Equations for the Doppler Effect of Sound (DP IB Physics): Revision Note
The Doppler Effect of Sound
When a source of sound waves moves relative to a stationary observer, the observed frequency can be calculated using the equation below:
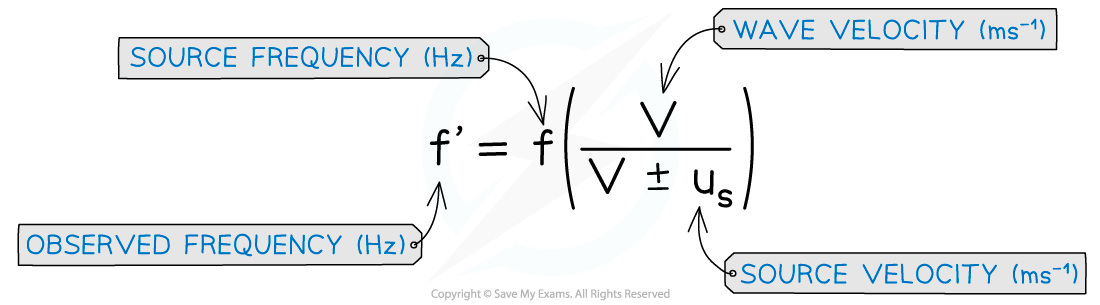
Doppler shift equation for a moving source
The wave velocity for sound waves is 340 ms-1
The ± depends on whether the source is moving towards or away from the observer
If the source is moving towards the observer, the denominator is v - us
If the source is moving away from the observer, the denominator is v + us
When a source of sound waves remains stationary, but the observer is moving relative to the source, the observed frequency can be calculated using the equation below:
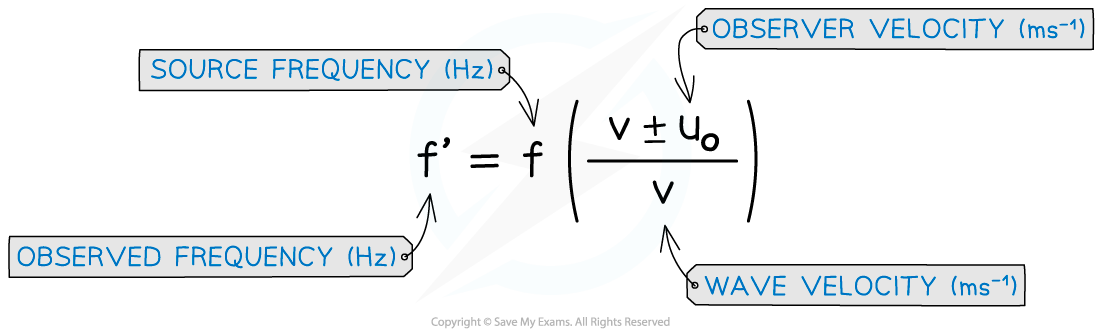
Doppler shift equation for a moving observer
The ± depends on whether the observer is moving towards or away from the source
If the observer is moving towards the source, the numerator is v + uo
If the observer is moving away from the source, the numerator is v − uo
These equations can also be written in terms of wavelength
For example, the equation for a moving source is shown below:
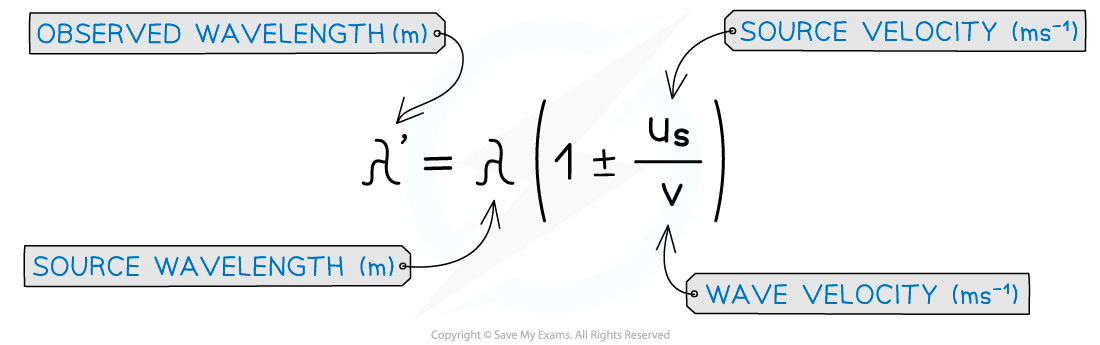
Doppler shift equation for a moving source in terms of wavelength
The ± depends on whether the source is moving towards or away from the observer
If the source is moving towards, the term in the brackets is
If the source is moving away, the term in the brackets is
Worked Example
A police car siren emits a sound wave with a frequency of 450 Hz. The car is travelling away from an observer at a speed of 45 m s−1.
The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
What frequency of sound does the observer hear?
A. 519 Hz
B. 483 Hz
C. 397 Hz
D. 358 Hz
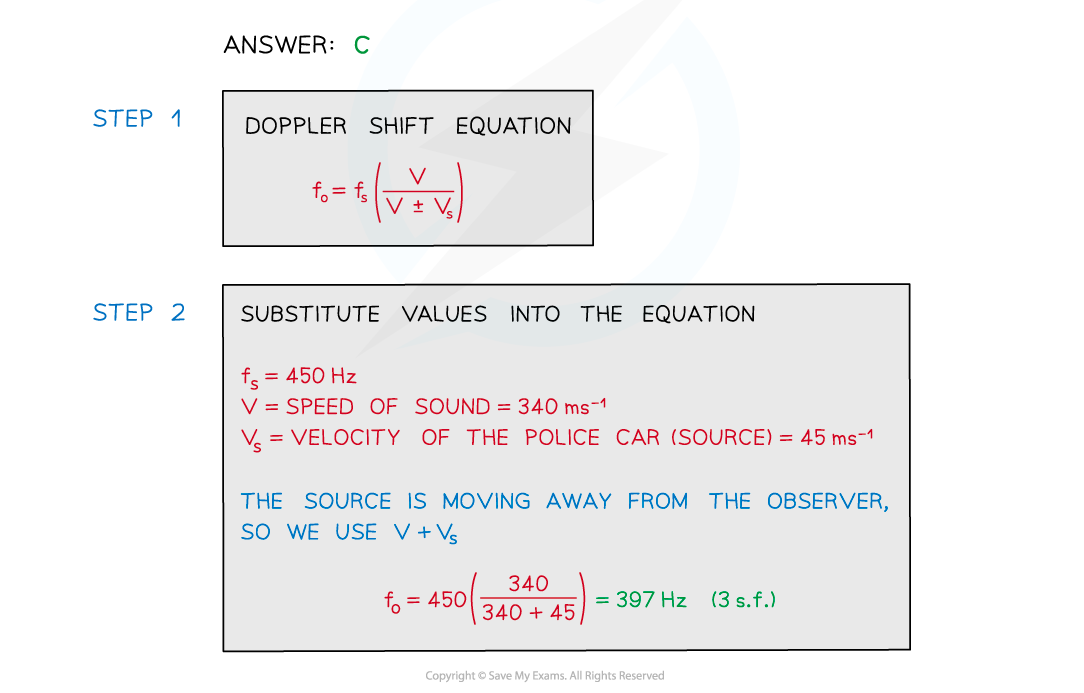
Worked Example
A bank robbery has occurred and the alarm is sounding at a frequency of 3 kHz. The robber jumps into a car which accelerates and reaches a constant speed.
As he drives away at a constant speed, he hears the frequency of the alarm decrease to 2.85 kHz.
Determine the speed at which the robber must be driving away from the bank.
Speed of sound = 340 m s−1
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Source frequency,
= 3 kHz
Observed frequency,
= 2.85 kHz
Speed of sound,
= 340 m s−1
Step 2: Write down the Doppler shift equation
The observer is moving away from a stationary source of sound, so the equation to use is
Step 3: Rearrange to find the desired quantity
Step 4: Substitute the values into the equation
The robber must be driving away at a constant speed of 17 m s−1 based on the change in frequency heard
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Pay careful attention as to whether you need to + or – sign in the relevant equation! If it helps, label the 'observer' and 'source' on in your question on the exam paper.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?