Nuclear Notation (DP IB Physics) : Revision Note
Nuclear Notation
All matter is made from atoms
Atoms are made up of three subatomic particles:
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Structure of the Atom

Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom while electrons orbit the nucleus
Each of these subatomic particles has a mass and a charge
Charge can be expressed in coulombs (C), or units of elementary charge e
Mass can be expressed in kilograms (kg), or in atomic mass units u
Table of properties of subatomic particles
particle | charge / C | charge / e | mass / kg | mass / u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
proton | +1.60 × 10−19 | +1 | 1.673 × 10−27 | 1.007276 |
neutron | 0 | 0 | 1.675 × 10−27 | 1.008665 |
electron | −1.60 × 10−19 | −1 | 9.109 × 10−31 | 0.000549 |
A nucleus can be described using
notation
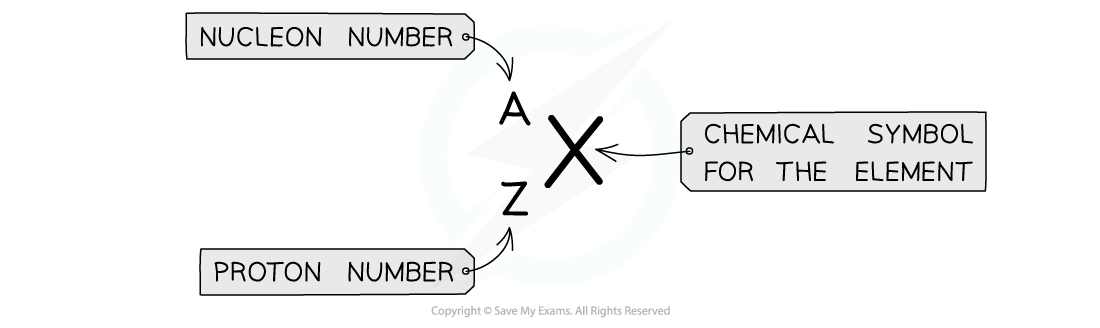
notation is used to describe the constituents of a nucleus
The top number A represents the nucleon number or the mass number
Nucleon number (A) = total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
The lower number Z represents the proton or atomic number
Proton number (Z) = total number of protons in the nucleus
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In Chemistry, you may see nucleon number referred to as mass number and proton number as atomic number. Both of these are valid, just make sure you don't mistake mass number for atomic number, or vice versa.
Make sure you know that the periodic table is ordered by atomic number

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
