Linear Trigonometric Equations (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Trigonometric Equations: sinx = k
How are trigonometric equations solved?
Trigonometric equations can have an infinite number of solutions
For an equation in sin or cos you can add 360° or 2π to each solution to find more solutions
For an equation in tan you can add 180° or π to each solution
When solving a trigonometric equation you will be given a range of values within which you should find all the values
Solving the equation normally and using the inverse function on your calculator or your knowledge of exact values will give you the primary value
The secondary values can be found with the help of:
The unit circle
The graphs of trigonometric functions
How are trigonometric equations of the form sin x = k solved?
It is a good idea to sketch the graph of the trigonometric function first
Use the given range of values as the domain for your graph
The intersections of the graph of the function and the line y = k will show you
The location of the solutions
The number of solutions
You will be able to use the symmetry properties of the graph to find all secondary values within the given range of values
The method for finding secondary values are:
For the equation sin x = k the primary value is x1 = sin -1 k
A secondary value is x2 = 180° - sin -1 k
Then all values within the range can be found using x1 ± 360n and
x2 ± 360n where n ∈
For the equation cos x = k the primary value is x1 = cos -1 k
A secondary value is x2 = - cos -1 k
Then all values within the range can be found using x1 ± 360n and
x2 ± 360n where n ∈
For the equation tan x = k the primary value is x = tan -1 k
All secondary values within the range can be found using x ± 180n where n ∈
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are using your GDC it will only give you the principal value and you need to find all other solutions for the given interval
Sketch out the CAST diagram and the trig graphs on your exam paper to refer back to as many times as you need to
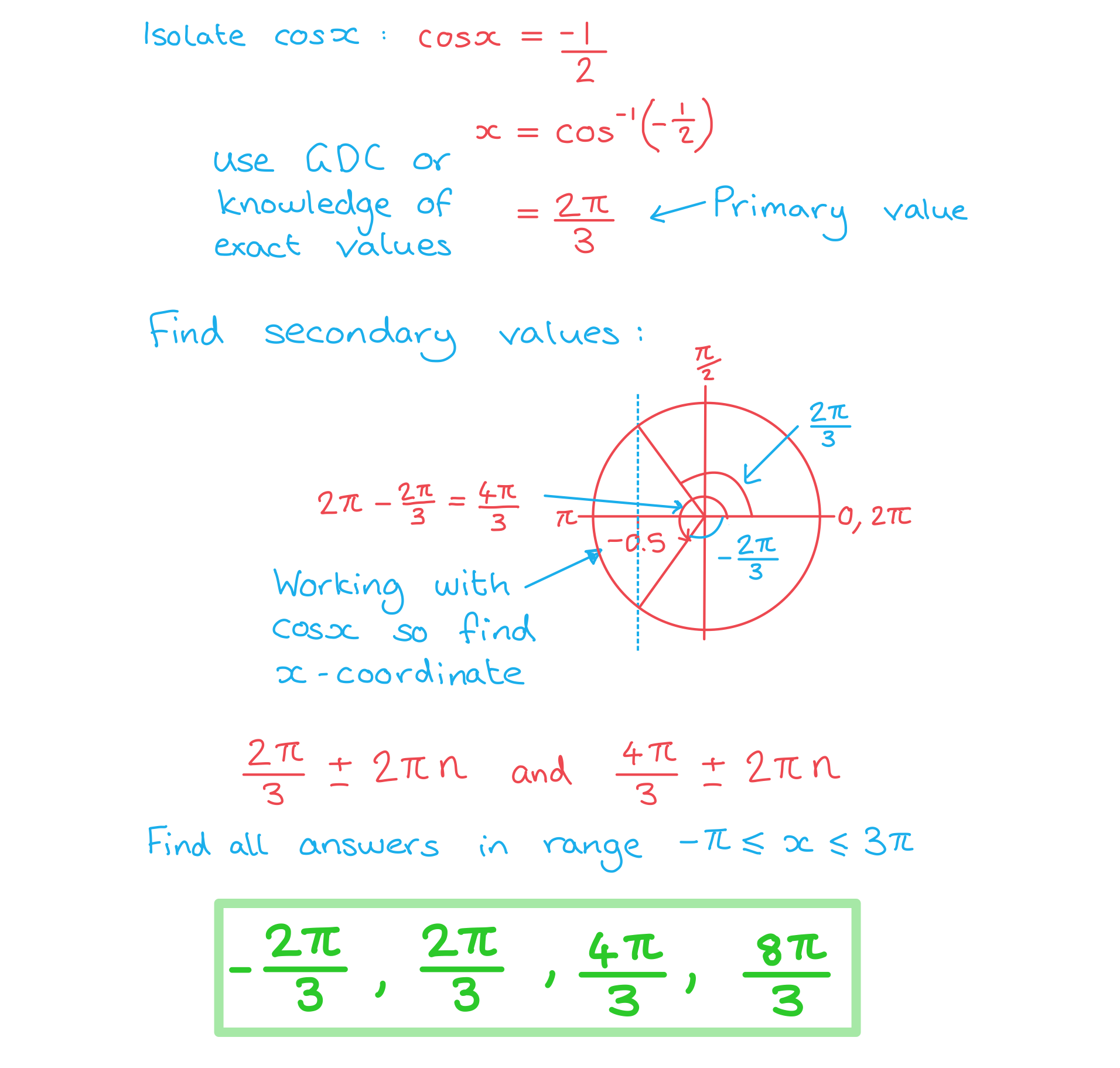
Worked Example
Solve the equation , finding all solutions in the range
.
Did this video help you?
Trigonometric Equations: sin(ax + b) = k
How can I solve equations with transformations of trig functions?
Trigonometric equations in the form sin(ax + b) can be solved in more than one way
The easiest method is to consider the transformation of the angle as a substitution
For example let u = ax + b
Transform the given interval for the solutions in the same way as the angle
For example if the given interval is 0° ≤ x ≤ 360° the new interval will be
(a (0°) + b) ≤ u ≤ (a (360°) + b)
Solve the function to find the primary value for u
Use either the unit circle or sketch the graph to find all the other solutions in the range for u
Undo the substitution to convert all of the solutions back into the corresponding solutions for x
Another method would be to sketch the transformation of the function
If you use this method then you will not need to use a substitution for the range of values
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you transform the interval, remember to convert the found angles back to the final values at the end!
If you are using your GDC it will only give you the principal value and you need to find all other solutions for the given interval
Sketch out the CAST diagram and the trig graphs on your exam paper to refer back to as many times as you need to
Worked Example
Solve the equation , finding all solutions in the range
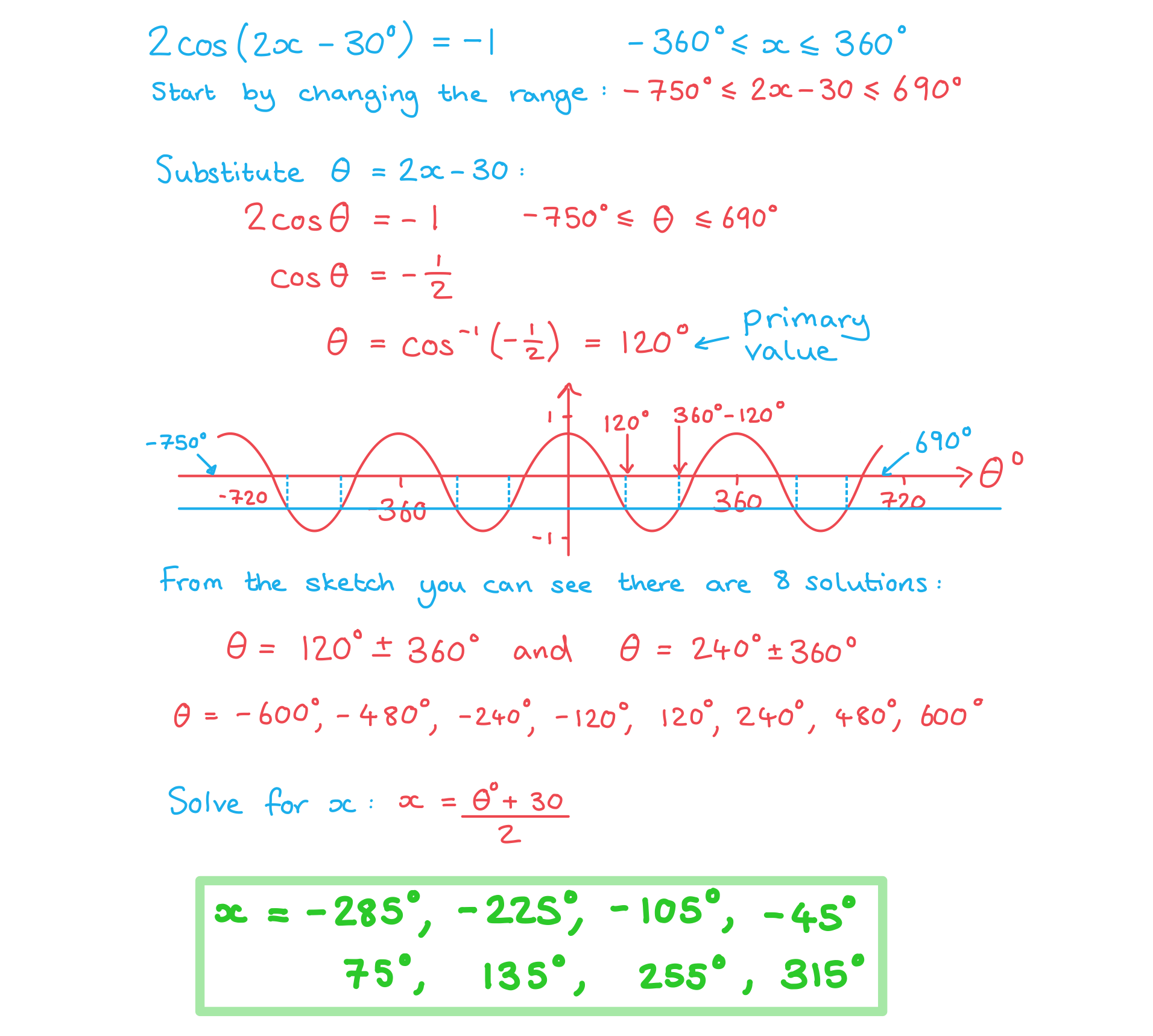

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
