Cell Differentiation (OCR GCSE Biology A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J247
Cell Specialisation
Humans are made from trillions of cells, but only of about 250 different cell types
Specialised cells are cells that have a particular structure and composition of sub-cellular structures
The structural differences between different types of cells enables them to perform specific functions
This allows organisms to operate more efficiently
Cells specialise by undergoing a process known as differentiation
e.g. to develop into a nerve cell the cytoplasm and cell membrane of an undifferentiated cell must elongate to form connections over large distances
Most animal cells (except stem cells) differentiate at an early stage during development to become specialised
They then lose their ability to differentiate
The majority of plant cells never lose the ability to differentiate into specialised cell types
They retain the ability to fully differentiate throughout the life of a plant

Diagram showing the differentiation of a human cell
Examples of Specialised Cells
Examples of Specialised Cells in Animals Table


Ciliated epithelial cells - the hair-like cilia beat to move mucus and any trapped particles

Nerve cells are long with extensions and branches to allow communication with other nerve cells or organs

Red blood cells are biconcave and contain no nucleus to maximise transport of oxygen

Sperm cells have a tail to enable the sperm to move

An egg cell contains a lot of cytoplasm rich in nutrients
Examples of Specialised Cells in Plants Table

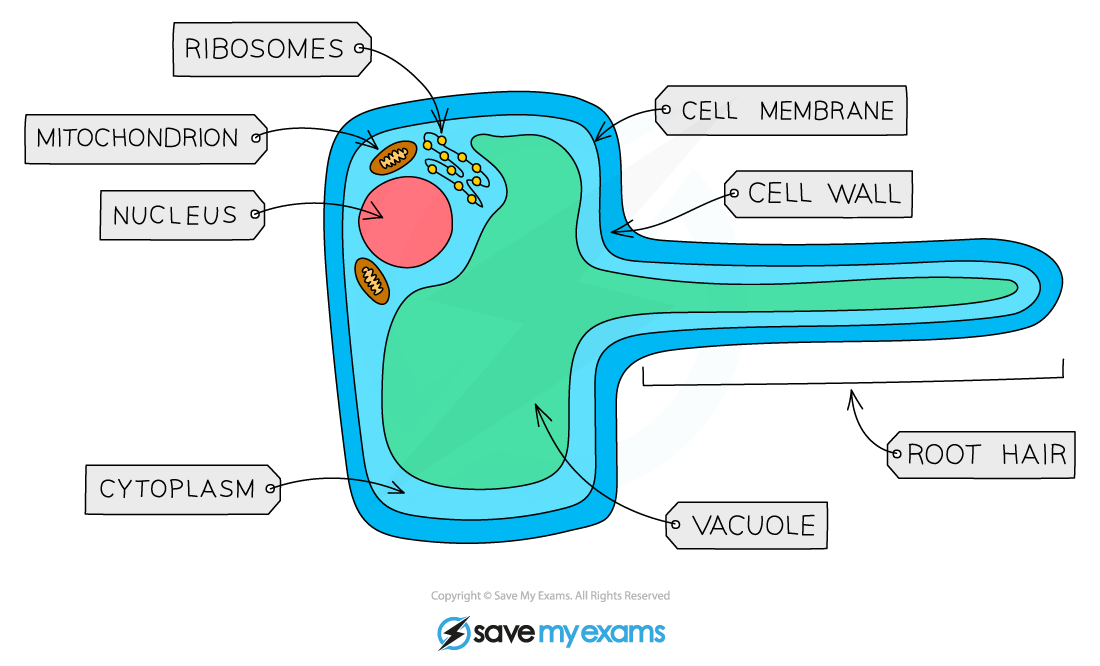
Root hair cell have a large surface area to maximise absorption of water and minerals

Xylem cells lose their top and bottom walls to form a continuous tube through which water moves through

Palisade mesophyll cell contain many chloroplasts to help maximise photosynthesis

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
