Simple Identities (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Simple identities
What are the trigonometric identities relating sin, cos and tan?
Two trigonometric identities you must know are
This is the identity for tan θ
This is the Pythagorean identity
Note that the notation
is the same as
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both identities can be found in the formula booklet.
How do I derive these identities?
Draw a right-angled triangle with a hypotenuse equal to 1
Label one of the other angles θ
Use right-angled trigonometry to find the lengths of the other sides
The side adjacent to this angle is cosθ
The side opposite to this angle is sinθ
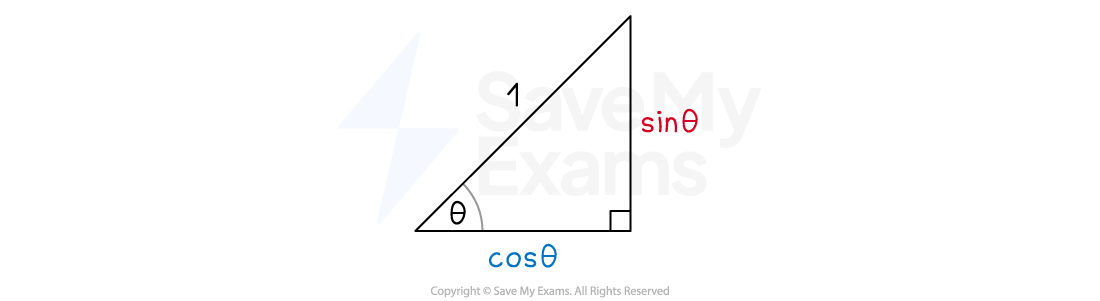
The Pythagorean identity is found using Pythagoras' theorem
The tan identity is found using the definition
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to learn these derivations, but they might help you with your internal assessment.
How are the trigonometric identities used?
Trigonometric identities are used to change an equation into a form that allows it to be solved
Rearranging the Pythagorean identity often makes it easier to work with
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are asked to show that one thing is identical to another, look at what parts are missing – for example, if tan x has gone it must have been substituted
Worked Example
Show that the equation can be written in the form
, where
,
and
are integers to be found.
Answer:
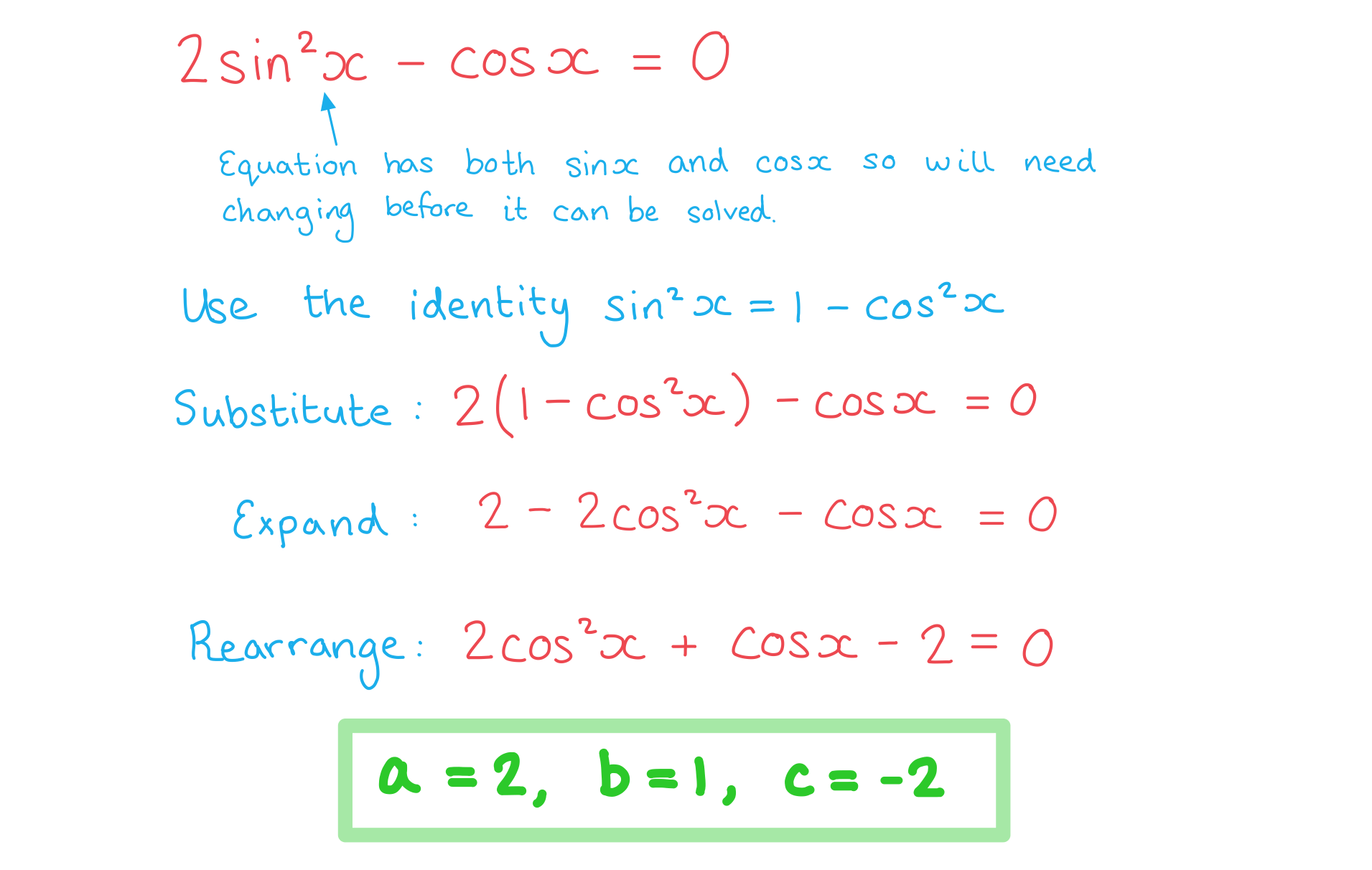

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
