Did this video help you?
Differentiating Special Functions (DP IB Maths: AI HL): Revision Note
Differentiating Trig Functions
How do I differentiate sin, cos and tan?
- The derivative of
is
- The derivative of
is
- The derivative of
is
- This result can be derived using quotient rule
- All three of these derivatives are given in the formula booklet
- For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
- For the general function
,
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
- These last three results can be derived using the chain rule
- For calculus with trigonometric functions angles must be measured in radians
- Ensure you know how to change the angle mode on your GDC
Examiner Tip
- As soon as you see a question involving differentiation and trigonometry put your GDC into radians mode
Worked example
a)
Find %3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAXWhlYWQQC2qxAAAB7AAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAiQAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAJIAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACUAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAAlwAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAAJ8AAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEHAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABDwAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAACf%2F%2FwAAACf%2F%2F%2F%2FaAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAABAFUB1QDVAysAAwAbGAGwBBCxAAX0sQED9LEFBfQAsAQQsQAC9DAxEzMDI1WAVioDK%2F6qAAAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVASsAVQAAAAAAAAAoAAAAXQABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%227.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Ef%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2215.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E'%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2228.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2236.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) for the functions
for the functions

b) A curve has equation%3C%2Fmo%3E%3Cmo%3E%26%23xA0%3B%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math1e9c1d970bf1dedebfe90fae9eb'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAAERjdnQgDVUNBwAAAWAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGcAAABi2hlYWQQC2qxAAADKAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAA2AAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAOEAAAAEGxvY2EAHTwYAAADlAAAABRtYXhwBT0FPgAAA6gAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAAPIAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAFaAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABYgAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEADAAAAAIAAgAAgAAAD0DwCIS%2F%2F8AAAA9A8AiEv%2F%2F%2F8T8Qt3xAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAVQDLACAAQAAVgAqAlgCHgEOASwCLABaAYACgACgANQAgAAAAAAAAAArAFUAgACrANUBAAErAAcAAAACAFUAAAMAA6sAAwAHAAAzESERJSERIVUCq%2F2rAgD%2BAAOr%2FFVVAwAAAgCAAOsC1QIVAAMABwBlGAGwCBCwBtSwBhCwBdSwCBCwAdSwARCwANSwBhCwBzywBRCwBDywARCwAjywABCwAzwAsAgQsAbUsAYQsAfUsAcQsAHUsAEQsALUsAYQsAU8sAcQsAQ8sAEQsAA8sAIQsAM8MTATITUhHQEhNYACVf2rAlUBwFXVVVUAAQBVAAACwAJAABkAQRgBsBoQsA3UsA0QsAfUsAcQsATUsAQQsBjUALAaELAL1LAaELAC1LAaELAP1LAPELAU1LAPELAGPLAPELAXPDAxJQYjIjUDIxEUBisBNjU0JyIVIzQzIRUjExQCwBVAgAGqKQFVKgFVQGoCAYEBVVXVARb%2B6pVAQJWAliuAVf7qwAABAIABVQLVAasAAwAwGAGwBBCxAAP2sAM8sQIH9bABPLEFA%2BYAsQAAExCxAAblsQABExCwATyxAwX1sAI8EyEVIYACVf2rAatWAAABAAAAAQAA1XjOQV8PPPUAAwQA%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3P%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTcwAA%2FyAEgAOrAAAACgACAAEAAAAAAAEAAAPo%2F2oAABdwAAD%2FtgSAAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAEA1IAVQNWAIADFgBVA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAsgAAAUEAAAGLAAEAAAAEAF4ABQAAAAAAAgCABAAAAAAABAAA3gAAAAAAAAAVAQIAAAAAAAAAAQASAAAAAAAAAAAAAgAOABIAAAAAAAAAAwAwACAAAAAAAAAABAASAFAAAAAAAAAABQAWAGIAAAAAAAAABgAJAHgAAAAAAAAACAAcAIEAAQAAAAAAAQASAAAAAQAAAAAAAgAOABIAAQAAAAAAAwAwACAAAQAAAAAABAASAFAAAQAAAAAABQAWAGIAAQAAAAAABgAJAHgAAQAAAAAACAAcAIEAAwABBAkAAQASAAAAAwABBAkAAgAOABIAAwABBAkAAwAwACAAAwABBAkABAASAFAAAwABBAkABQAWAGIAAwABBAkABgAJAHgAAwABBAkACAAcAIEATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAUgBlAGcAdQBsAGEAcgBNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAIABNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABNAGEAdABoACAARgBvAG4AdABWAGUAcgBzAGkAbwBuACAAMQAuADBNYXRoX0ZvbnQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAADAAAAAAAAAfQA%2BgAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAuQcRAACNhRgAsgAAABUUE7EAAT8%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7PH4UAAADMAAAATmNtYXA3kjw6AAABHAAAADxjdnQgAQYDiAAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZkyYQ7YAAAFsAAAAkWhlYWQLyR8fAAACAAAAADZoaGVhAq0XCAAAAjgAAAAkaG10eDEjA%2FUAAAJcAAAADGxvY2EAAEKZAAACaAAAABBtYXhwBJsEcQAAAngAAAAgbmFtZW7QvZAAAAKYAAAB5XBvc3QArQBVAAAEgAAAACBwcmVwu5WEAAAABKAAAAAHAAACDAGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg9AMD%2FP%2F8AAABVAABAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACI5wjn%2F%2F%2FAAAjnCOf%2F%2F%2FcZdxjAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFQBAAArAIwAgACoAAcAAAACAAAAAADVAQEAAwAHAAAxMxEjFyM1M9XVq4CAAQHWqwABAAAAAABVAVgAAwAfGAGwAy%2BwADyxAgL1sAE8ALEDAD%2BwAjx8sQAG9bABPBEzESNVVQFY%2FqgAAQDXAAABLAFUAAMAIBgBsAUvsAE8sAI8sQAC9bADPACwAy%2BwAjyxAAH1sAE8EzMRI9dVVQFU%2FqwAAAAAAQAAAAEAAIsesexfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre5k%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7mT%2FgP%2F%2FAdYBWAAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAABVP%2F%2FAAAXcP%2BA%2F4AB1gABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAABLAAAASwA1wAAAAAAAAAhAAAAWAAAAJEAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABlAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABACYAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AJgAAAAAAAAADAEQANAAAAAAAAAAEACYAeAAAAAAAAAAFABYAngAAAAAAAAAGABMAtAAAAAAAAAAIABwAxwABAAAAAAABACYAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AJgABAAAAAAADAEQANAABAAAAAAAEACYAeAABAAAAAAAFABYAngABAAAAAAAGABMAtAABAAAAAAAIABwAxwADAAEECQABACYAAAADAAEECQACAA4AJgADAAEECQADAEQANAADAAEECQAEACYAeAADAAEECQAFABYAngADAAEECQAGABMAtAADAAEECQAIABwAxwBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAQgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAcwBtAGEAbABsACAAcwBpAHoAZQBCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABzAG0AYQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMEJyYWNrZXRzX3NtYWxsX3NpemUATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAAAqgBVAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAo2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7RIisAAADMAAAATmNtYXBi7uzYAAABHAAAAExjdnQgBAkDLgAAAWgAAAASZ2x5Zo64f%2BkAAAF8AAABSWhlYWQLniGcAAACyAAAADZoaGVhBK4XLAAAAwAAAAAkaG10eCWq%2F90AAAMkAAAAFGxvY2EAABknAAADOAAAABhtYXhwBJIESAAAA1AAAAAgbmFtZRAA8I4AAANwAAAB3nBvc3QBwwDgAAAFUAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABXAAAAAHAAACggGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg9AMEAAAAAAADgAAAAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEADgAAAAKAAgAAgACI5sjnSOeI6D%2F%2FwAAI5sjnSOeI6D%2F%2F9xm3GXcZdxkAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABVABWAQAALACoA4AAMgAHAAAAAgAAACoA1QNVAAMABwAANTMRIxMjETPV1auAgCoDK%2F0AAtUAAQAAAAABgAOAAAUAJBgBsAAvsAPFsQEC%2FbADELEEBP0AsQAAP7ABPLEEBj%2BwAzwwMTEzEAEjAFUBKyv%2BqwH8AYT%2BqgABAAAAAAGAA4AABQAmGAGwAC6wA8WxBQL9sAMQsQIE%2FQB8sQAGPxiwBTyxAwb2sAI8MDEREgEzABMBAVQr%2FtMCA4D91v6qAYQB%2FAAB%2F6wAAAEsA4AABQAnGAGwAC%2BwBzywA8WxAQL9sAMQsQQE%2FQCxAAA%2FsAE8sQQGP7ADPDAxISMSATMAASxVAf7UKwFVAfwBhP6rAAH%2FrAAAASwDgAAFACkYAbABL7AHPLAExbEAAv2wBBCxAwT9AHyxAQY%2FsAA8GLEEAD%2BwAzwwMRMzEAEjANdV%2FqsrASsDgP3V%2FqsBhgAAAAABAAAAAQAAeuTcpl8PPPUAAwQA%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7o7%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1a3ujv%2BsAAABgAOAAAAACgACAAEAAAAAAAEAAAOAAAAAABdw%2F6z%2FrAGAAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAFANUAAAEsAAABLAAAASz%2FrAEs%2F6wAAAAAAAAAJAAAAGgAAACzAAAA%2FQAAAUkAAQAAAAUACAACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAAA%2BAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABACQAAAAAAAAAAAACAA4AJAAAAAAAAAADAEIAMgAAAAAAAAAEACQAdAAAAAAAAAAFABYAmAAAAAAAAAAGABIArgAAAAAAAAAIABwAwAABAAAAAAABACQAAAABAAAAAAACAA4AJAABAAAAAAADAEIAMgABAAAAAAAEACQAdAABAAAAAAAFABYAmAABAAAAAAAGABIArgABAAAAAAAIABwAwAADAAEECQABACQAAAADAAEECQACAA4AJAADAAEECQADAEIAMgADAAEECQAEACQAdAADAAEECQAFABYAmAADAAEECQAGABIArgADAAEECQAIABwAwABCAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIABmAHUAbABsACAAcwBpAHoAZQBSAGUAZwB1AGwAYQByAE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAgAEIAcgBhAGMAawBlAHQAcwAgAGYAdQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAEIAcgBhAGMAawBlAHQAcwAgAGYAdQBsAGwAIABzAGkAegBlAFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMEJyYWNrZXRzX2Z1bGxfc2l6ZQBNAGEAdABoAHMAIABGAG8AcgAgAE0AbwByAGUAAAADAAAAAAAAAcAA4AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAuQf%2FAAGNhQA%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1e9c1d970bf1dedebfe90fae9eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2242.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Etan%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2219%22%3E%26%23x239B%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2225%22%3E%26%23x239C%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E%26%23x239D%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2268.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E6%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2277.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2286.5%22%20y%3D%2222%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1e9c1d970bf1dedebfe90fae9eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2298.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E%26%23x2212%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%22109.5%22%20x2%3D%22124.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1e9c1d970bf1dedebfe90fae9eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22117.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22117.5%22%20y%3D%2238%22%3E4%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22128.5%22%20y%3D%2219%22%3E%26%23x239E%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22brack_sm2882ad605b1e27be87c7468%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22128.5%22%20y%3D%2225%22%3E%26%23x239F%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22bracketse552f5417ff4680c6b50499%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22start%22%20x%3D%22128.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3E%26%23x23A0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.
Find the gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point where format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%224.5%22%20y%3D%2231%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1da1748c56a8e6b097a67ee67c2%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2218.5%22%20y%3D%2231%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2229.5%22%20x2%3D%2262.5%22%20y1%3D%2224.5%22%20y2%3D%2224.5%22%2F%3E%3Cpolyline%20fill%3D%22none%22%20points%3D%2214%2C-19%2013%2C-19%206%2C0%202%2C-7%22%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22translate(31.5%2C20.5)%22%2F%3E%3Cpolyline%20fill%3D%22none%22%20points%3D%226%2C0%202%2C-7%201%2C-6%22%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22translate(31.5%2C20.5)%22%2F%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2245.5%22%20x2%3D%2260.5%22%20y1%3D%221.5%22%20y2%3D%221.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1da1748c56a8e6b097a67ee67c2%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2253.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2246.5%22%20y%3D%2242%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.
Give your answer as an exact value.

Did this video help you?
Differentiating e^x & lnx
How do I differentiate exponentials and logarithms?
- The derivative of
is
where
- The derivative of
is
where
- For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- in the special case
,
(
's cancel)
- in the special case
- the derivative of
- For the general function
,
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
is
- the derivative of
- The last two sets of results can be derived using the chain rule
Examiner Tip
- Remember to avoid the common mistakes:
- the derivative of
with respect to
is
, NOT
- the derivative of
with respect to
is
, NOT
- the derivative of
Worked example
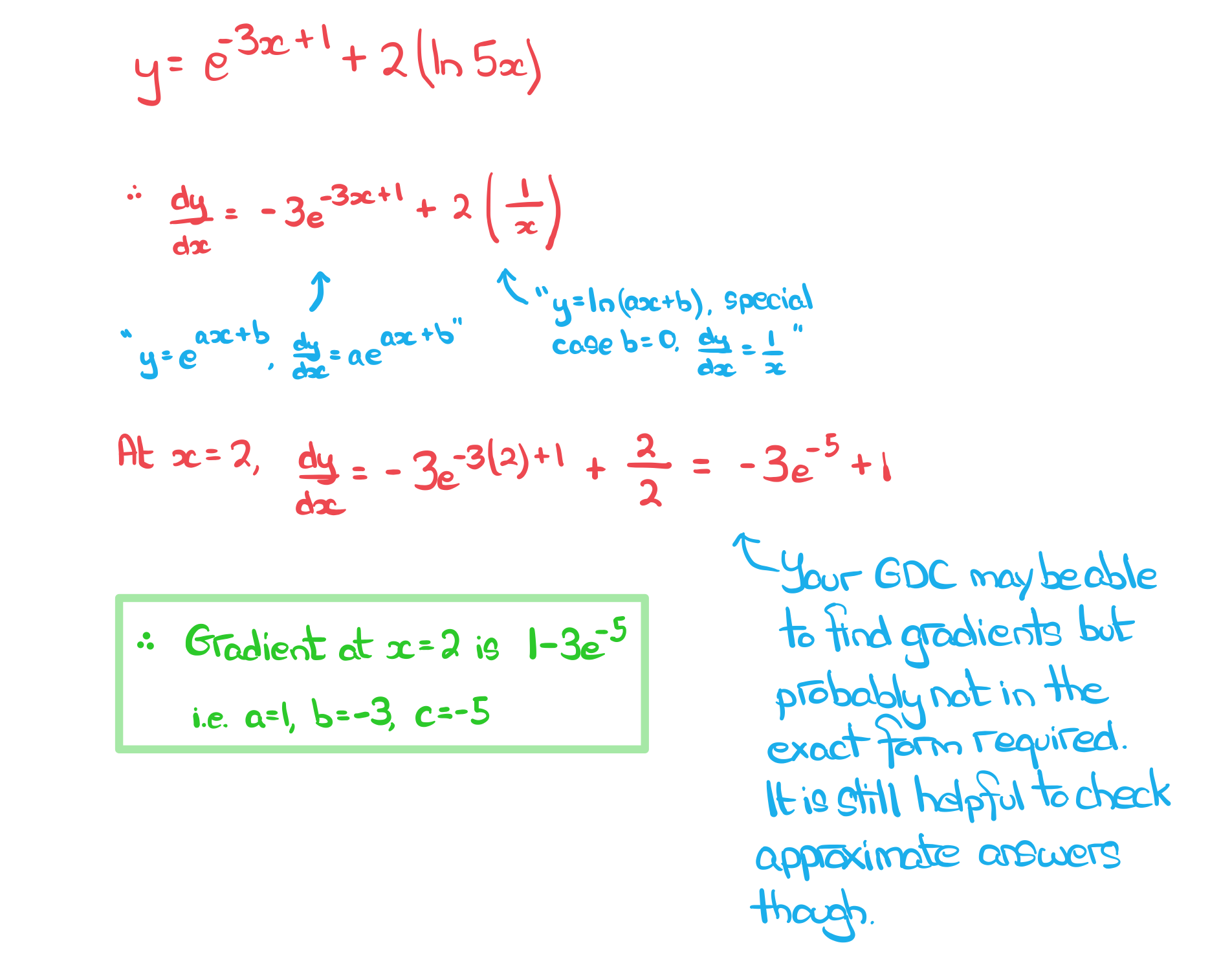
A curve has the equation.
Find the gradient of the curve at the point where gving your answer in the form
, where
and
are integers to be found.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
