over millions of years
The fossils collected of Ardi, Lucy and Turkana Boy showed progressive physical changes which reinforce that humans and chimpanzees evolved from a common ancestor
There is a large amount of fossil evidence suggesting that modern-day humans (Homo sapiens) evolved from a common ancestor with other apes
For example, fossil evidence shows that humans (Homo sapiens) and chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) evolved from a common ancestor that existed approximately 6 million years ago
Humans and their ancestors are known as hominids
Fossils from several different hominid species have been discovered, all with various characteristics that lie somewhere between apes and humans:
'Ardi' the female fossil hominid of the species Ardipithecus ramidus
Ardi was found in Ethiopia and is 4.4 million years old
Ardi's features are a mixture of those seen in apes and humans. For example:
Her foot structure suggests that she climbed trees (the fossils show she had an ape-like big toe to help grip onto branches)
She had short legs but long arms (more similar to an ape than to a human)
Ardi's brain was around the same size as a chimpanzee's
But Ardi's leg bone structure suggests she walked upright. This theory is supported by her hand bone structure, which suggests she did not use her hands when walking (like apes do)

Ardi - a fossil hominid of the species Ardipithecus ramidus
'Lucy' is the fossil hominid of a female individual of the species Australopithecus afarensis
Lucy was also found in Ethiopia but is less old than Ardi (Lucy is 3.2 million years old)
Lucy's features are more human-like than Ardi. For example:
Lucy's foot structure shows she had arched feet (better adapted to walking compared to climbing) and did not have an ape-like big toe
The size of her legs and arms were still somewhere between those of an ape and those of a human but were less ape-like than Ardi's
Lucy's brain was slightly larger than Ardi's (although still similar in size to a chimpanzee's brain)
Like Ardi, Lucy's leg bone structure suggests she walked upright (but more efficiently than Ardi)
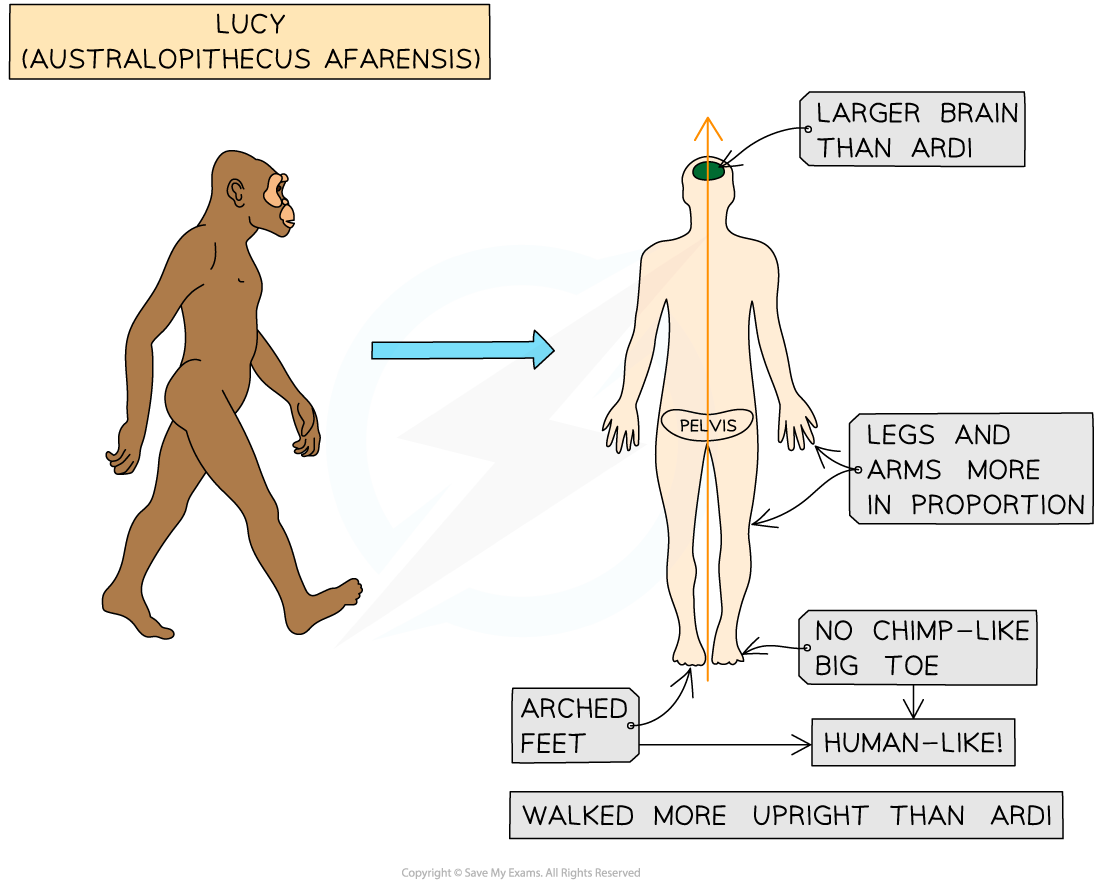
Lucy - a fossil hominid of the species Australopithecus afarensis
'Turkana Boy' is the name given to another hominid fossil skeletons of a male individual of the species Homo erectus
Turkana Boy was found, in Kenya, by a scientist called Richard Leakey in 1984
He is 1.6 million years old (less old than Lucy)
Turkana Boy's features are even more human-like than Lucy. For example:
The size of his legs and arms were much closer to those of a human than of an ape
His brain was much larger than Lucy's (similar in size to a human brain)
The structure of his legs and feet suggests he walked upright even more efficiently than Lucy

Turkana Boy - a fossil hominid of the species Homo erectus
Antibiotic resistance as evidence for evolution by natural selection
An antibiotic is a chemical that can kill or inhibit the growth and reproduction of bacteria
Antibiotics are extremely useful to humans as some bacteria are pathogenic and can cause life-threatening disease
Bacteria reproduce, on average, every 20 minutes and therefore evolution occurs in a much shorter time span
Over time, antibiotic resistance in bacteria has evolved through the following process:
Like all other organisms, within a population, there will be variation caused by mutations
A chance mutation might cause some bacteria to become resistant to an antibiotic (eg penicillin)
When the population is treated with this antibiotic, the resistant bacteria do not die
This means they can continue to reproduce with less competition from non-resistant bacteria, which are now dead
Therefore, the genes for antibiotic resistance are passed on with a much greater frequency to the next generation
Over time the whole population of bacteria becomes antibiotic-resistant because the bacteria are best suited to their environment

Antibiotic resistance in bacteria provides evidence for evolution
Antibiotic resistance is a clear representation of how the process of natural selection drives evolution of a population towards a phenotype which will promote maximum survival and reproductive success
Unfortunately, it also means that diseases which have previously been controlled using antibiotics may no longer be treatable. This could have severe consequences
The Work of Darwin & Wallace
Charles Robert Darwin
Charles Darwin spent five years on a voyage around the world on a ship called HMS Beagle
During the voyage, he studied the plants and animals at all the different locations around the world that the ship visited
He noticed that there was variation in members of the same species
He also noted that those individuals with characteristics most suited to their environment were more likely to survive, reproduce and, therefore, pass on their characteristics to their offspring
To explain his observations, Darwin developed his theory of evolution by natural selection
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace was a scientist who, after conducting his own travels around the world and gathering much evidence, independently developed his own theory of evolution based on the process of natural selection
He published scientific papers on this theory with Darwin in 1858 (Darwin published his book, On the Origin of Species, the following year)
Wallace is best known for:
His work studying the warning colouration of species (particularly butterflies) and how this must be an example of a beneficial characteristic that had evolved by natural selection, as the warning colouration helps to deter predators
Developing the theory of speciation
The impact of Darwin and Wallace on modern biology
The theory of evolution by natural selection is still very important to this day and helps modern scientists and biologists to understand many areas of biology
For example:
Evolution: We now know that all life forms (i.e. all species) change through the process of evolution
Common ancestry: We now know that all life forms on the planet today are descended from a common ancestor
Classification: The knowledge that all life forms are related to some extent has affected the way we classify species (arrange them into groups); modern biologists now do this based on how closely related species are to each other
Biodiversity: The theory of evolution by natural selection eventually led to the realisation that conserving the genetic diversity (the variety in the genes) of a species is very important as it helps species to adapt to changing environments. This knowledge has helped guide conservation projects in protecting endangered species and preventing them going extinct
Seed banks
Seeds will remain dormant as long as conditions promote dormancy, this can be thousands of years
Seed banks are used as a way of storing biodiversity of plant species
They will store seeds from a huge variety of species with a wide variety of alleles
These seeds can be used to grow new plants if wild plants of that species become extinct
Careful selection of seeds is possible to maintain variety so that seeds can be selected for particular advantageous characteristics which might make them more successful when they are germinated e.g. seeds that have alleles for pest resistance or drought resistance

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
