Correlation Coefficients (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
PMCC
What is Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient?
Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient (PMCC) is a way of giving a numerical value to a linear relationship of bivariate data
The PMCC of a sample is denoted by the letter
r can take any value such that
A positive value of r describes positive correlation
A negative value of r describes negative correlation
r = 0 means there is no linear correlation
r = 1 means perfect positive linear correlation
r = -1 means perfect negative linear correlation
The closer to 1 or -1 the stronger the correlation
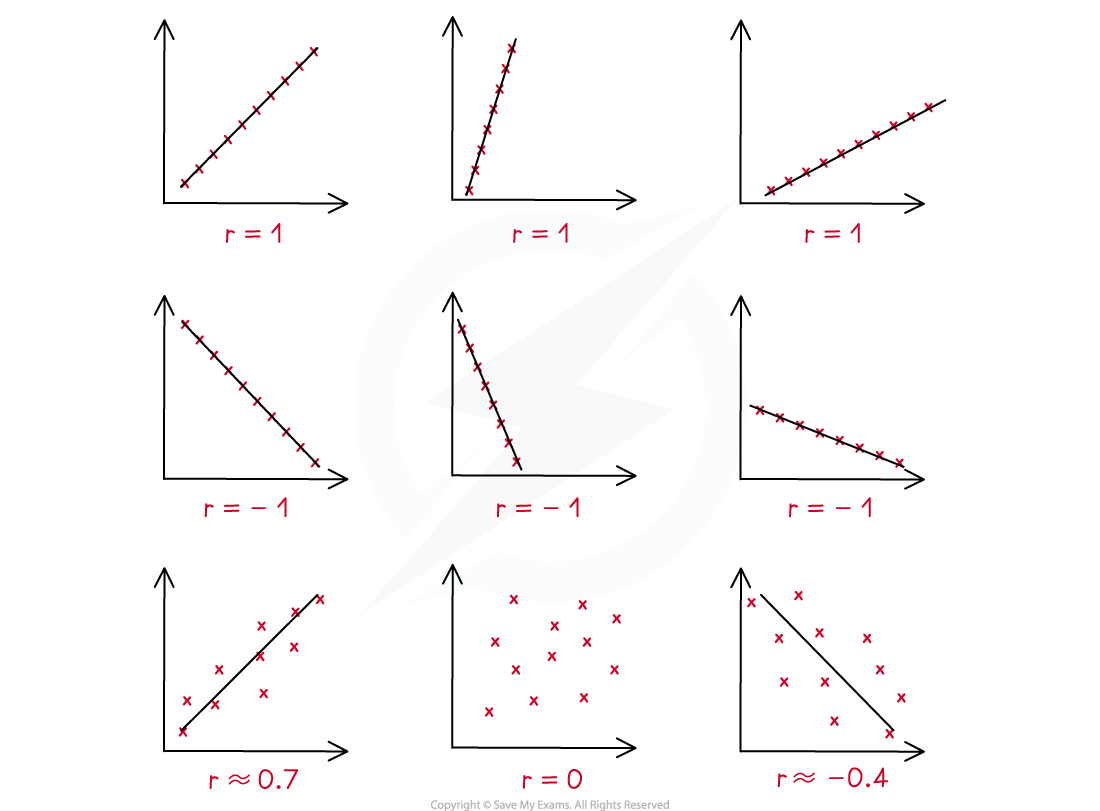
How do I calculate Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient (PMCC)?
You will be expected to use the statistics mode on your GDC to calculate the PMCC
The formula can be useful to deepen your understanding
is linked to the covariance
and
are linked to the variances
You do not need to learn this as using your GDC will be expected
When does the PMCC suggest there is a linear relationship?
Critical values of r indicate when the PMCC would suggest there is a linear relationship
In your exam you will be given critical values where appropriate
Critical values will depend on the size of the sample
If the absolute value of the PMCC is bigger than the critical value then this suggests a linear model is appropriate
Did this video help you?
Spearman’s Rank
What is Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient?
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient is a measure of how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function
Monotonic means the points are either always increasing or always decreasing
This can be used as a way to measure correlation in linear models
Though Spearman's Rank correlation coefficient can also be used to assess a non-linear relationship
Each data is ranked, from biggest to smallest or from smallest to biggest
For n data values, they are ranked from 1 to n
It doesn't matter whether variables are ranked from biggest to smallest or smallest to biggest, but they must be ranked in the same order for both variables
Spearman’s rank of a sample is denoted by
rs can take any value such that
A positive value of rs describes a degree of agreement between the rankings
A negative value of rs describes a degree of disagreement between the rankings
rs = 0 means the data shows no monotonic behaviour
rs = 1 means the rankings are in complete agreement: the data is strictly increasing
An increase in one variable means an increase in the other
rs = -1 means the rankings are in complete disagreement: the data is strictly decreasing
An increase in one variable means a decrease in the other
The closer to 1 or -1 the stronger the correlation of the rankings
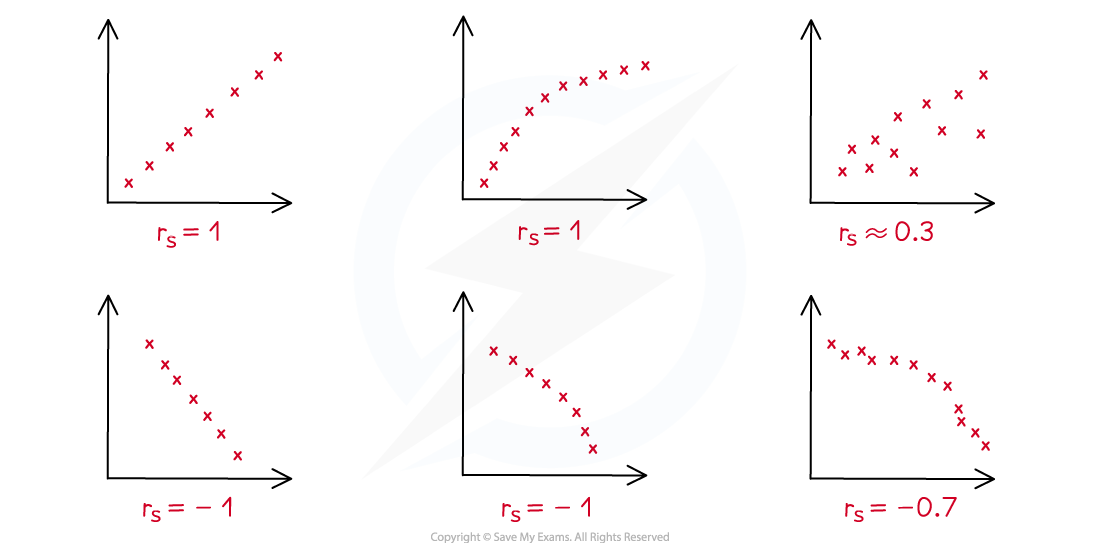
How do I calculate Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (PMCC)?
Rank each set of data independently
1 to n for the x-values
1 to n for the y-values
If some values are equal then give each the average of the ranks they would occupy
For example: if the 3rd, 4th and 5th highest values are equal then give each the ranking of 4
Calculate the PMCC of the rankings using your GDC
This value is Spearman's rank correlation coefficient
Did this video help you?
Appropriateness & Limitations
Which correlation coefficient should I use?
Pearson’s PMCC tests for a linear relationship between two variables
It will not tell you if the variables have a non-linear relationship
Such as exponential growth
Use this if you are interested in a linear relationship
Spearman’s rank tests for a monotonic relationship (always increasing or always decreasing) between two variables
It will not tell you what function can be used to model the relationship
Both linear relationships and exponential relationships can be monotonic
Use this if you think there is a non-linear monotonic relationship
How are Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation coefficients connected?
If there is linear correlation then the relationship is also monotonic
However the converse is not true
It is possible for Spearman’s rank to be 1 (or -1) but for the PMCC to be different
For example: data that follows an exponential growth model
as the points are always increasing
as the points do not lie on a straight line
Are Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation coefficients affected by outliers?
Pearson’s PMCC is affected by outliers
as it uses the numerical value of each data point
Spearman’s rank is not usually affected by outliers
as it only uses the ranks of each data point
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can use your GDC to plot the scatter diagram to help you visualise the data
Worked Example
The table below shows the scores of eight students for a maths test and an English test.
Maths | 7 | 18 | 37 | 52 | 61 | 68 | 75 | 82 |
English | 5 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 17 | 41 | 49 | 97 |
a) Write down the value of Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient, .

b) Find the value of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, .
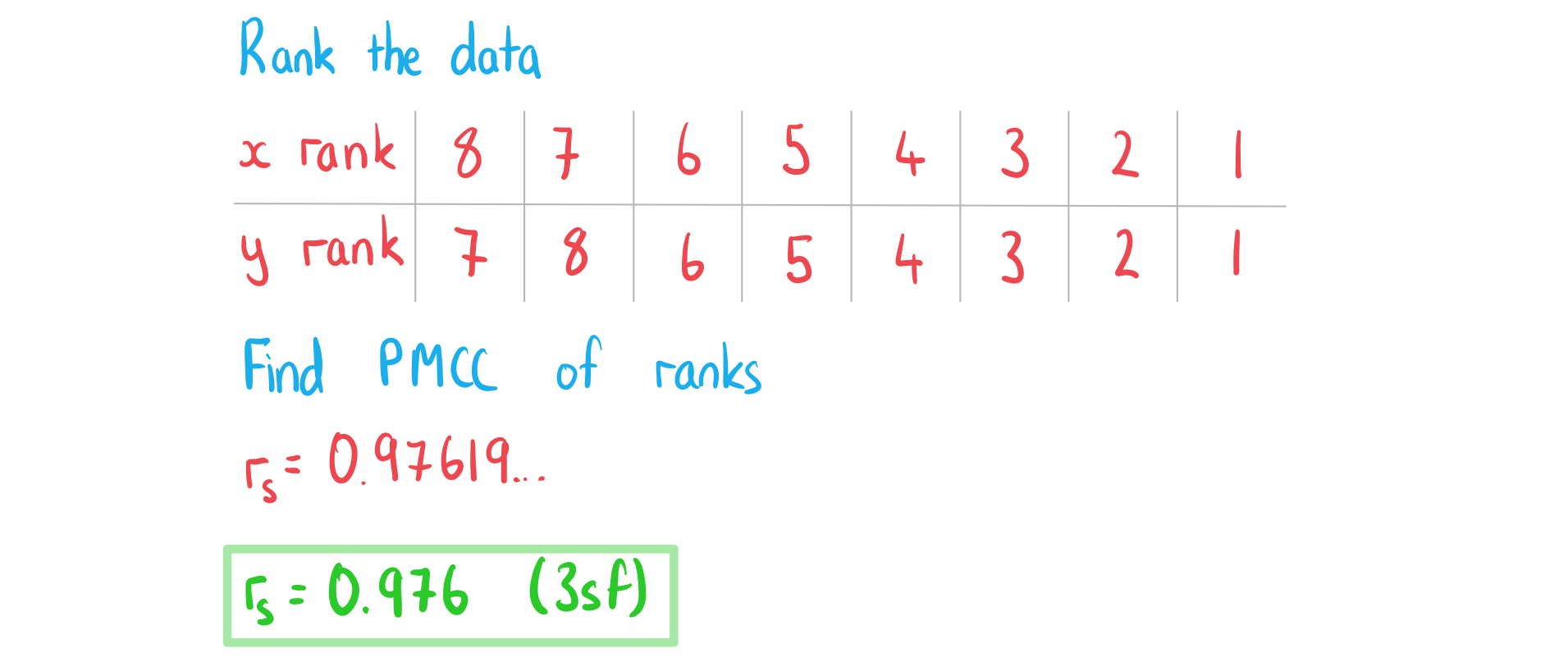
c) Comment on the values of the two correlation coefficients.


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
