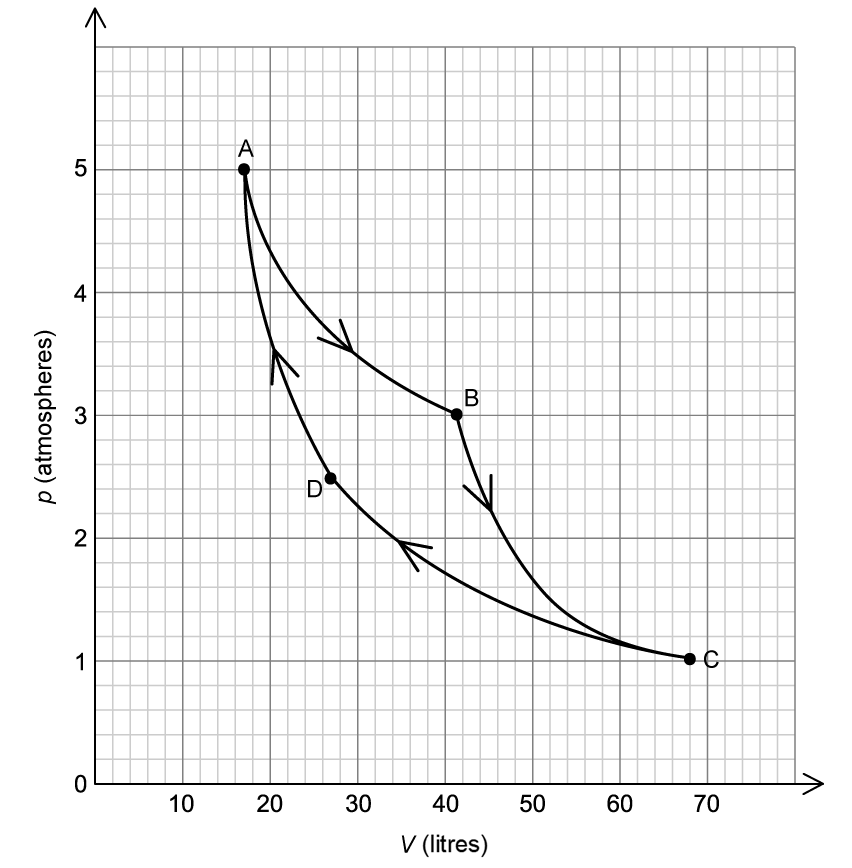
The incomplete pressure volume (pV) diagram represents a Carnot cycle for an ideal monatomic gas.
Process AB is an isothermal change. The grey dashed lines represent isotherms.

Sketch, on the pV diagram, the remaining three processes BC, CD, and CA that the gas undergoes.
State whether work is done on the gas, by the gas, or not at all for the change
(i) C ⇒ D
(ii) B ⇒ C
There are energy changes throughout the cycle.
State the processes in the cycle in which:
(i) there is no change in internal energy
[1]
(ii) no thermal energy is transferred.
[1]
(i) Explain why the work done on the gas during the process CD is less than the work done by the gas during the process AB.
[1]
(ii) State how the net work done by the heat engine after one cycle can be determined from the pV diagram.
[1]
Was this exam question helpful?