Introduction to Graph Theory (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
Graph Theory
What is a graph?
A graph is a mathematical structure that is used to represent objects and the connections between them
They can be used in modelling many real-life applications
e.g. electrical circuits, flight paths, maps etc.
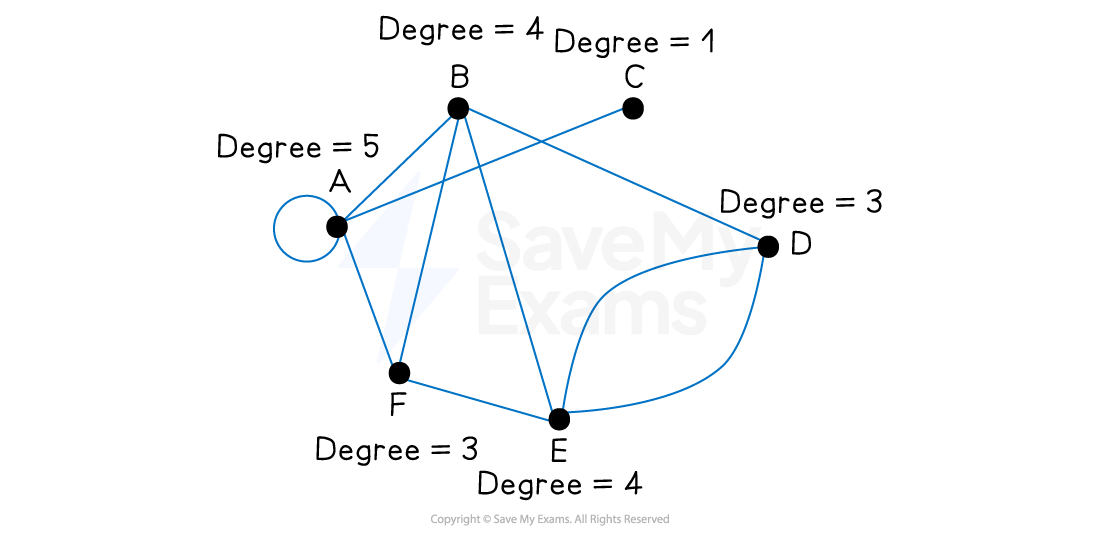
A vertex (point) represents an object or a place
Vertices are labelled with letters or names
e.g. A, B, C, ... or England, Spain, France, ...
An edge (line) forms a connection between two vertices
Adjacent edges share a common vertex
An edge that starts and ends at the same vertex is called a loop
There may be multiple edges connecting two vertices
The degree of a vertex is the number of edges that are immediately connected to it
A loop counts as two edges when calculating the degree
An odd vertex has an odd degree and even vertex has an even degree
Two vertices are adjacent if there is an edge between them
It is possible for a vertex to be adjacent to every other vertex
It is also possible for a vertex to not be adjacent to any other vertex
Two edges are adjacent if they share a common vertex
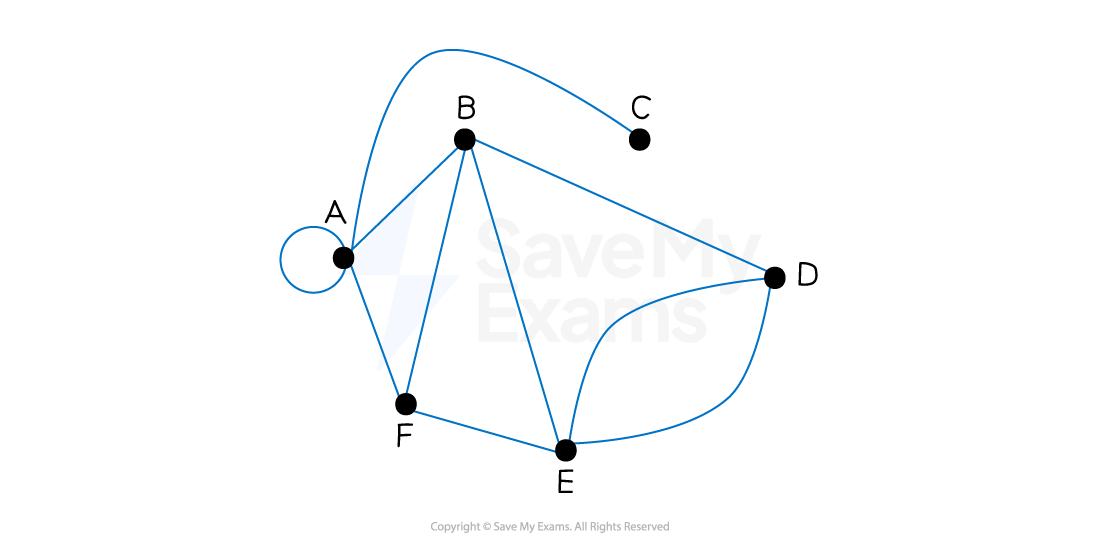
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Do not label an intersection of two edges as a vertex. If possible, it is better to draw a graph without any intersections to avoid confusion. However, this is not always possible.
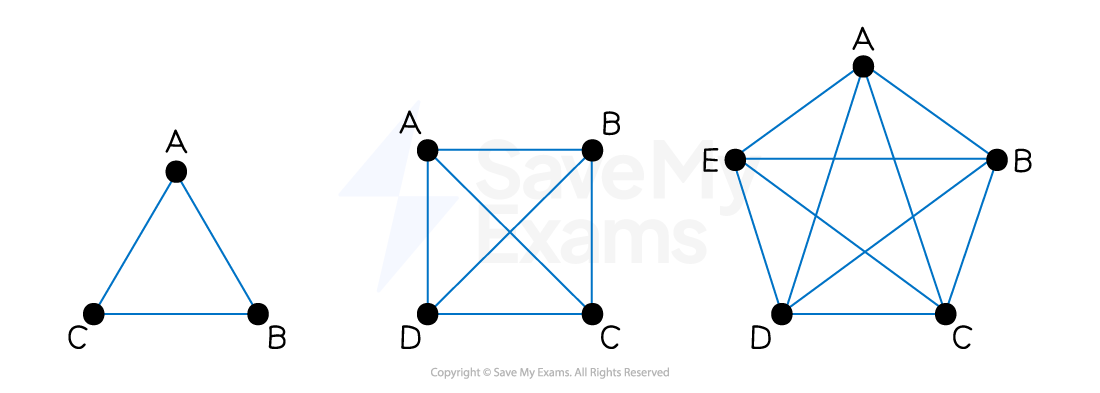
What is a complete graph?
A complete graph is a graph in which each vertex is adjacent to every other vertex
There is exactly one edge between each pair of vertices
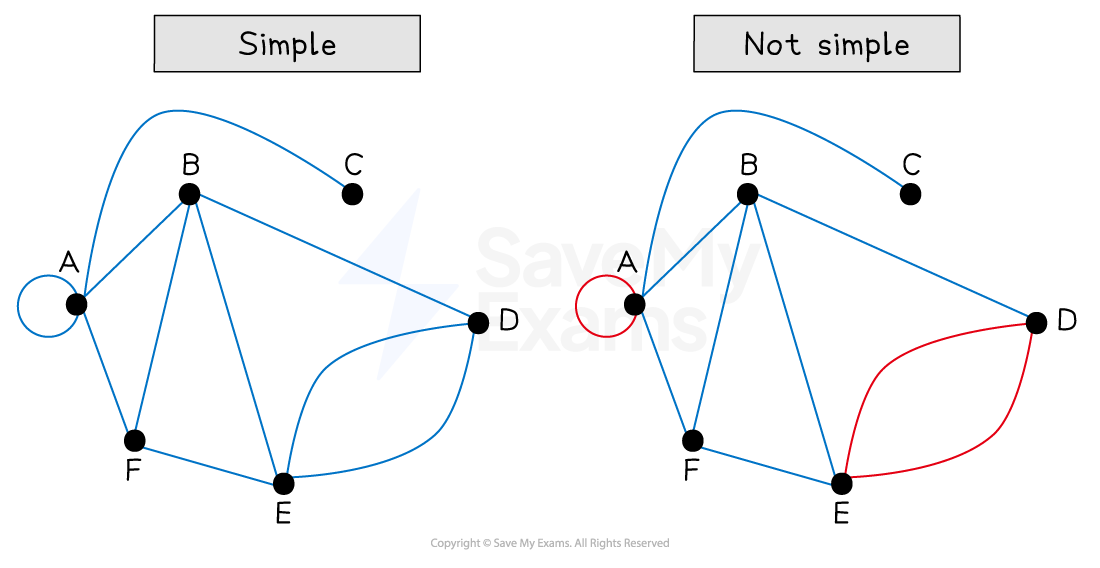
What is a simple graph?
A simple graph contains no loops or multiple edges
What is a weighted graph?
The edges in a weighted graph are assigned numerical values such as distance or money
For a simple graph
The sum of the weights of the edges is known as the weight of the graph
What are walks, trails, paths, circuits and cycles?
A walk is a route through the graph using the edges
It is a sequence of vertices
Each vertex in the sequence is adjacent to the previous one
e.g. ABDBDBAAC is a walk
A walk can be open or closed
It is open if the last vertex is different to the first vertex
It is closed if the last vertex is the same as the first vertex
Trails, paths, circuits and cycles are types of walks
Type of walk | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Trail | No edges are repeated |
|
Path | No vertices are repeated |
|
Circuit | Closed trail
|
|
Cycle | Closed path
|
|
What is a directed graph?
The edges in a directed graph can only be travelled along in the direction indicated
the in-degree of a vertex is the number of edges that lead to that vertex
the out-degree is the number of edges that leave from that vertex
Each edge needs a direction
If an edge between a pair of vertices can be traversed in either direction then
then there should be a repeated edge
each one goes in opposite directions
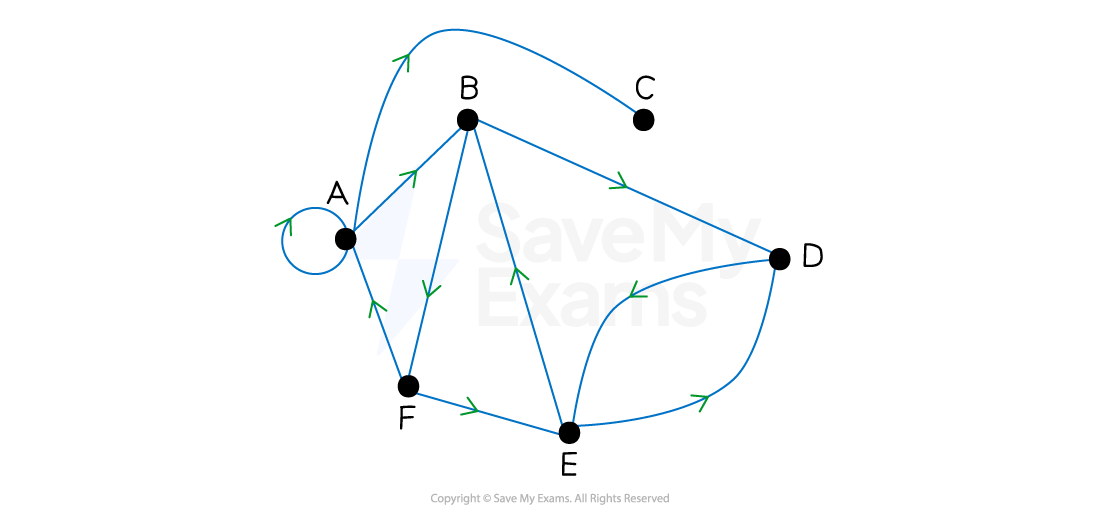
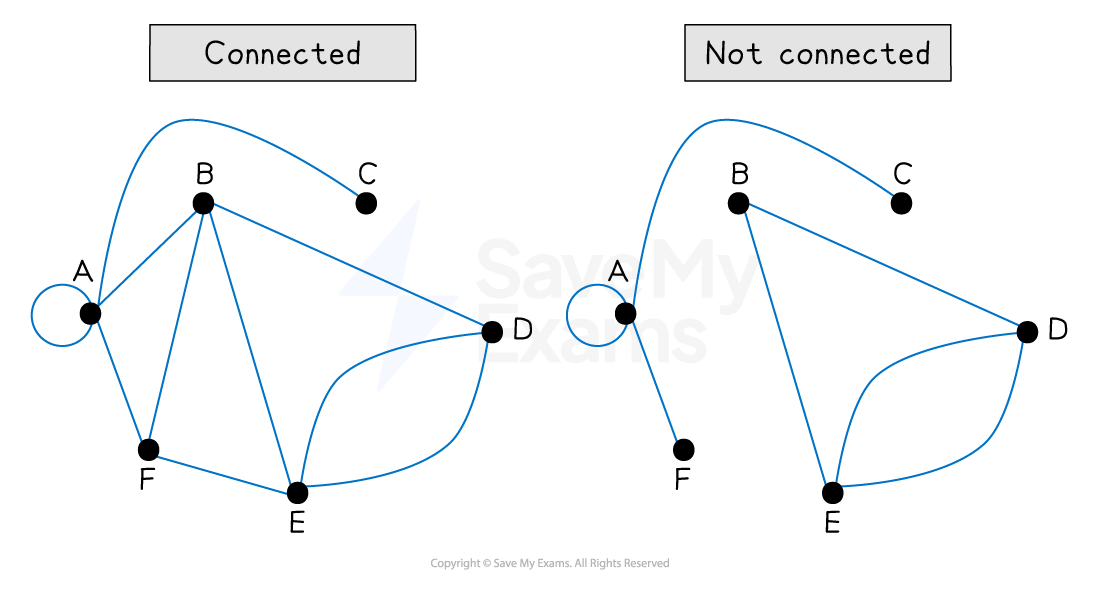
What is a connected graph?
An undirected graph is connected if there is a path between any pair of vertices
This means you can get from any vertex to any other vertex
There does not need to be an edge between each pair of vertices
A directed graph is strongly-connected if there is a path from any vertex to any other vertex
This means you can get from any vertex to any other vertex and back again
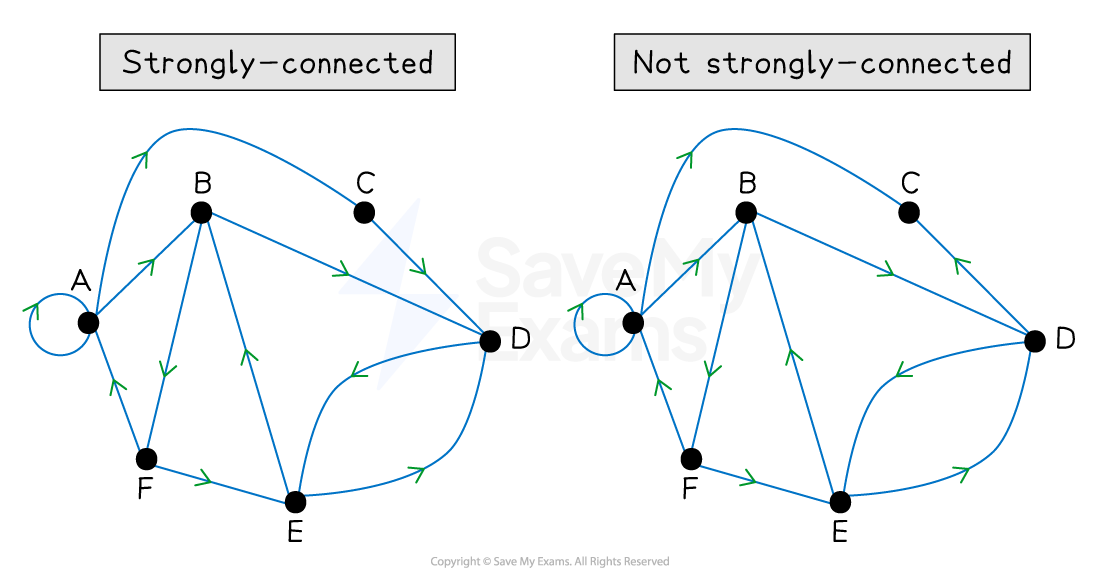
What is a tree?
A tree is connected and does not contain cycles
A tree with n vertices has n - 1 edges
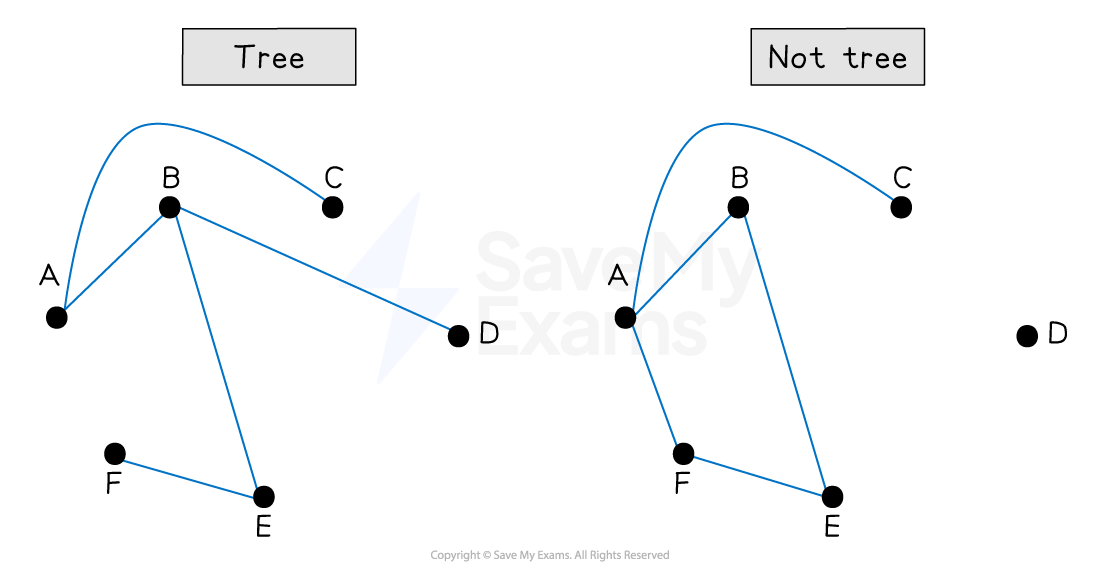
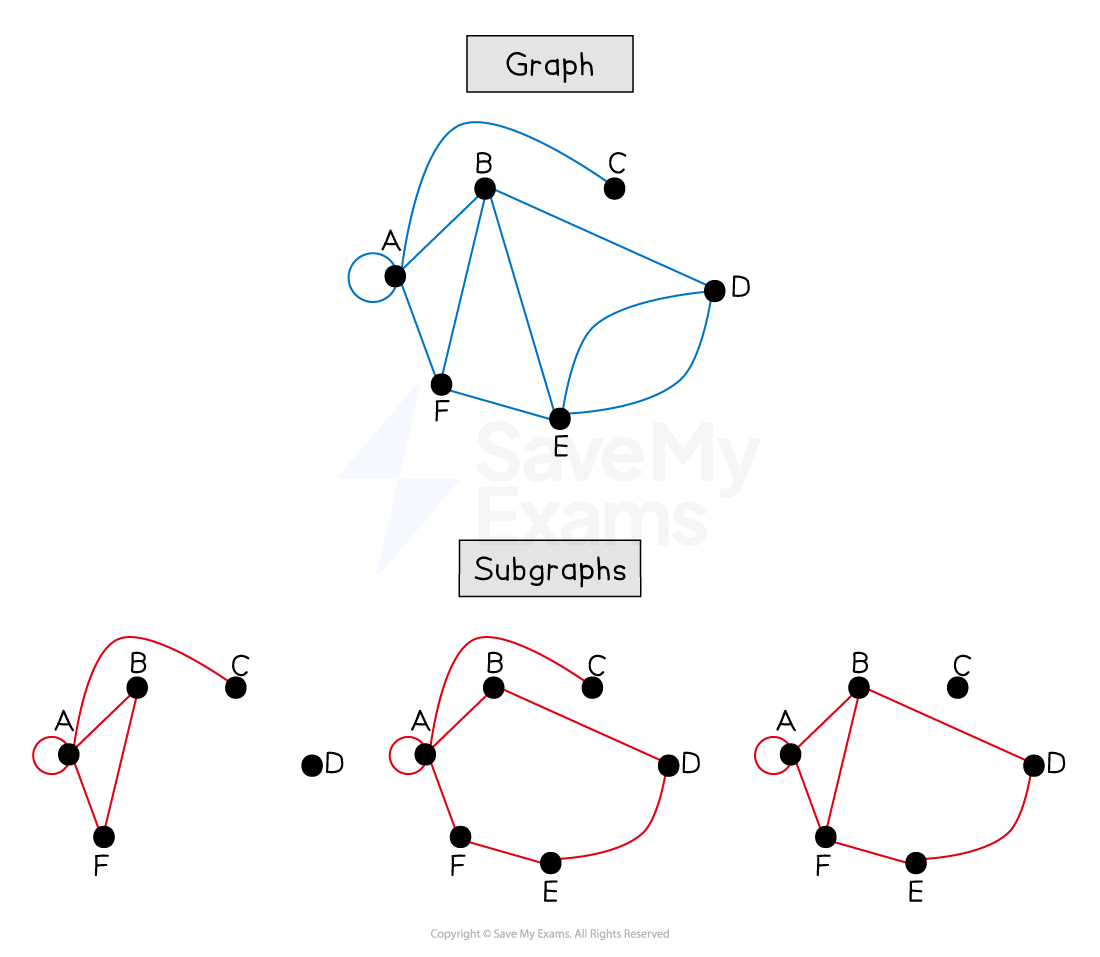
What is a subgraph?
A subgraph of a graph only contain edges and vertices that appear in the graph
A subgraph is a graph itself
A spanning tree is a subgraph that:
is a tree
includes all the vertices of the original graph
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There are a lot of specific terms involved in graph theory and you are often asked to describe them in an exam - make sure you learn the definitions.
Make sure that any graphs you draw are big and clear so they are easy for the examiner to read.
Worked Example
The graph G shown below is a strongly connected, unweighted, directed graph with 5 vertices.

a) State the in-degree of vertex A.
Answer:

b) Explain why the graph is considered to be strongly connected.
Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
