Applications to Kinematics (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Kinematics using Vectors
How are vectors related to kinematics?
Vectors are often used in questions in the context of forces, acceleration or velocity
If an object is moving in one dimension then its velocity, displacement and time are related using the formula s = vt
where s is displacement, v is velocity and t is the time taken
If an object is moving in more than one dimension then vectors are needed to represent its velocity and displacement
Whilst time is a scalar quantity, displacement and velocity are both vector quantities
For an object moving at a constant speed in a straight line its velocity, displacement and time can be related using the vector equation of a line
r = a +
b
Letting
r be the position of the object at the time, t
a be the position vector, r0 at the start (t = 0)
represent the time, t
b be the velocity vector, v
Then the position of the object at the time, t can be given by
r = r0 + t v
The speed of the object will be the magnitude of the velocity |v |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Kinematics questions can have a lot of information in, read them carefully and pick out the parts that are essential to the question
Look out for where variables used are the same and/or different within vector equations, you will need to use different techniques to find these
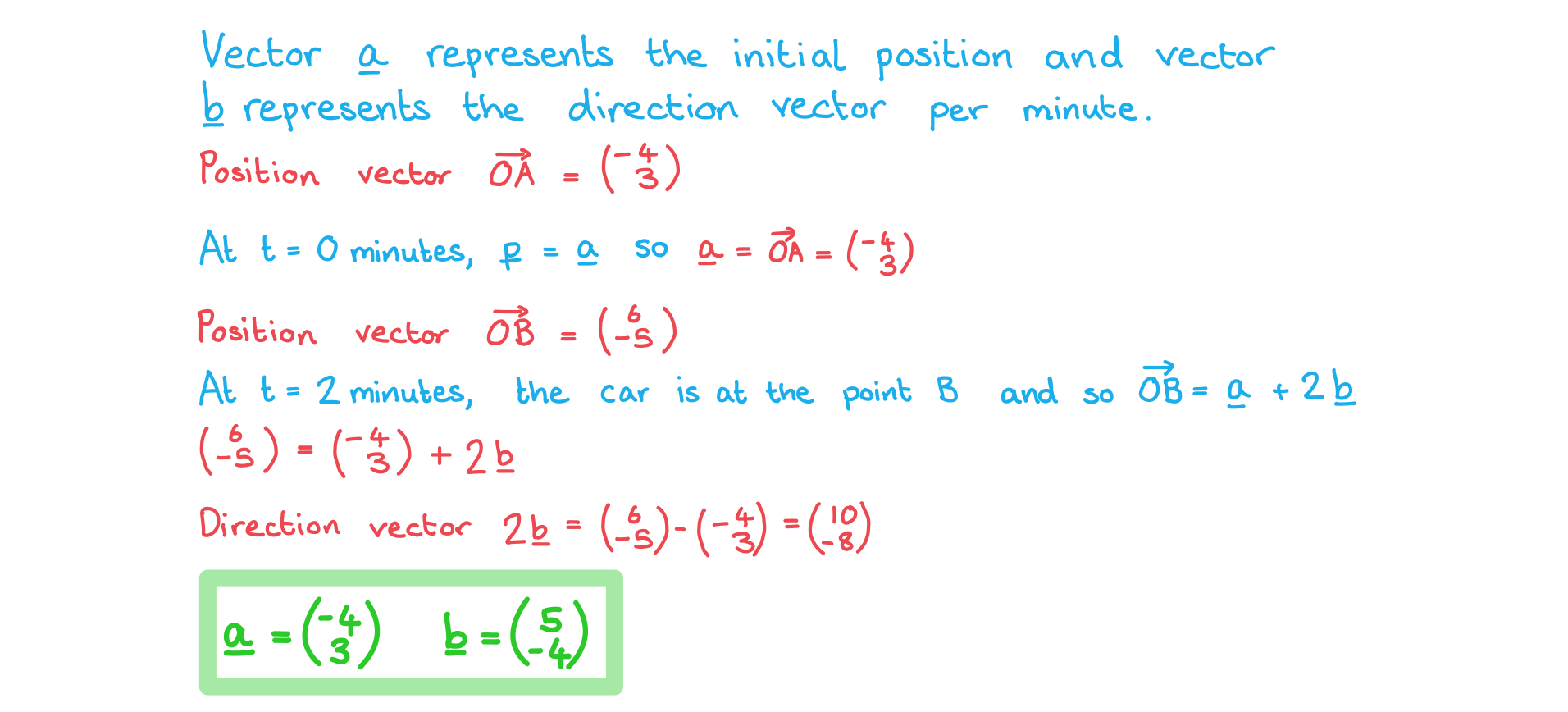
Worked Example
A car, moving at constant speed, takes 2 minutes to drive in a straight line from point A (-4, 3) to point B (6, -5).
At time t, in minutes, the position vector (p) of the car relative to the origin can be given in the form .
Find the vectors a and b.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
