Isotopes & Radioactive Decay (DP IB Physics): Revision Note
Isotopes
Atoms of an element are defined by the fixed number of protons in their nuclei
For example, all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton, and all carbon atoms have 6 protons
However, atoms of an element can have different numbers of neutrons
These different versions of elements are called isotopes
Isotopes are defined as:
Nuclei that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
For example, hydrogen has two isotopes, deuterium and tritium
All three isotopes contain 1 proton, but different numbers of neutrons
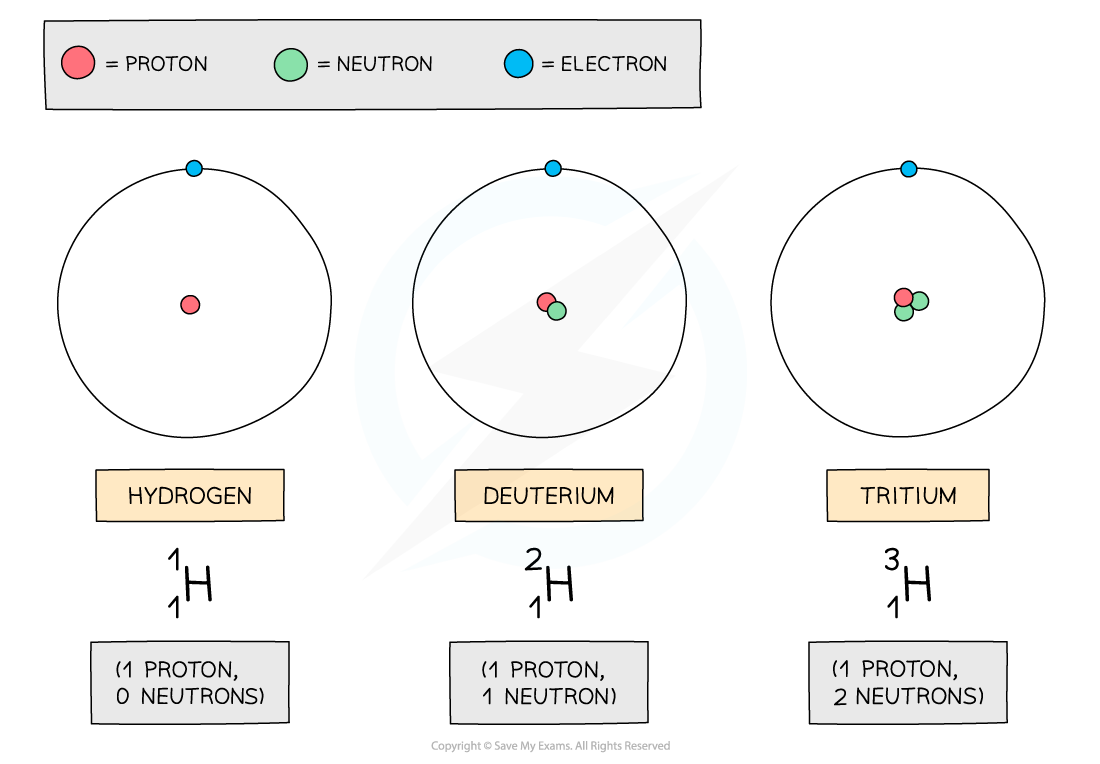
The three atoms shown above are all forms of hydrogen, but they each have different numbers of neutrons
Since nucleon number A includes the number of protons and neutrons, an isotope of an element will have
a fixed proton number, Z
a different nucleon number, A
Some isotopes have an imbalance of neutrons and protons, which makes them unstable
This means they constantly decay and emit radiation to achieve a more stable form
This can happen from anywhere between a few nanoseconds to 100,000 years
Isotopic data
Isotopic data is defined as:
The relative amounts of different isotopes of an element present within a substance
The mass of an element is displayed on the periodic table as relative atomic mass
This takes the masses and abundances of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element into account
Isotopic data is used to determine the relative atomic masses of elements on the periodic table
The relative atomic mass of an element can be calculated using the relative abundance values
The percentage abundance of different isotopes in a sample can be obtained using a mass spectrometer
Table of isotopic data for a sample of oxygen
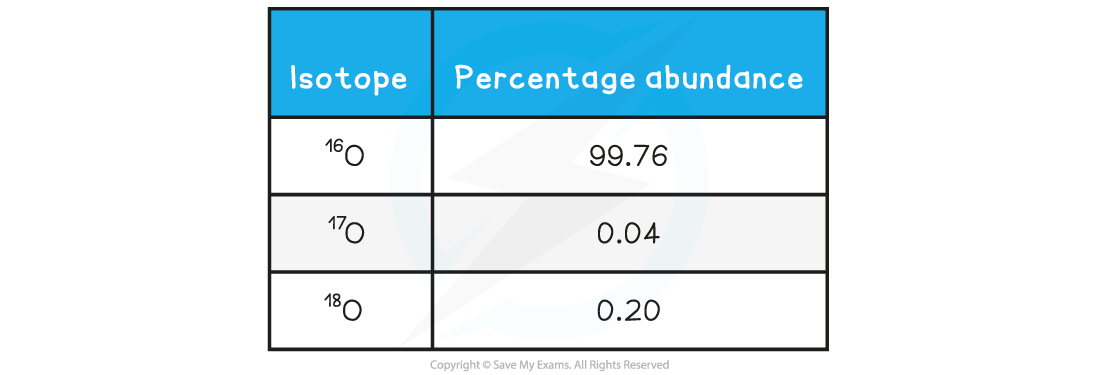
For example, a sample of oxygen may contain three isotopes:
,
and
The relative atomic mass of this sample of oxygen can be calculated using:
(16 × 0.9976) + (17 × 0.0004) + (18 × 0.002) = 16.0044
To two decimal places, the relative atomic mass of the sample of oxygen is 16.00
A common use of isotopic data is carbon dating of archaeological artefacts
This involves using the ratio of the amount of stable isotope carbon-12 to the amount of unstable isotope carbon-14
The age of a sample of dead tissue can be determined by comparing the ratio of these isotopes to the ratio in a sample of living tissue
Worked Example
Which of the following rows shows a pair of nuclei that are isotopes of one another?
|
| nucleon number | number of neutrons |
A. | nucleus 1 nucleus 2 | 39 35 | 19 22 |
B. | nucleus 1 nucleus 2 | 37 35 | 20 18 |
C. | nucleus 1 nucleus 2 | 37 35 | 18 20 |
D. | nucleus 1 nucleus 2 | 35 35 | 20 18 |
Answer: B
In Nucleus 1:
Nucleon number: 37
Neutrons: 20
Protons = 37 − 20 = 17
In Nucleus 2:
Nucleon number: 35
Neutrons: 18
Protons = 35 − 18 = 17
They have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons hence, they are isotopes of each other
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay is defined as:
The spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus to form a more stable nucleus, resulting in the emission of an alpha, beta or gamma particle
The random nature of radioactive decay can be demonstrated by observing the count rate of a Geiger-Muller (GM) tube
When a GM tube is placed near a radioactive source, the counts are found to be irregular and cannot be predicted
Each count represents the decay of an unstable nucleus
These fluctuations in count rate on the GM tube provide evidence for the randomness of radioactive decay

The variation of count rate over time of a sample radioactive gas. The fluctuations show the randomness of radioactive decay
Characteristics of radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is both spontaneous and random
A spontaneous process is defined as:
A process which cannot be influenced by environmental factors
This means radioactive decay cannot be affected by environmental factors such as:
temperature
pressure
chemical conditions
A random process is defined as:
A process in which the exact time of decay of a nucleus cannot be predicted
Instead, the nucleus has a constant probability, i.e. the same chance, of decaying in a given time
Therefore, with large numbers of nuclei, it is possible to statistically predict the behaviour of the entire group

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?