Natural Logarithmic Models (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)) : Revision Note
Natural Logarithmic Models
What are the parameters of natural logarithmic models?
A natural logarithmic model is of the form
The a represents the value of the function when x = 1
The b determines the rate of change of the function
A bigger absolute value of b leads to a faster rate of change
What can be modelled as a natural logarithmic model?
A natural logarithmic model can be used when the variable increases rapidly for a period followed by a much slower rate of increase with no limiting value
M(I) is the magnitude of an earthquake with an intensity of I
d(I) is the decibels measured of a noise with an intensity of I
What are possible limitations a natural logarithmic model?
A natural logarithmic graph is unbounded
However in real-life the variable might have a limiting value
Worked Example
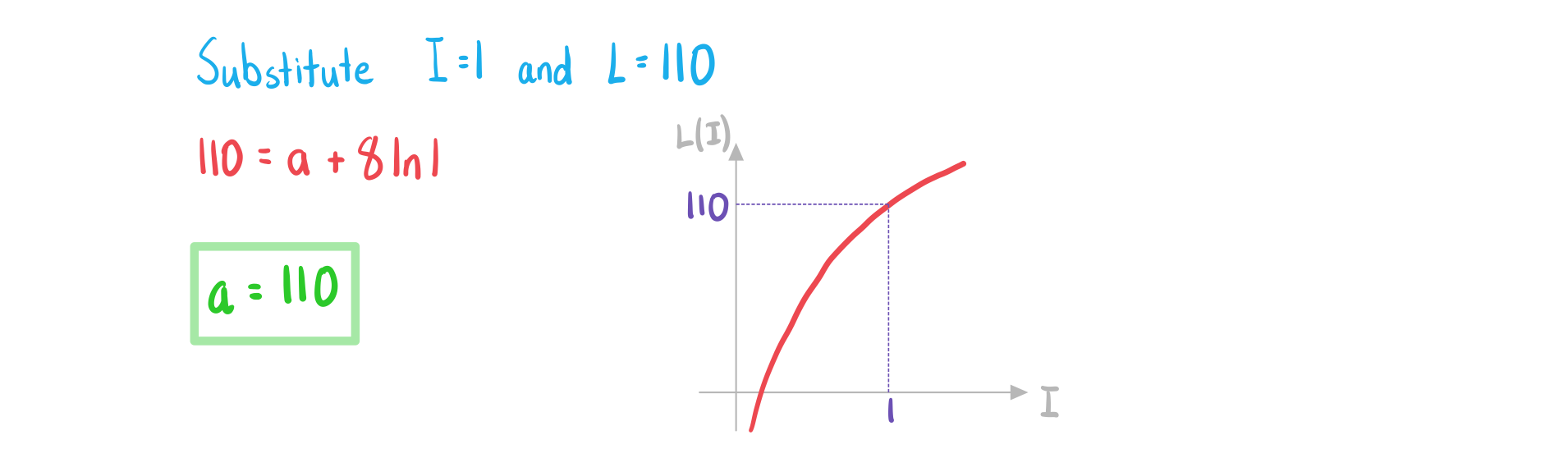
The sound intensity level, , in decibels (dB) can be modelled by the function
,
where is the sound intensity, in watts per square metre (Wm-2).
a) Given that a sound intensity of 1 Wm-2 produces a sound intensity level of 110 dB, write down the value of .
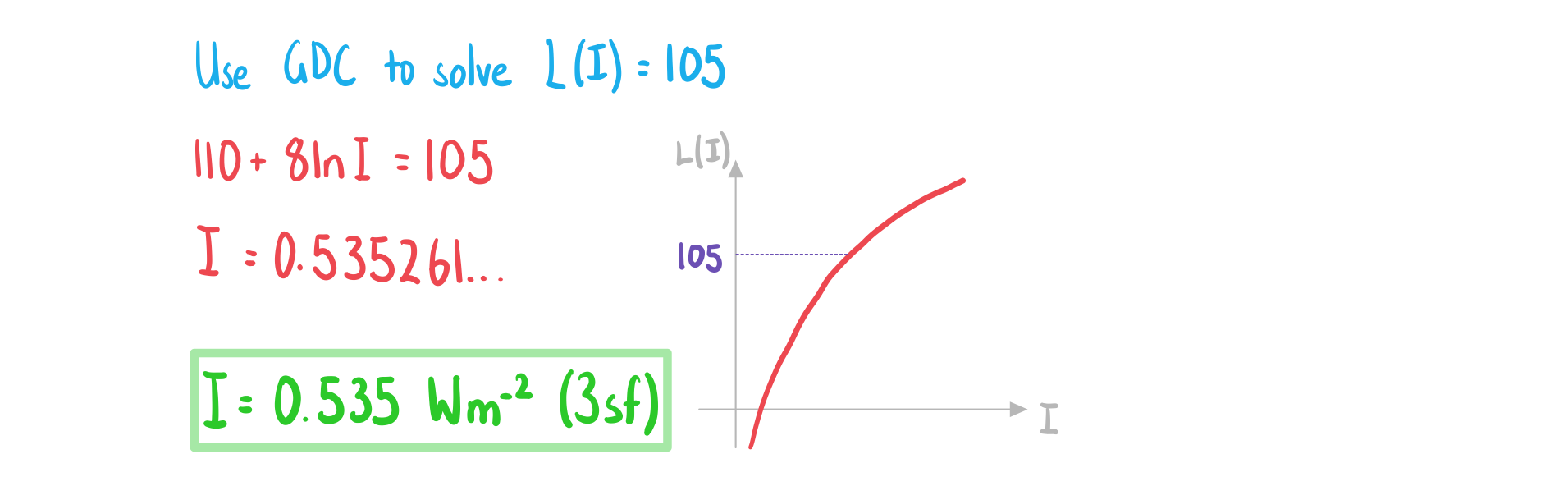
b) Find the sound intensity, in Wm-2, of a car alarm that has a sound intensity level of 105 dB.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
