Inverse Functions (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Inverse functions
What is an inverse function?
An inverse function,
, reverses (or undoes) the effect of
for example
if
then
if
then
Inverse functions can be used to solve equations
e.g. the solution of
is

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Note that the inverse function is not the same as the reciprocal of the function
.
What is the identity function?
The identity function
maps each value to itself
e.g.
Applying a function
to an input
then applying the inverse,
gives back the original input
This also works if you swap the order of
and
i.e. the composite function
has the same effect as the identity function
How do I sketch an inverse function?
The graph of
is a reflection of the graph
in the line
e.g. if
and
then
and
which reflect in
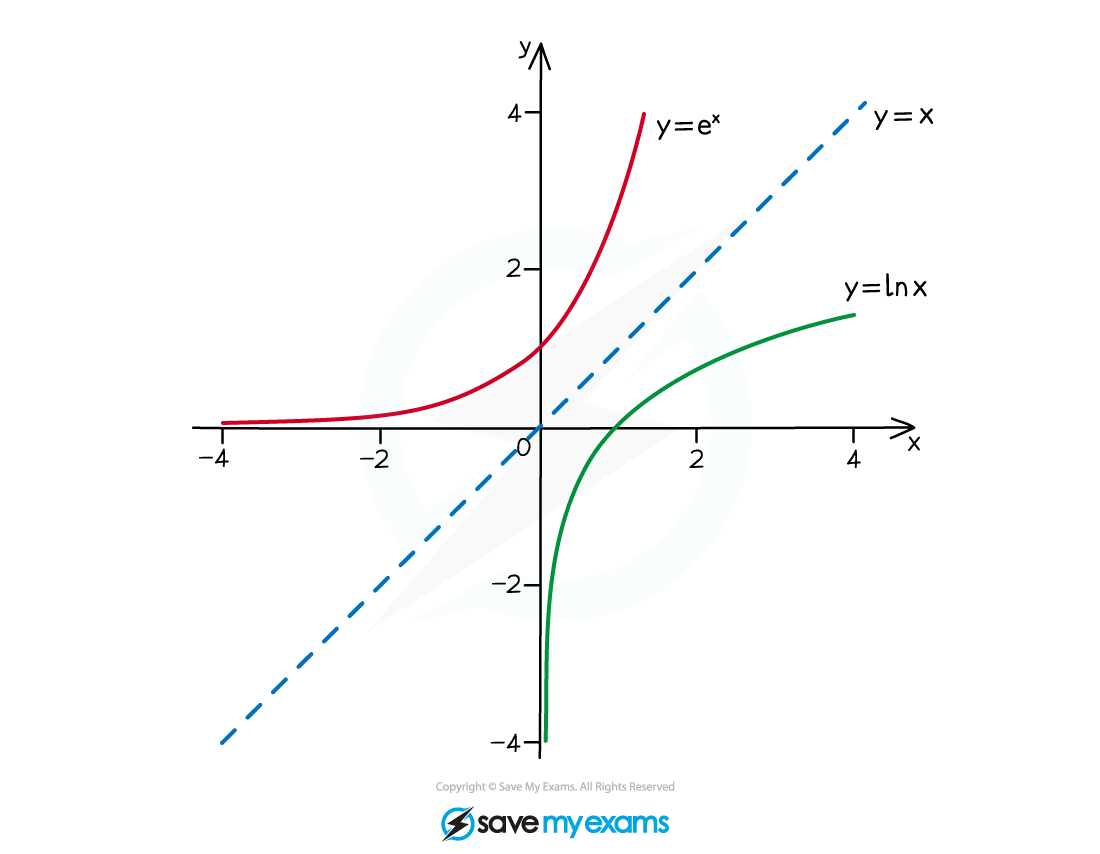
If
intersects
then
also intersects
at the same point
i.e. solutions to either
or
are solutions to
There may be other solutions to
that don't lie on the line
How do I find the inverse of a function?
To find the inverse function using algebra, following these steps:
STEP 1
Swap theand
in
STEP 2
Rearrangeto make
the subject
The result is
How do I find the domain and range of an inverse function?
The domain of a function becomes the range of its inverse
e.g. if
has domain
then the range of
is
The range of a function becomes the domain of its inverse
e.g. if
has range
then the domain of
is
What condition is needed for an inverse function to exist?
For an inverse function
to exist
the original function
must be one-to-one
This ensures
never gives out two or more outputs
which functions are not allowed to do
Worked Example
For the function :
(a) Find the inverse of .
Answer:

(b) Find the domain of .
Answer:

(c) Find the value of such that
.
Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?