Gravitational Field Lines (DP IB Physics) : Revision Note
Point Mass Approximation
For a point outside a uniform sphere, the mass of the sphere may be considered to be a point mass at its centre
A uniform sphere is one where its mass is distributed evenly
The gravitational field lines around a uniform sphere are therefore identical to those around a point mass
An object can be regarded as a point mass when:
A body covers a very large distance compared to its size, so, to study its motion, its size or dimensions can be neglected
An example of this is field lines around planets

Gravitational field lines around a uniform sphere are identical to those on a point mass
Radial fields are considered non-uniform fields
So, the gravitational field strength g is different depending on how far an object is from the centre of mass of the sphere
Newton’s universal law of gravitation is extended to spherical masses of uniform density by assuming that their mass is concentrated at their centre i.e point masses
Representing Gravitational Fields
Gravitational fields represent the action of gravitational forces between masses, the direction of these forces can be shown using vectors
The direction of the vector shows the direction of the gravitational force that would be exerted on a mass if it was placed at that position in the field
These vectors are known as field lines (or 'lines of force')
The direction of a gravitational field is represented by gravitational field lines
Therefore, gravitational field lines also show the direction of acceleration of a mass placed in the field
Gravitational field lines are always directed toward the centre of mass of a body
This is because gravitational forces are attractive only (they are never repulsive)
Therefore, masses always attract each other via the gravitational force
The gravitational field around a point mass will be radial in shape and the field lines will always point towards the centre of mass

The direction of the gravitational field is shown by the vector field lines
The gravitational field lines around a point mass are radially inwards
The gravitational field lines of a uniform field, where the field strength is the same at all points, is represented by equally spaced parallel lines
For example, the fields lines on the Earth’s surface
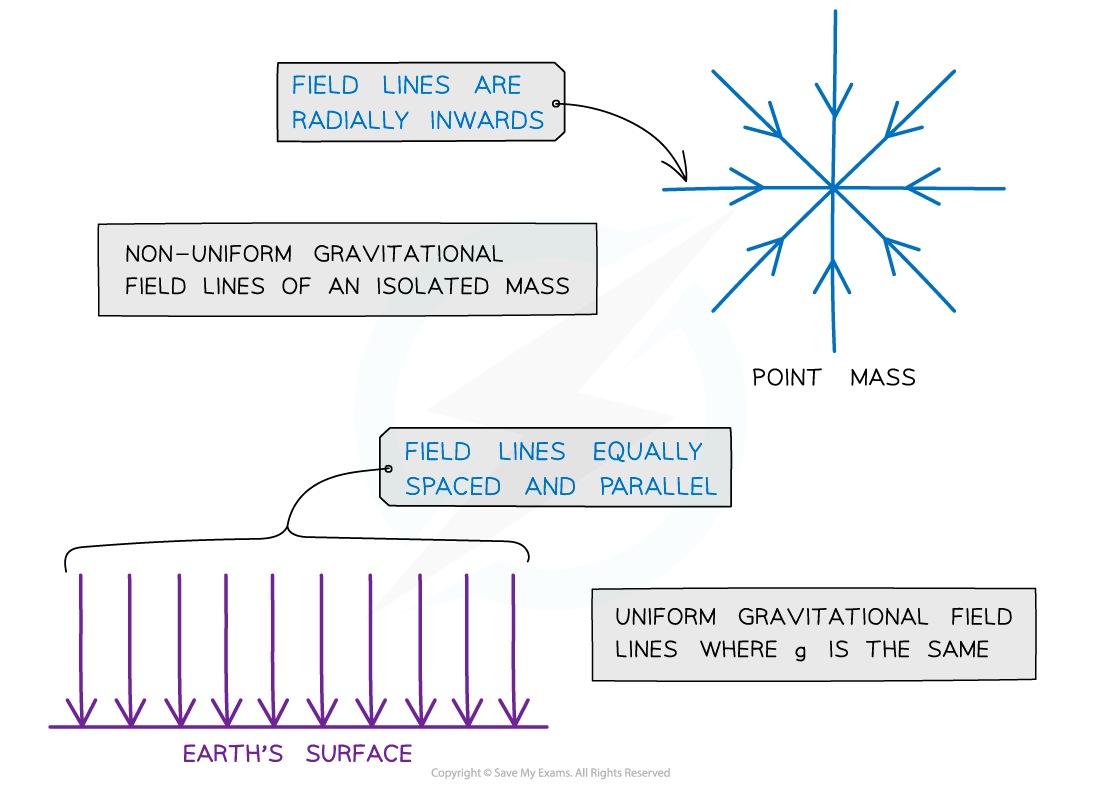
Gravitational field lines for a point mass and a uniform gravitational field
Radial fields are considered non-uniform fields
The gravitational field strength g is different depending on how far you are from the centre
Parallel field lines on the Earth’s surface are considered a uniform field
The gravitational field strength g is the same throughout
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always label the arrows on the field lines! Gravitational forces are attractive only. Remember:
For a radial field: it is towards the centre of the sphere or point charge
For a uniform field: towards the surface of the object e.g. Earth

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
