Nodes & Antinodes (DP IB Physics) : Revision Note
Nodes & Antinodes
A standing wave is made up nodes and antinodes
Nodes are locations of zero amplitude and they are separated by half a wavelength (λ/2)
Antinodes are locations of maximum amplitude
The nodes and antinodes do not move along the wave
Nodes are fixed and antinodes only oscillate in the vertical direction
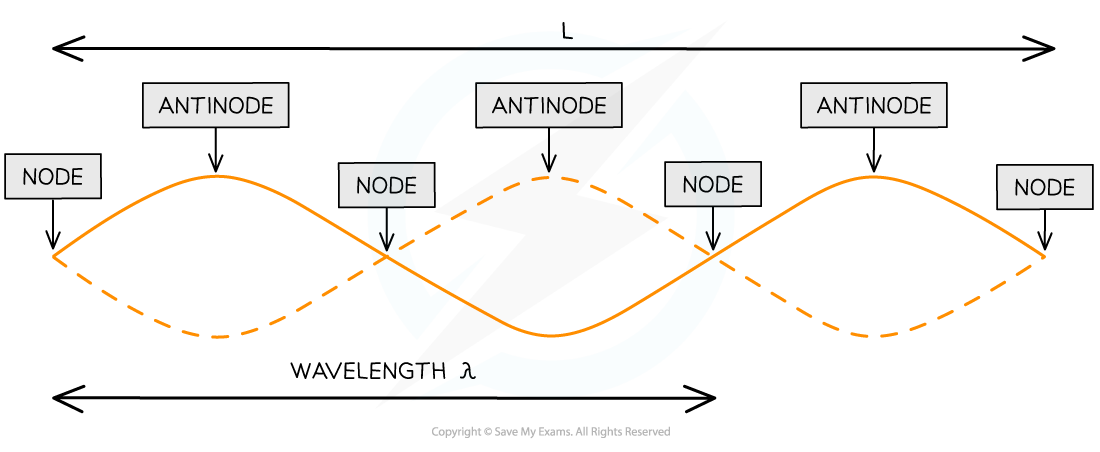
Nodes and antinodes of a stationary wave of wavelength λ on a string of length L at a point in time
The Formation of Nodes and Antinodes
At the nodes:
The waves are in anti-phase meaning destructive interference occurs
The crest of one wave meets the trough of another
This causes the two waves to cancel each other out
At the antinodes:
The waves are in phase meaning constructive interference occurs
The crest of one wave meets the crest of another (same for troughs)
This causes the waves to add together
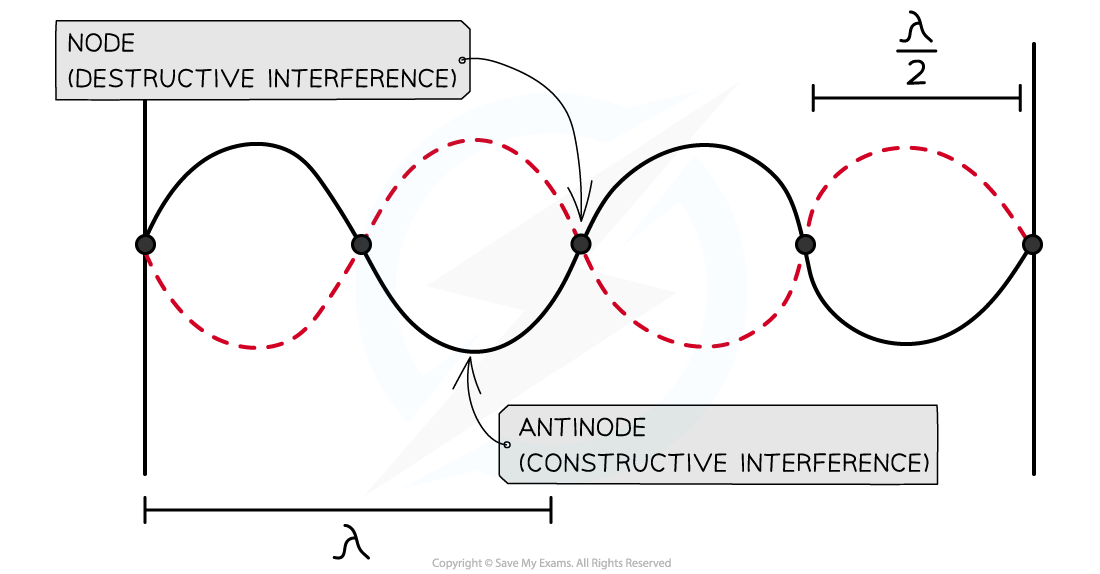
Nodes and antinodes are a result of destructive and constructive interference respectively
Phase on a Standing Wave
Two points on a standing wave are either in phase or in anti-phase
Points that have an odd number of nodes between them are in anti-phase
Points that have an even number of nodes between them are in phase
All points within a "loop" are in phase
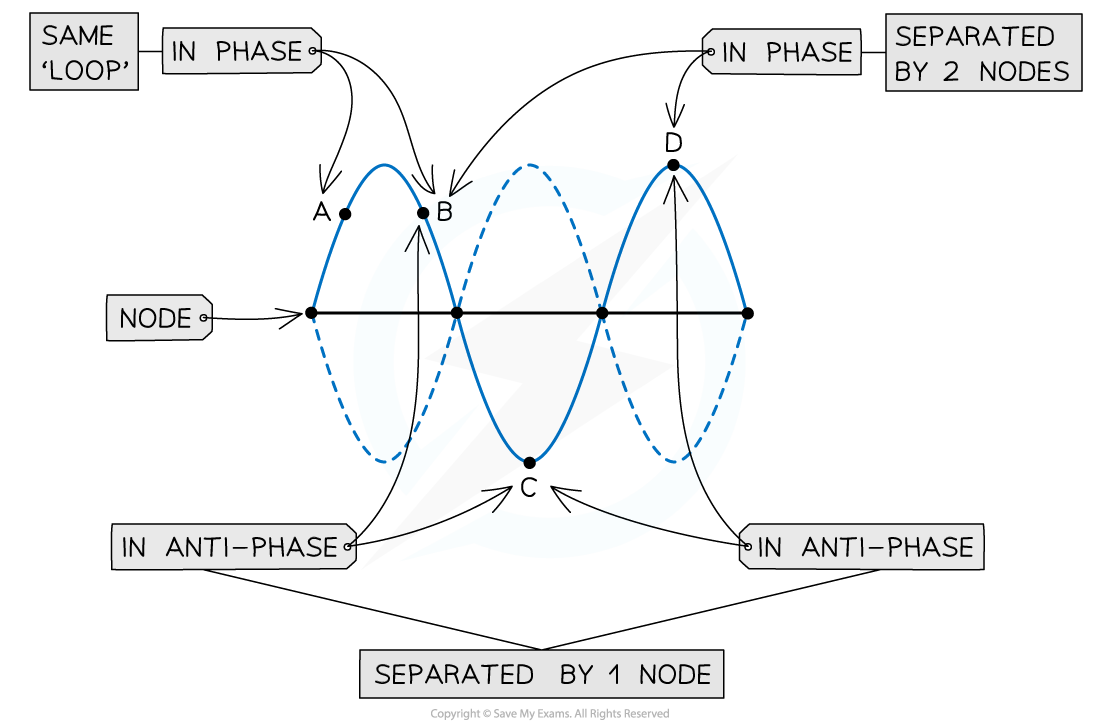
Points A, B and D are all in phase. While points A and D are in antiphase with point C
Constructive and destructive interference can be seen from the phase differences between two waves
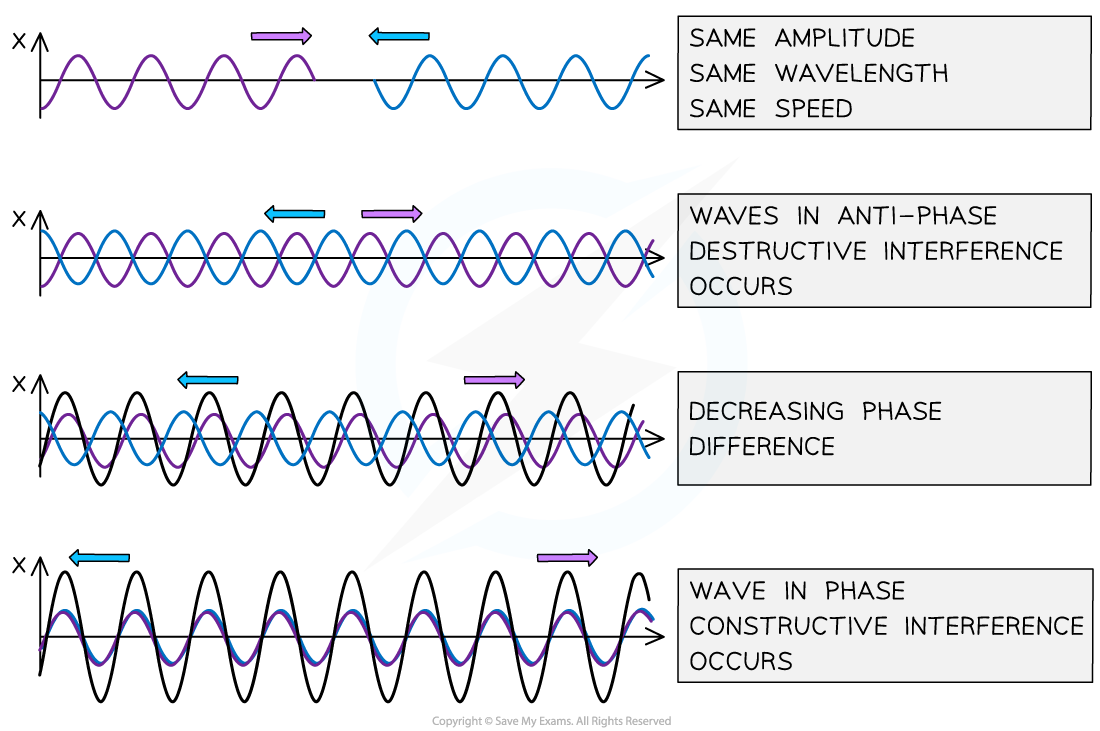
A graphical representation of how stationary waves are formed - the black line represents the resulting wave
Worked Example
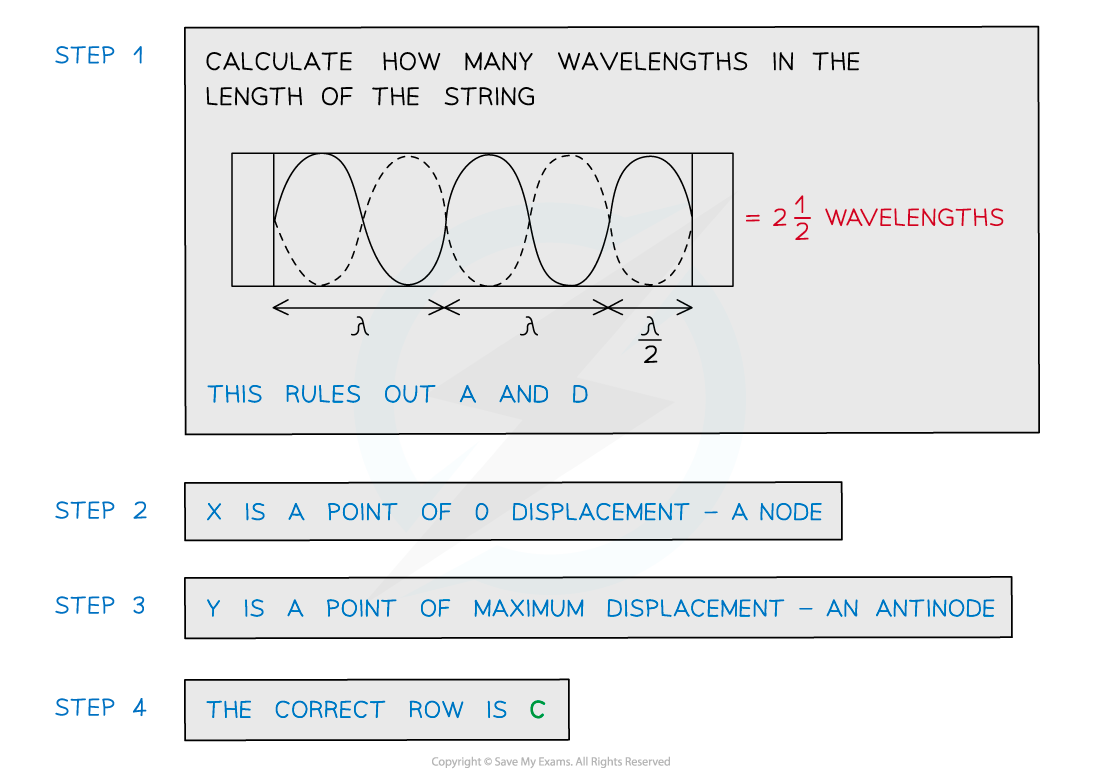
Which row in the table correctly describes the length of L and the name of X and Y?

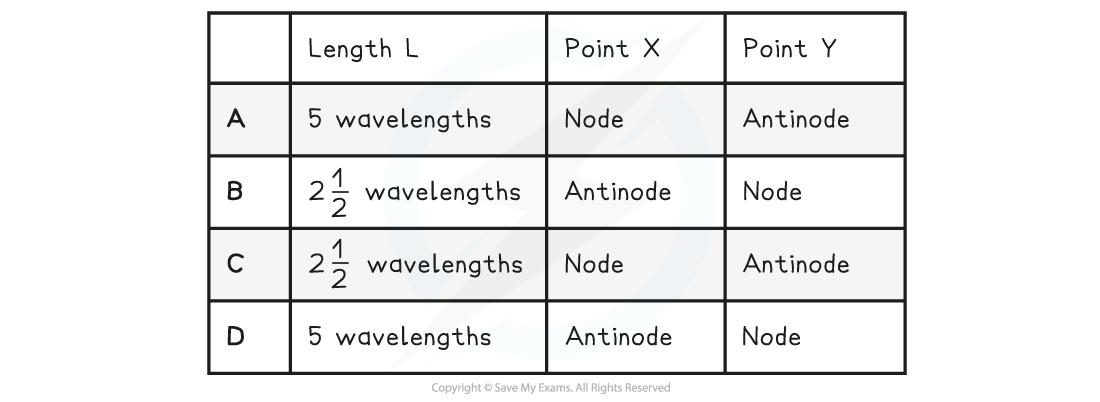
Answer: C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Phase difference on standing waves is different to travelling (progressive) waves.
Phase differences between two points on travelling waves can be anything from 0 to 2π. Between two points on a standing wave can only be in-phase (0 phase difference) or anti-phase (π out of phase).

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
