Exponential Models (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Exponential Models
What are the parameters of an exponential model?
An exponential model is of the form
or
for
Where e is the mathematical constant 2.718…
The c represents the boundary for the function
It can never be this value
The a or r describes the rate of growth or decay
The bigger the value of a or the absolute value of r the faster the function increases/decreases
What can be modelled as an exponential model?
Exponential growth or decay
Exponential growth is represented by
where
where
where
Exponential decay is represented by
where
where
where
They can be used when there a constant percentage increase or decrease
Such as functions generated by geometric sequences
Examples include:
V(t) is the value of car after t years
S(t) is the amount in a savings account after t years
B(t) is the amount of bacteria on a surface after t seconds
T(t) is the temperature of a kettle t minutes after being boiled
What are possible limitations of an exponential model?
An exponential growth model does not have a maximum
In real-life this might not be the case
The function might reach a maximum and stay at this value
Exponential models are monotonic
In real-life this might not be the case
The function might fluctuate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Look out for the word "initial" or similar, as way of asking you to make the power equal to zero to simplify the equation
Questions regarding the boundary of the exponential model are also frequently asked
Worked Example
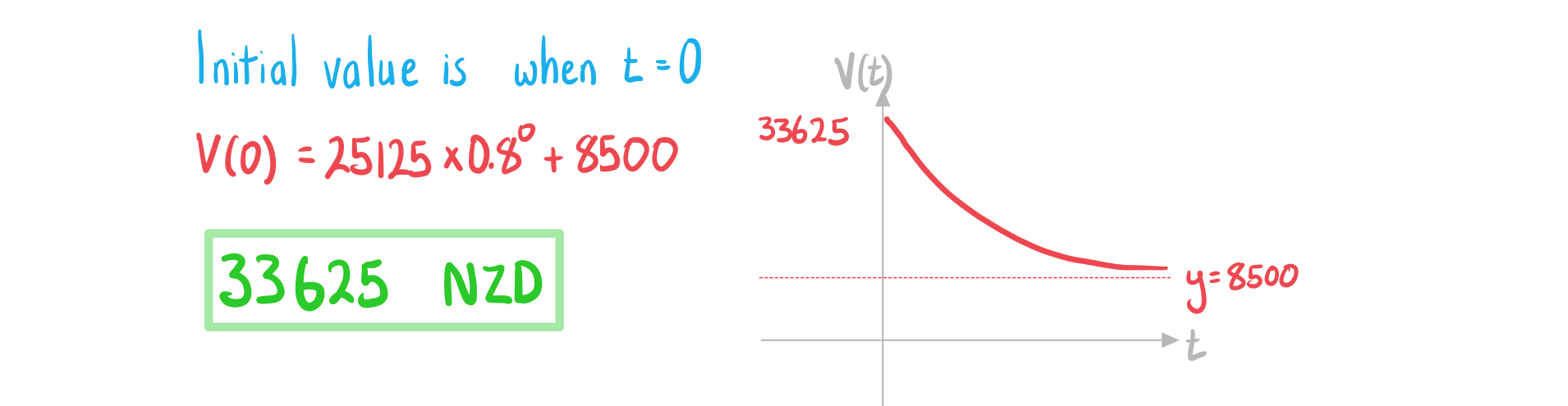
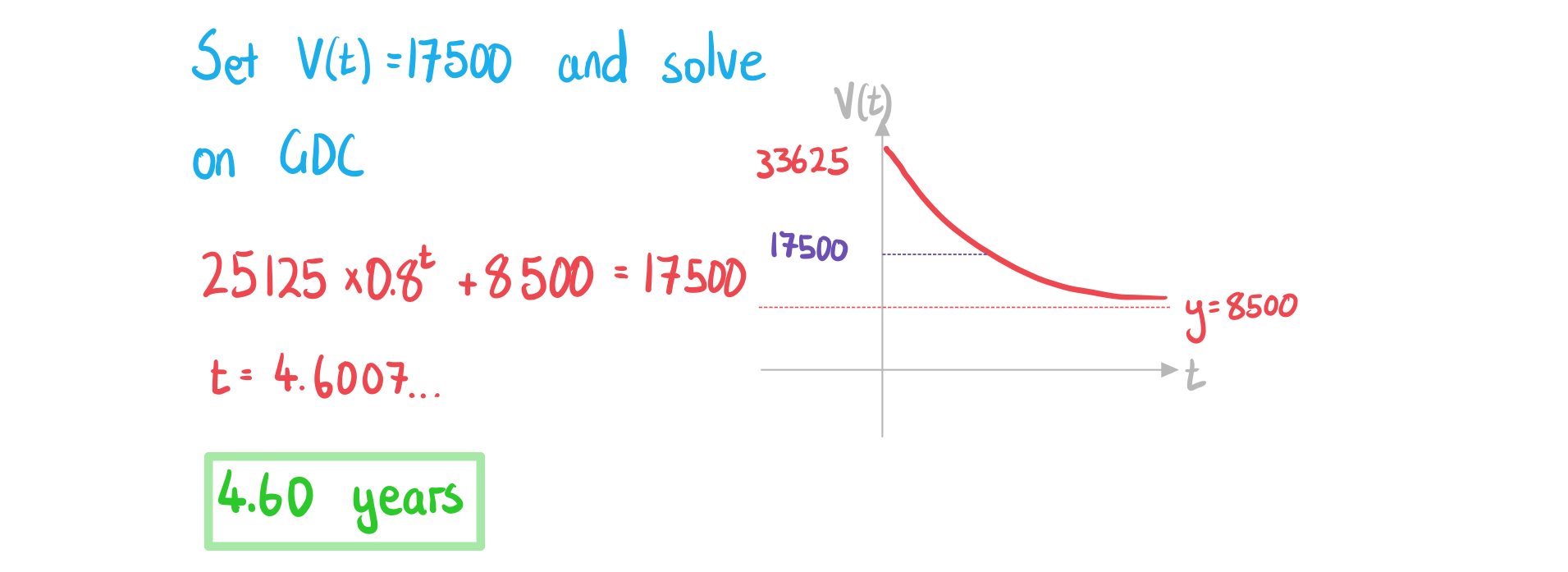
The value of a car, (NZD), can be modelled by the function
where is the age of the car in years.
a) State the initial value of the car.
b) Find the age of the car when its value is 17500 NZD.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
