Volume & Surface Area (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
What is a prism?
A prism is a 3D shape that has two identical base shapes connected by parallel edges
A prism has the cross-section all the way through
Examples of prisms include:
Cubes
Cuboids
Triangular prisms
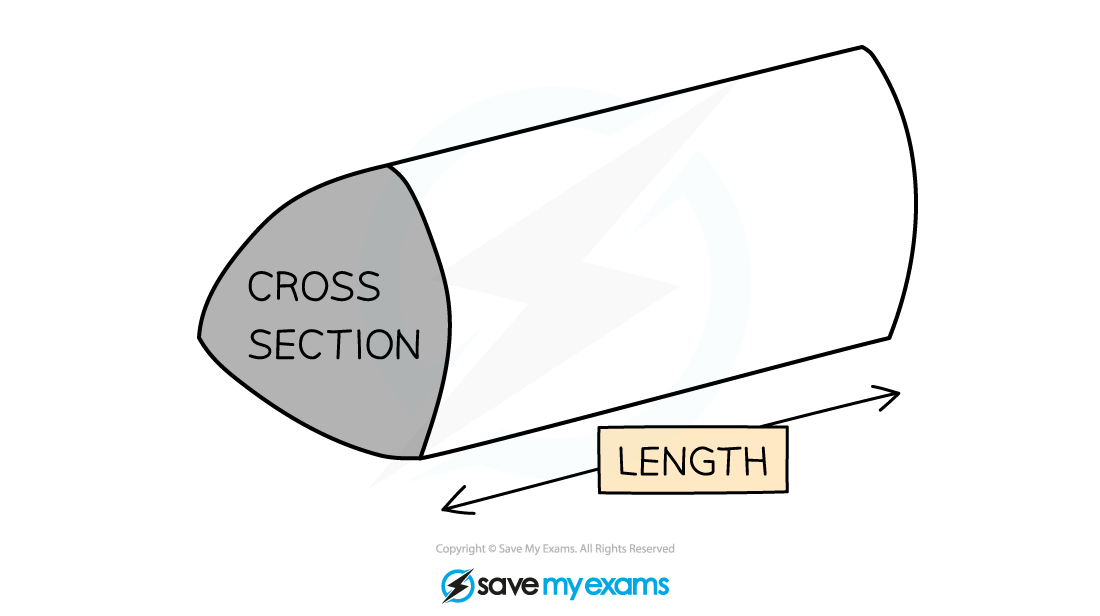
A cylinder is not a prism
But it works in the same way as a prism
What is a pyramid?
A pyramid is a 3D shape that is made up of a base shape and an apex
Edges join the vertices of the base shape to the apex
Examples of pyramids include:
Square-based pyramids
Tetrahedron
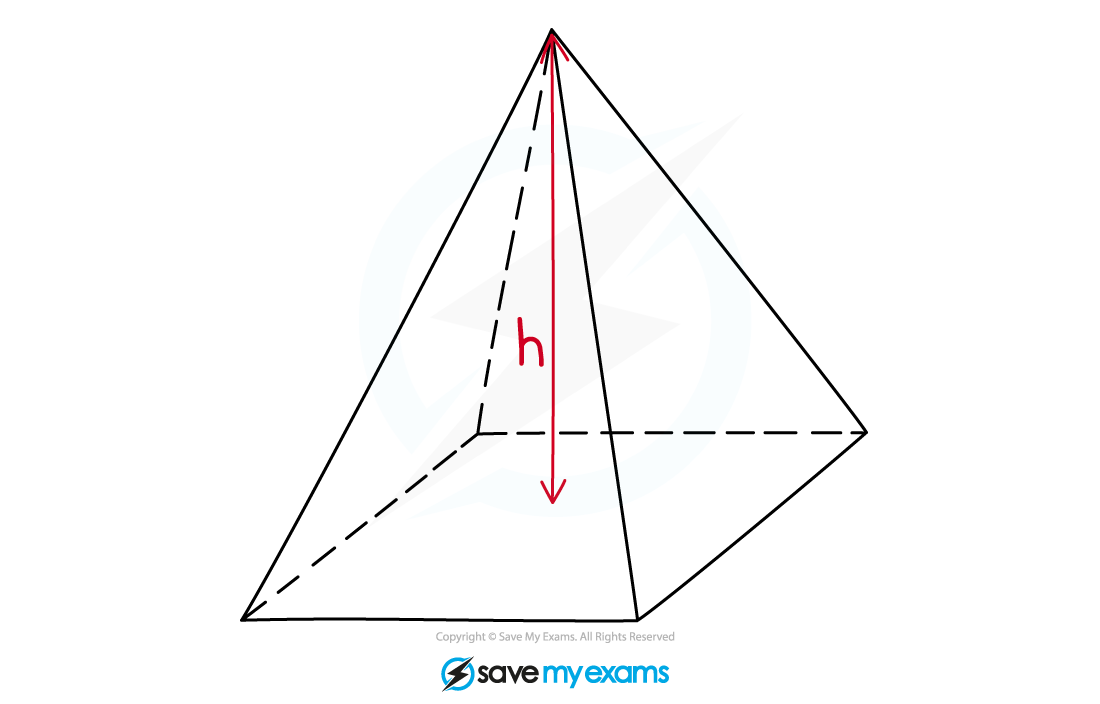
Example of a pyramid A cone is not a pyramid
But it works in the same way as a pyramid
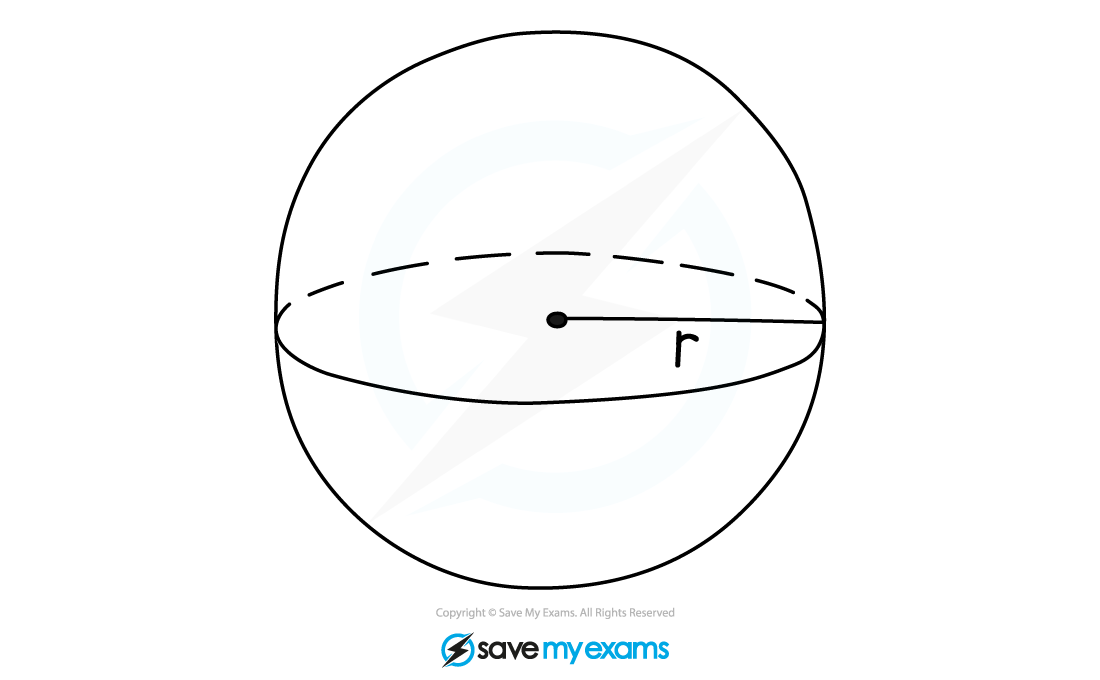
What is a sphere?
A sphere is a 3D shape created by all the points are a given distance from a centre
The distance is known as the radius
Did this video help you?
Volume of 3D shapes
How do I find the volume of prisms and cylinders?
The formula for the volume of a prism is
is the volume
is the area of the cross-section
is the height or length
The cross-section of a cuboid is a rectangle
The formula for the area of a rectangle is
is the length
is the width
The formula for the volume of a cuboid is
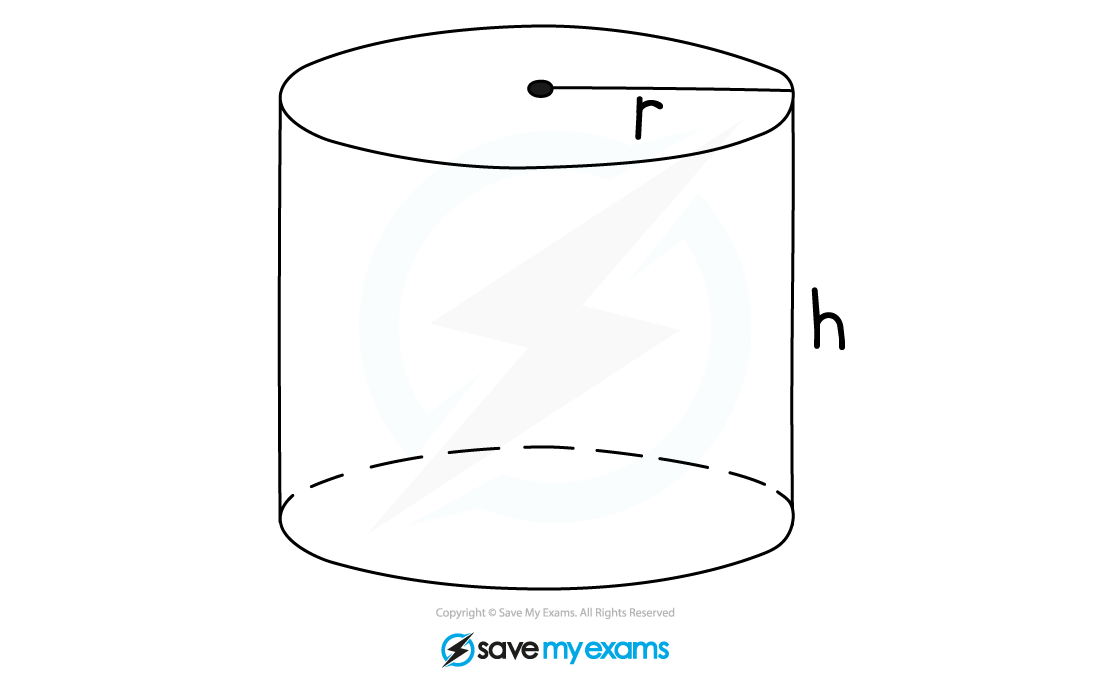
The cross-section of a cylinder is a circle
The formula for the area of a circle is
is the radius
The formula for the volume of a cylinder is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
All of these volume formulas are given in the formula booklet under the prior learning section.
How do I find the volume of pyramids and cones?
The formula for the volume of a pyramid is
is the volume
is the area of the base
is the height
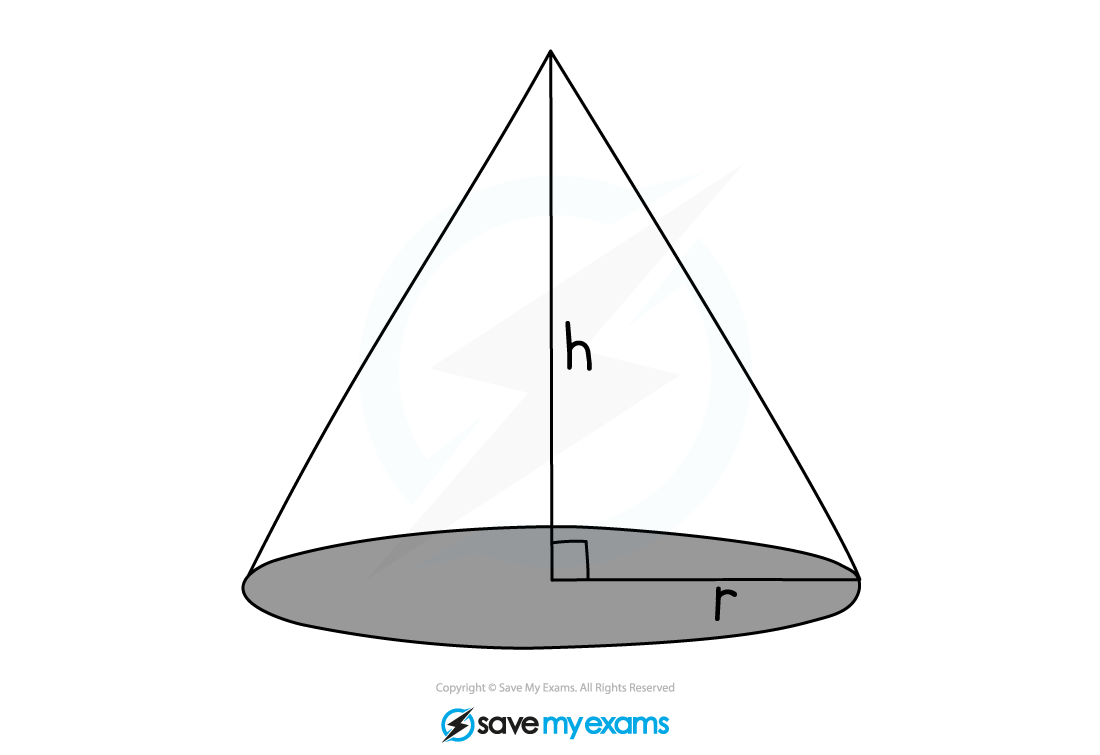
The base of a cone is a circle
The formula for the area of a circle is
is the radius
The formula for the volume of a cone is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
All of these volume formulas are given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
How do I find the volume of a sphere?
The formula for the volume of a sphere is
is the volume
is the radius
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This formula is given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
Worked Example
A dessert can be modelled as a right-cone of radius 3 cm and height 12 cm and a scoop of ice-cream in the shape of a sphere of radius 3 cm. Find the total volume of the ice-cream and cone.

Answer:

Did this video help you?
Surface area of 3D shapes
How do I find the surface area of pyramids and prisms?
Find the surface area of a prism by adding together:
The areas of the two identical shapes at each end of the prism
The areas of the rectangles joining the two shapes
Find the surface area of a pyramid by adding together:
The area of the base shape
The areas of the triangles joining the base shape to the apex
How do I find the surface area of cylinders?
A cylinder is made up of two circles and a curved surface
The formula for the area of the curved surface of a cylinder is
is the radius
is the height or length
The formula for the surface area of a cylinder is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The formula for the area of the curved surface is given in the formula booklet under the prior learning section. The formula for the surface area is not given.
How do I find the surface area of cones?
A cone is made up of a circle and a curved surface
The formula for the area of the curved surface of a cone is
is the radius
is the slant height
The formula for the surface area of a cone is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The formula for the area of the curved surface is given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section. The formula for the surface area is not given.
How do I find the surface area of spheres?
The formula for the surface area of a sphere is
is the radius
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This formula is given in the formula booklet under the geometry and trigonometry section.
Worked Example
In the diagram below ABCD is the square base of a right pyramid with vertex V . The centre of the base is M. The sides of the square base are 3.6 cm and the vertical height is 8.2 cm.

i) Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance VN.
Answer:

ii) Calculate the area of the triangle ABV.
Answer:

iii) Find the surface area of the right pyramid.
Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?