Sine Rule, Cosine Rule & Area of a Triangle (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
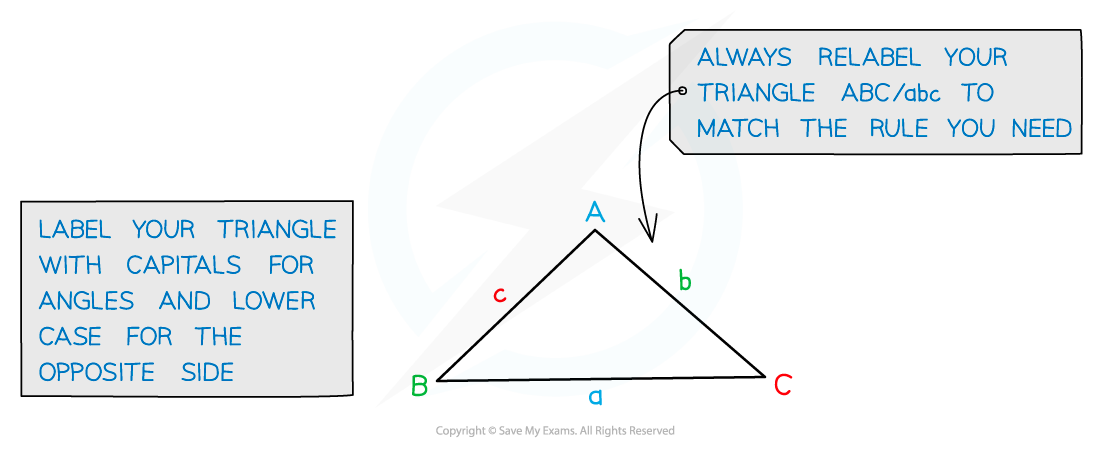
How should I label a non-right angled triangle?
Label the angles with uppercase letters (e.g. A, B, C)
Label each side with the lowercase version of the letter of the opposite angle (e.g. a, b, c)
Did this video help you?
Sine Rule
What is the sine rule?
The sine rule connects the angles and side lengths of any triangle
The formula is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This is given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
The formula can be rearranged to
How can I use sine rule?
You need to know an angle and the length of the side opposite the angle
Label these as
and
If you need to find a missing length (b)
Label the angle opposite the length as
Use
Rearrange to get
If you need to find a missing angle (B)
Label the side opposite the angle as
Use
Rearrange to get
Use the inverse sine function
Worked Example
The following diagram shows triangle ABC. ,
,
.
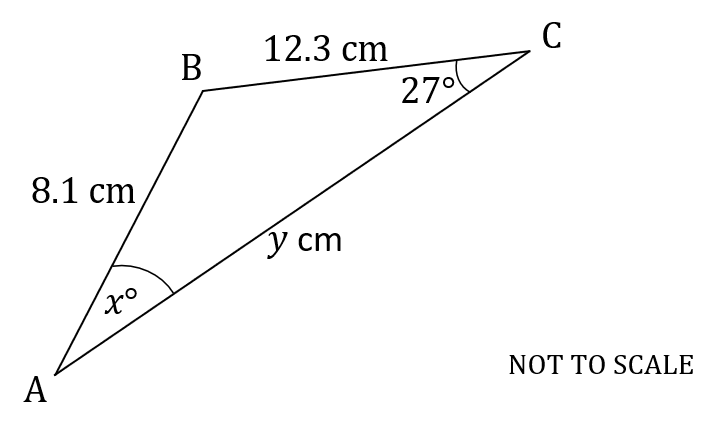
Use the sine rule to calculate the value of:
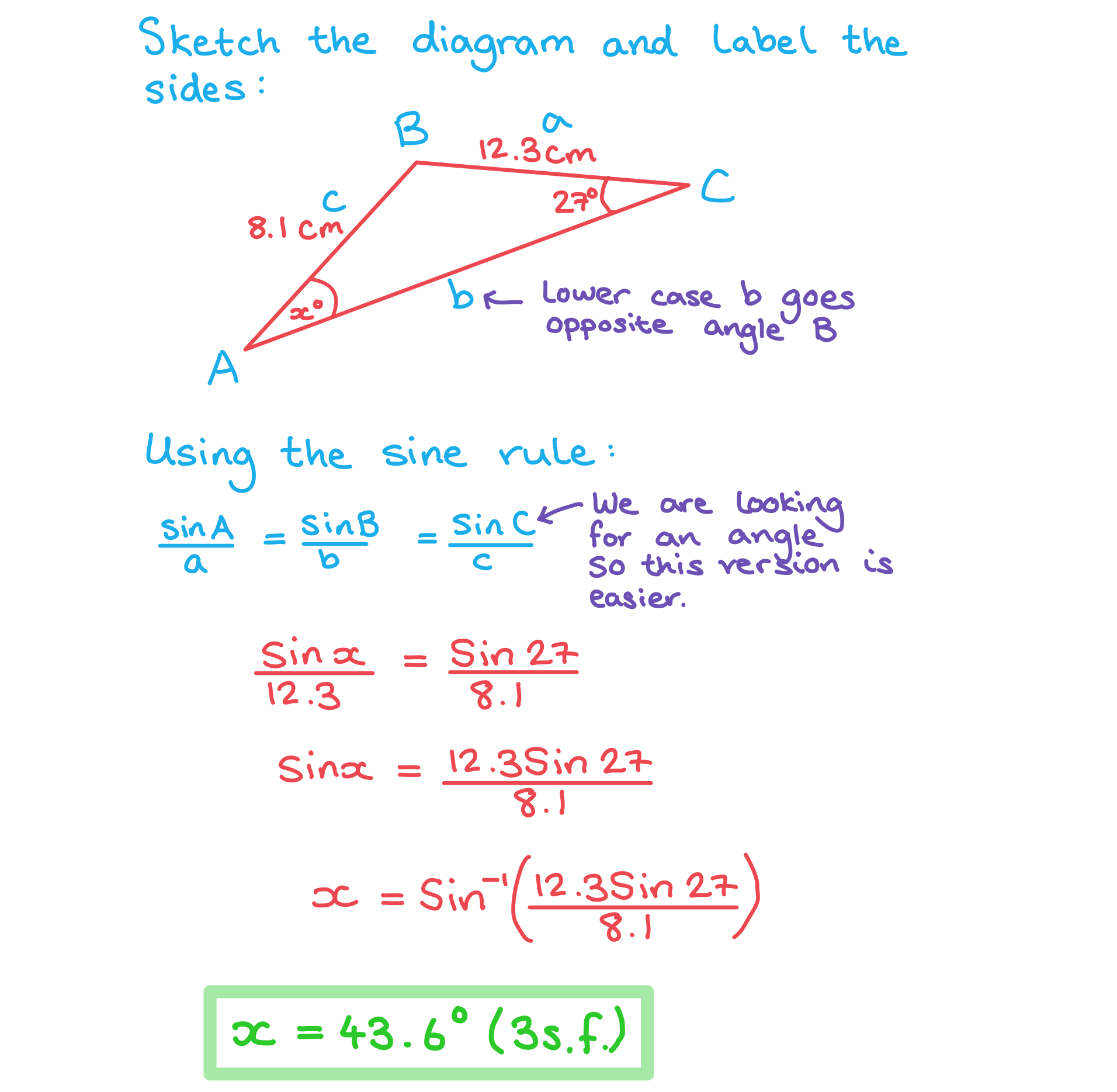
i) ,
Answer:
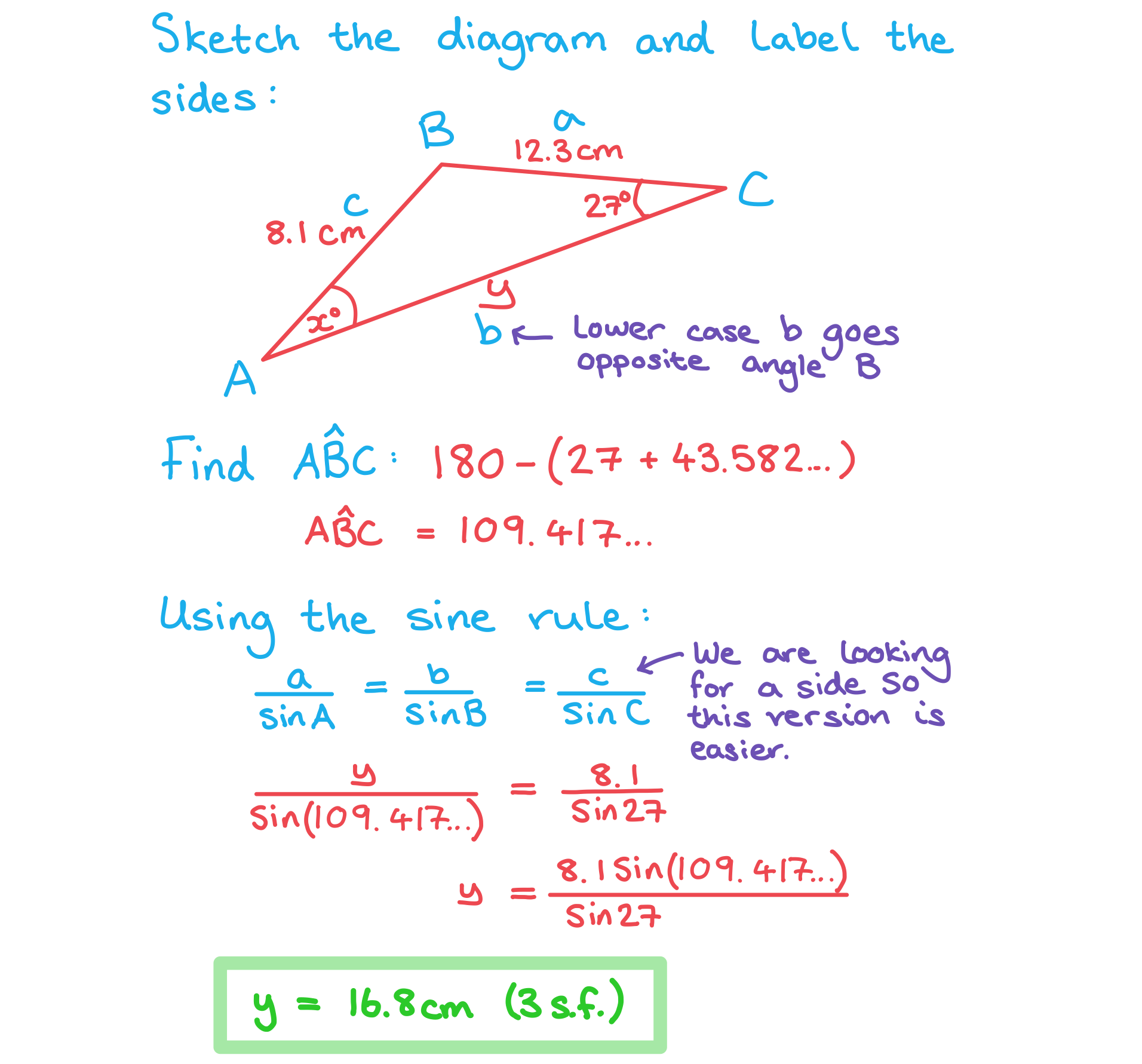
ii) .
Answer:
Did this video help you?
Cosine Rule
What is the cosine rule?
The cosine rule connects the angles and side lengths of any triangle
The formula is
The formula can be rearranged to
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both are given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
How can I use cosine rule?
If you need to find a missing length (c)
Label the angle opposite the length as
Use
Take the positive square root to get
If you need to find a missing angle (C)
Label the side opposite the angle as
Use
Use the inverse cosine function
Worked Example
The following diagram shows triangle .
,
,
.
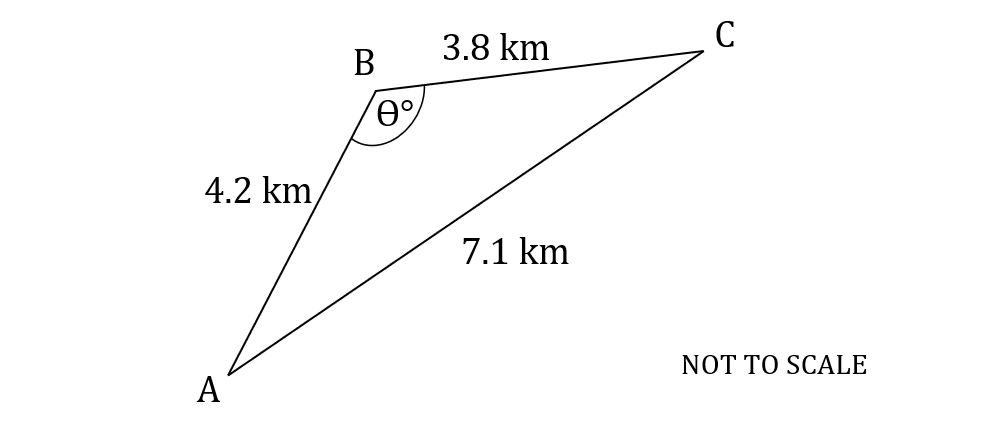
Calculate the value of .
Answer:

Did this video help you?
Area of a Triangle
How do I find the area of a non-right triangle?
The formula for the area of any triangle is
Make sure that the angle is the one formed by the two sides
You can rearrange the formula to find a missing side or angle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This is given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
Worked Example
The following diagram shows triangle .
,
,
.
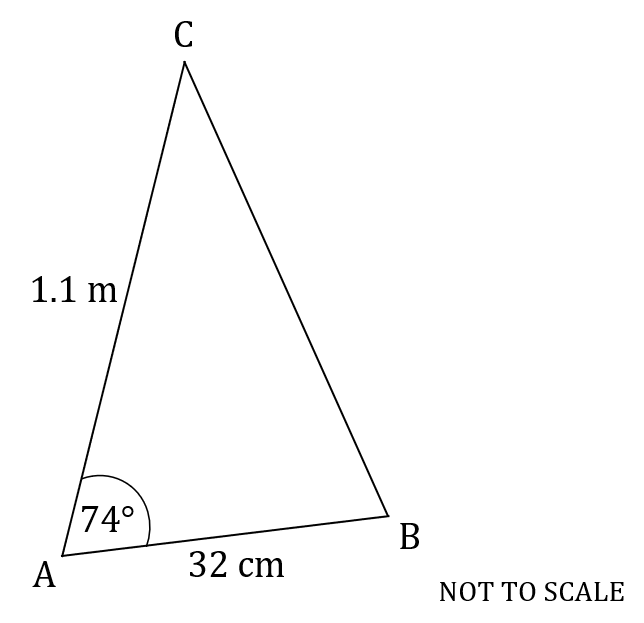
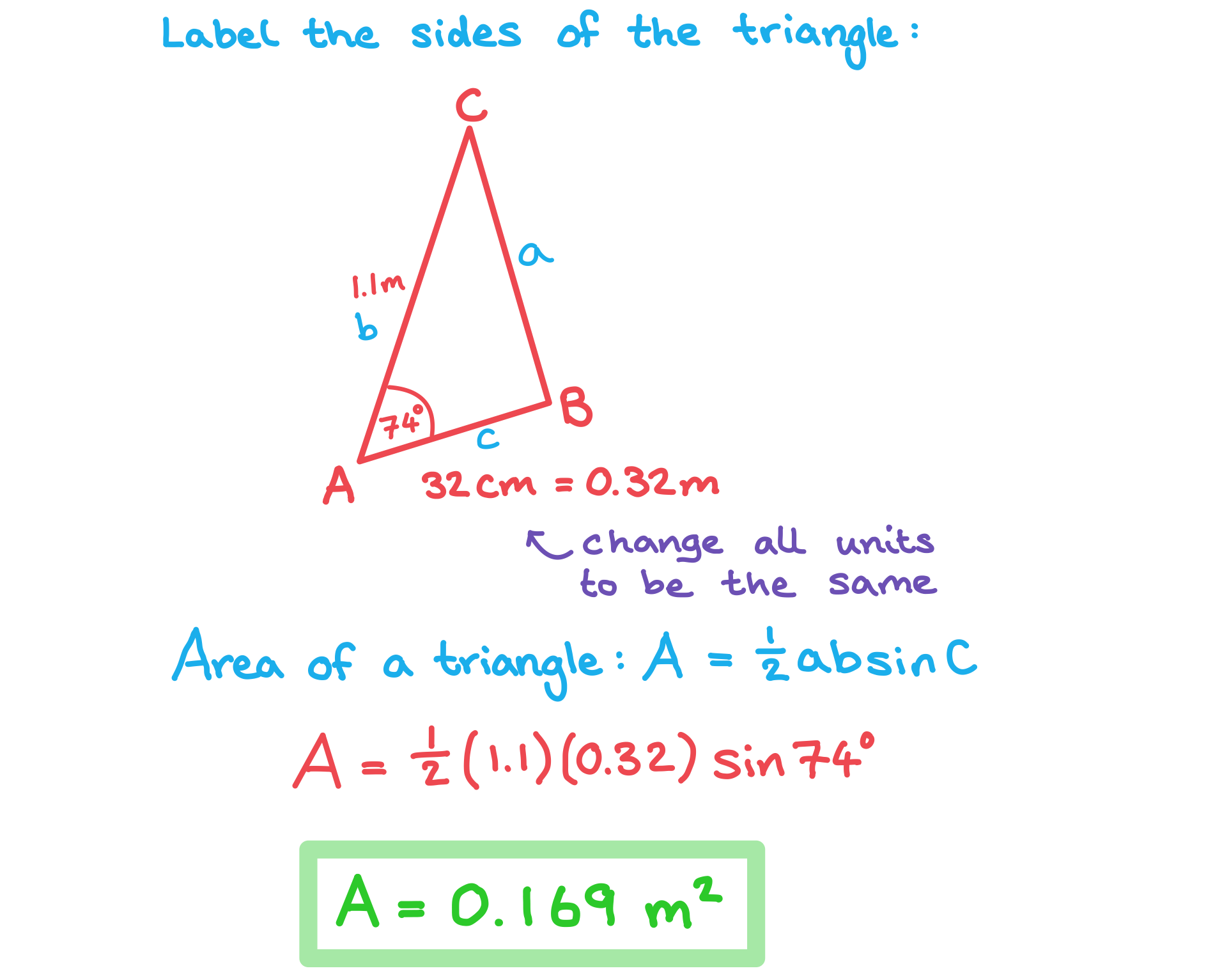
Calculate the area of triangle .
Answer:
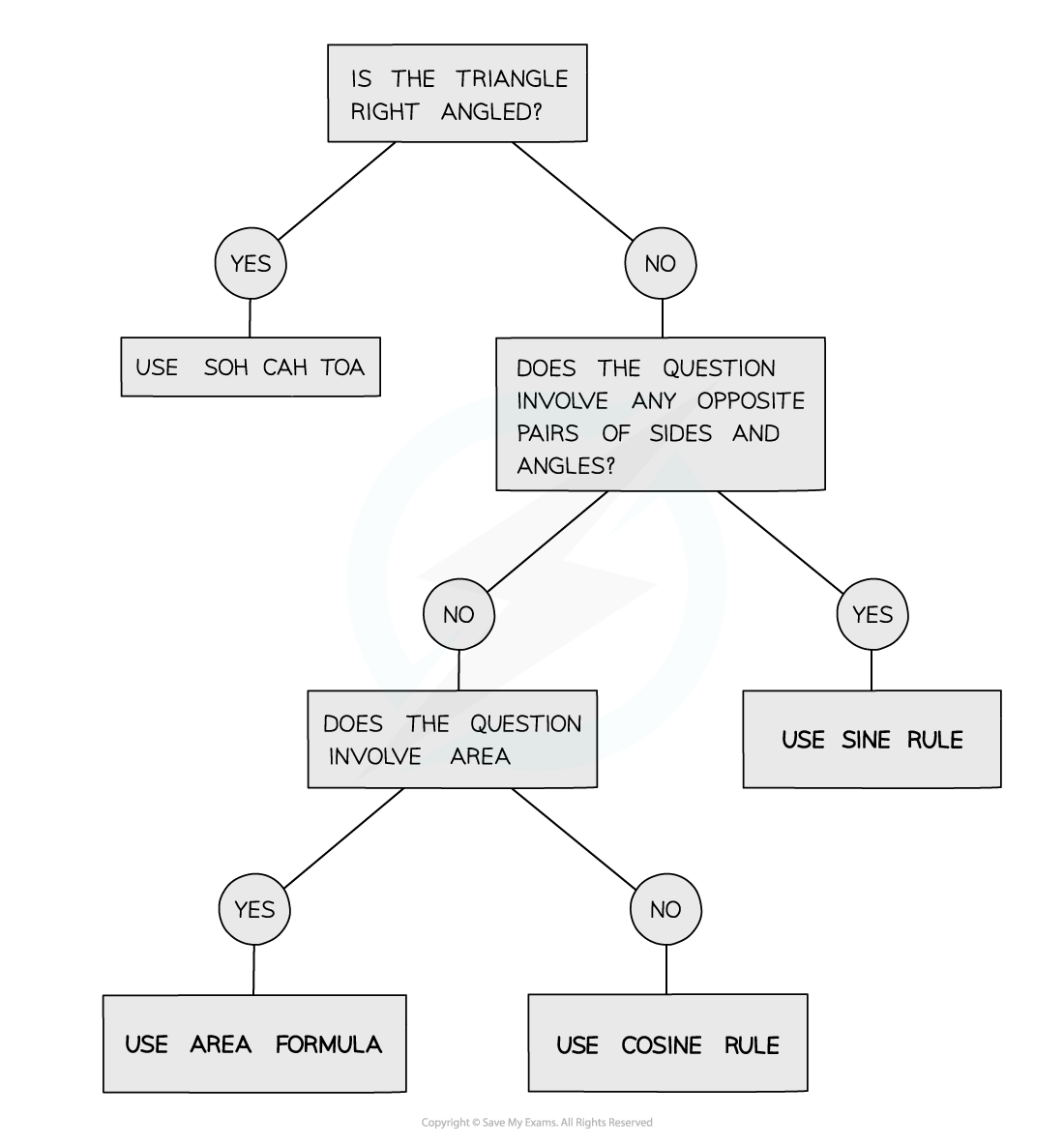
How do I decide which trig rule to use?
Different rules are required depending on the question
You need to be able to decide which is appropriate to use
Think about what information you have and what you want to find
This table summarises the possibilities:
If you know | And you want to know | Use |
|---|---|---|
Two sides and an angle opposite one of the sides | The angle opposite the other side | Sine rule |
Two angles and a side opposite one of the angles | The side opposite the other angle | Sine rule |
Two sides and the angle between them | The third side | Cosine rule |
All three sides | Any angle | Cosine rule |
Two sides and the angle between them | The area of the triangle | Area of a triangle rule |
The area and the two sides | The angle between the two sides | Area of a triangle rule |
The area, a side and an angle | The other side that forms the angle | Area of a triangle rule |
Can I use multiple trig rules in the same question?
Harder questions will require you to use more than one trig rule
For example, you may need the sine rule followed by the cosine rule
The area formula only works for an angle between two sides
If you are not given this setup, you may need to use the sine or cosine rule first
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If it looks like none of the rules work, then remember that all angles in a triangle sum to 180°. This often helps to find a missing angle, which then allows you to use one of the rules.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?