Solving Quadratics (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Solving Quadratic Equations
How do I decide the best method to solve a quadratic equation?
A quadratic equation is of the form
If it is a calculator paper then use your GDC to solve the quadratic
If it is a non-calculator paper then...
you can always use the quadratic formula
you can factorise if it can be factorised with integers
you can always complete the square
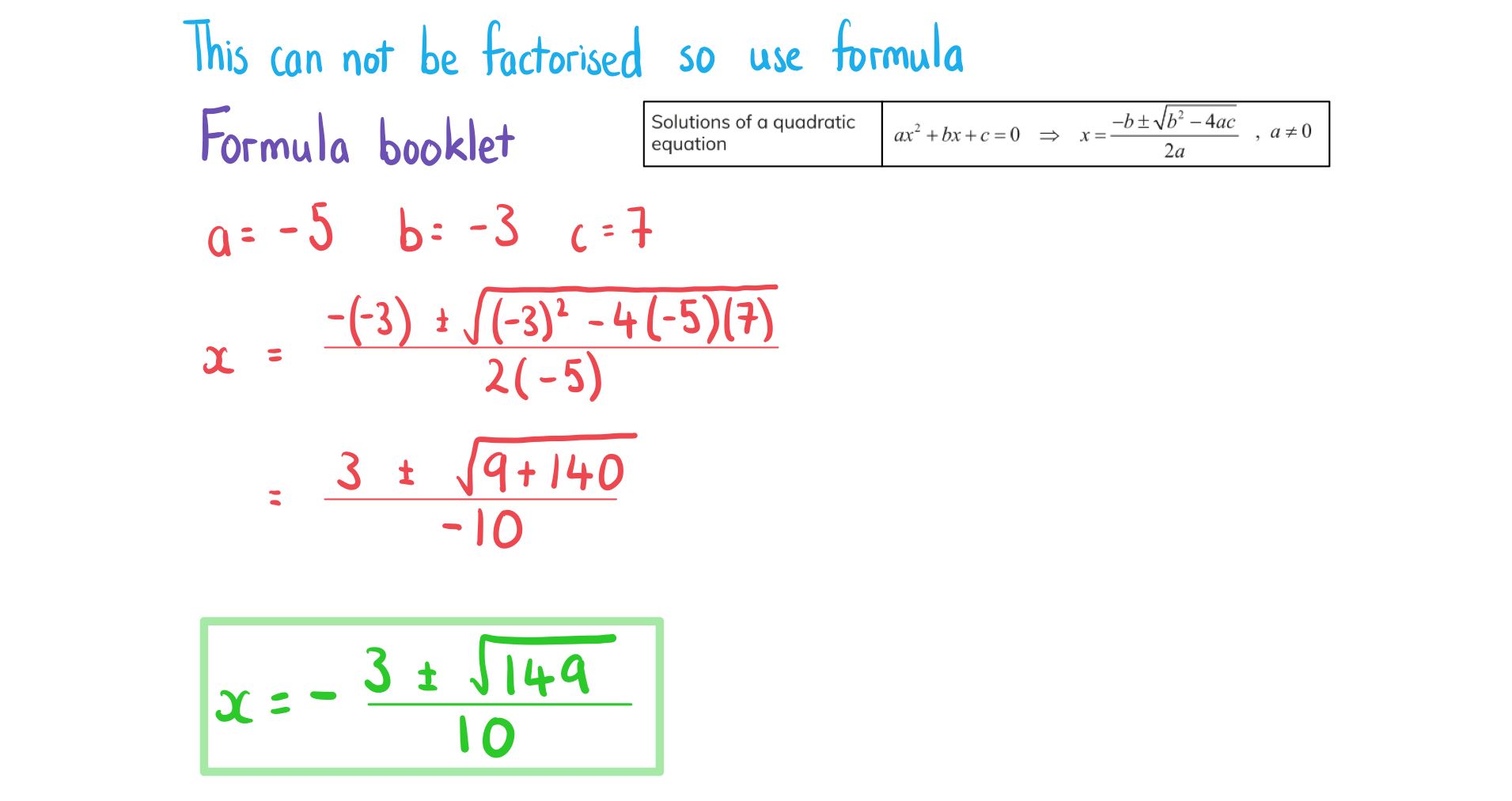
How do I solve a quadratic equation by the quadratic formula?
If necessary rewrite in the form
Clearly identify the values of a, b & c
Substitute the values into the formula
This is given in the formula booklet
Simplify the solutions as much as possible
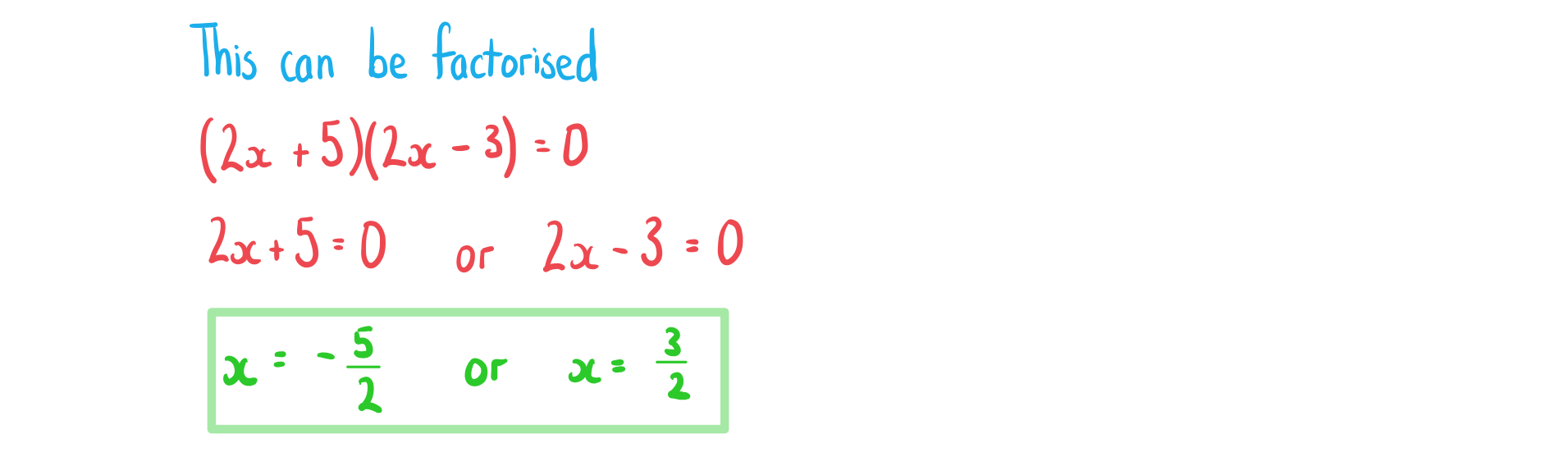
How do I solve a quadratic equation by factorising?
Factorise to rewrite the quadratic equation in the form
Set each factor to zero and solve
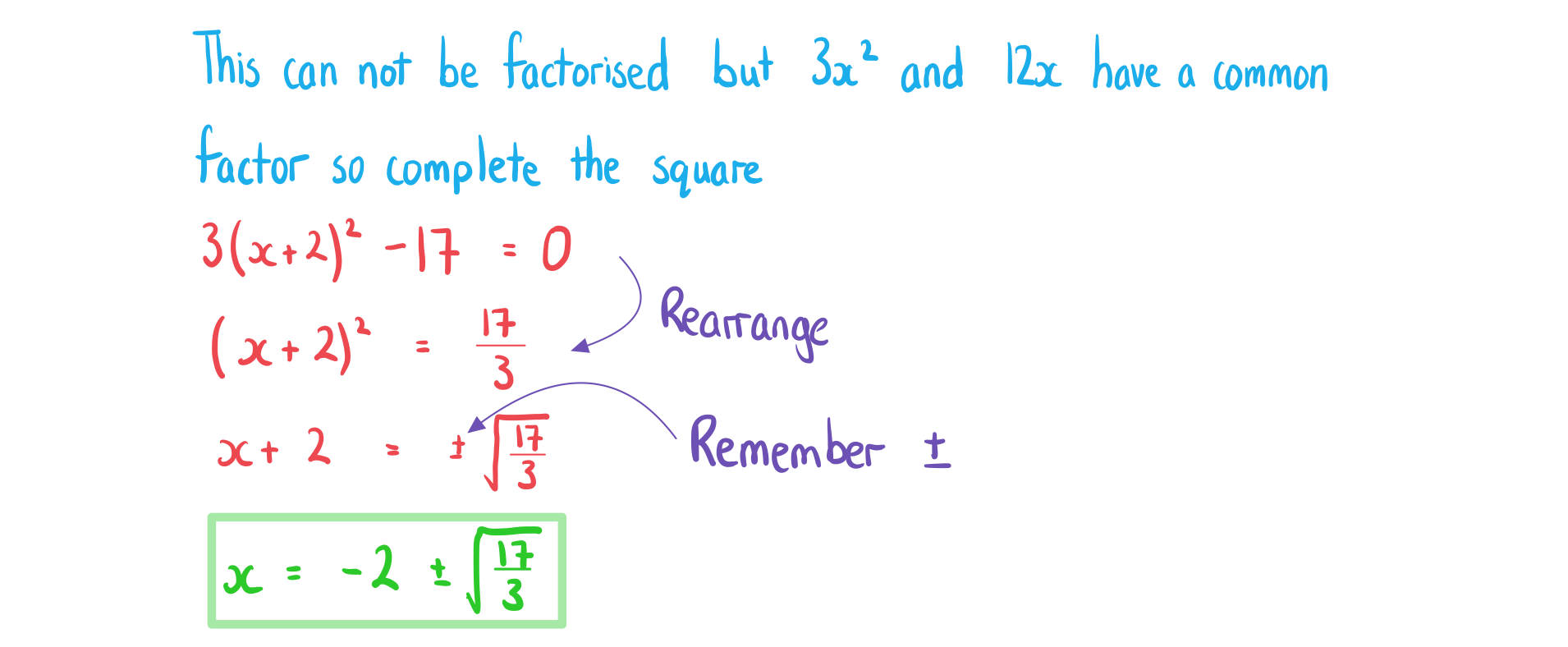
How do I solve a quadratic equation by completing the square?
Complete the square to rewrite the quadratic equation in the form
Get the squared term by itself
If
is negative then there will be no solutions
If
is positive then there will be two values for
Solve for x
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When using the quadratic formula with awkward values or fractions you may find it easier to deal with the "
" (discriminant) first
This can help avoid numerical and negative errors, improving accuracy
Worked Example
Solve the equations:
a) .
b) .
c) .

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
