Apparent Brightness & Luminosity (DP IB Physics) : Revision Note
Apparent Brightness & Luminosity
The apparent brightness b of a star is defined as:
The intensity of radiation received on Earth from a star
Apparent brightness is measured in watts per metre squared (W m−2)
The apparent brightness of a star depends on two main factors:
How much light the star emits
How far away the star is (more distant stars are usually fainter than nearby stars)
How much light the star emits is given by the luminosity L of the star, which is defined as:
The total power output of radiation emitted by a star
Luminosity is measured in units of watts (W)
What is the difference between apparent brightness and luminosity?

The luminosity is the total power output of the star, whereas the apparent brightness is what is measured on Earth
Knowing the luminosity and apparent brightness of a star is useful because it allows us to determine how far away it is from the Earth
This is because
Luminosity tells us how bright the star is at its surface
Apparent brightness tells us how bright the star is as observed from the Earth
Therefore, by the time the radiation from the distant star reaches the Earth, it will have spread out over a very large area
This means the intensity of the radiation detected on Earth will only be a fraction of the value of the star's luminosity
Inverse Square Law of Radiation
A light source which is further away appears fainter because the light it emits is spread out over a greater area
The moment the light leaves the surface of the star, it begins to spread out uniformly through a spherical shell
The surface area of a sphere is equal to 4πr2
The radius r of this sphere is equal to the distance d between the star and the Earth
By the time the radiation reaches the Earth, it has been spread over an area of 4πd2
This is called following an inverse square law
This phrase can be used to refer to any quantity whose intensity reduces by a factor equal to the square of the distance to the observer (e.g. the intensity of ionising radiation follows an inverse square law)
The inverse square law of radiation can be written as:
Where:
b = apparent brightness, or observed intensity on Earth (W m−2)
L = luminosity of the source (W)
d = distance between the star and the Earth (m)
This equation assumes:
The power from the star radiates uniformly through space
No radiation is absorbed between the star and the Earth
This equation tells us:
For a given star, the luminosity is constant
The intensity of the emitted light follows an inverse square law
For stars with the same luminosity, the star with the greater apparent brightness is closer to the Earth
Inverse square law of radiation
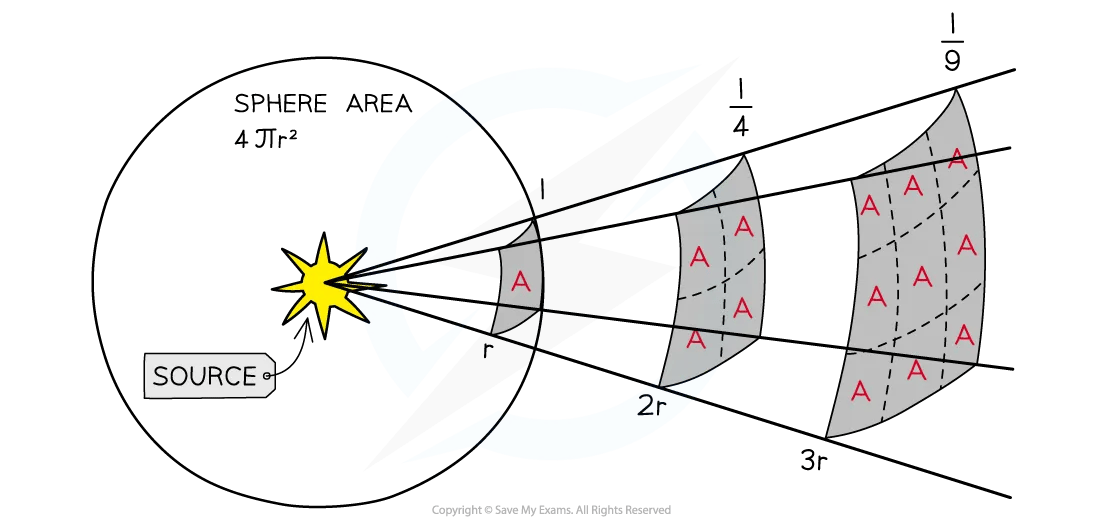
When the light is twice as far away, it has spread over four times the area, hence the intensity is four times smaller
Worked Example
A star has a known luminosity of 9.7 × 1027 W. Observations of the star show that the apparent brightness of light received on Earth from the star is 114 nW m–2.
Determine the distance of the star from Earth.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Luminosity, L = 9.7 × 1027 W
Apparent brightness, b = 114 nW m–2 = 114 × 10–9 W m–2
Step 2: Write down the inverse square law of radiation and rearrange for distance d
Step 3: Substitute in the values and calculate the distance d
distance, d = 8.2 × 1016 m

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
