Translations of Graphs (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Translations of Graphs
What are translations of graphs?
When you alter a function in certain ways, the effects on the graph of the function can be described by geometrical transformations
For a translation:
the graph is moved (up or down, left or right) in the xy plane
Its position changes
the shape, size, and orientation of the graph remain unchanged
A particular translation (how far left/right, how far up/down) is specified by a translation vector
:
x is the horizontal displacement
Positive moves right
Negative moves left
y is the vertical displacement
Positive moves up
Negative moves down

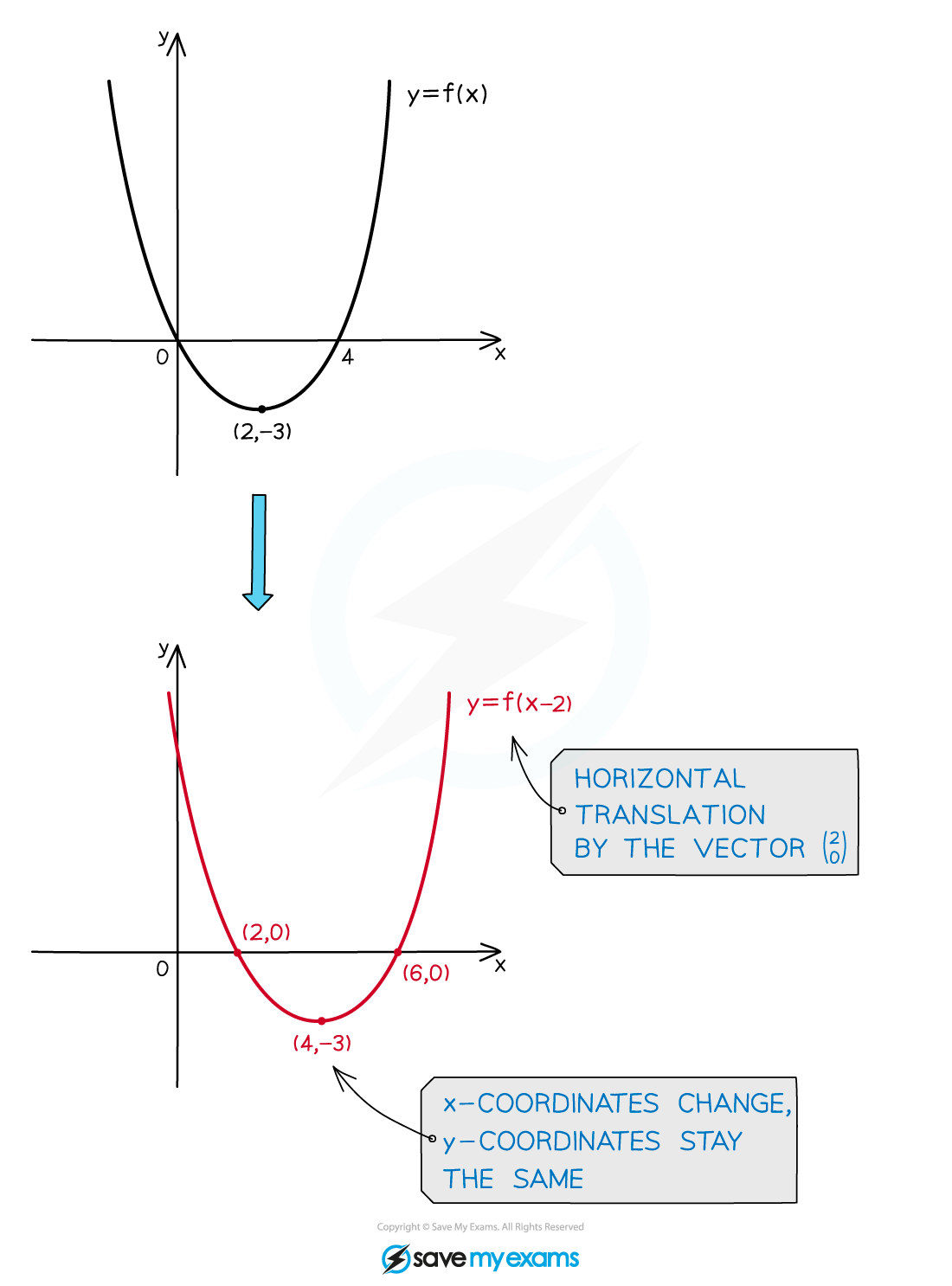
What effects do horizontal translations have on the graphs and functions?
A horizontal translation of the graph
by the vector
is represented by
The x-coordinates change
The value a is added to them
The y-coordinates stay the same
The coordinates
become
Horizontal asymptotes stay the same
Vertical asymptotes change
becomes
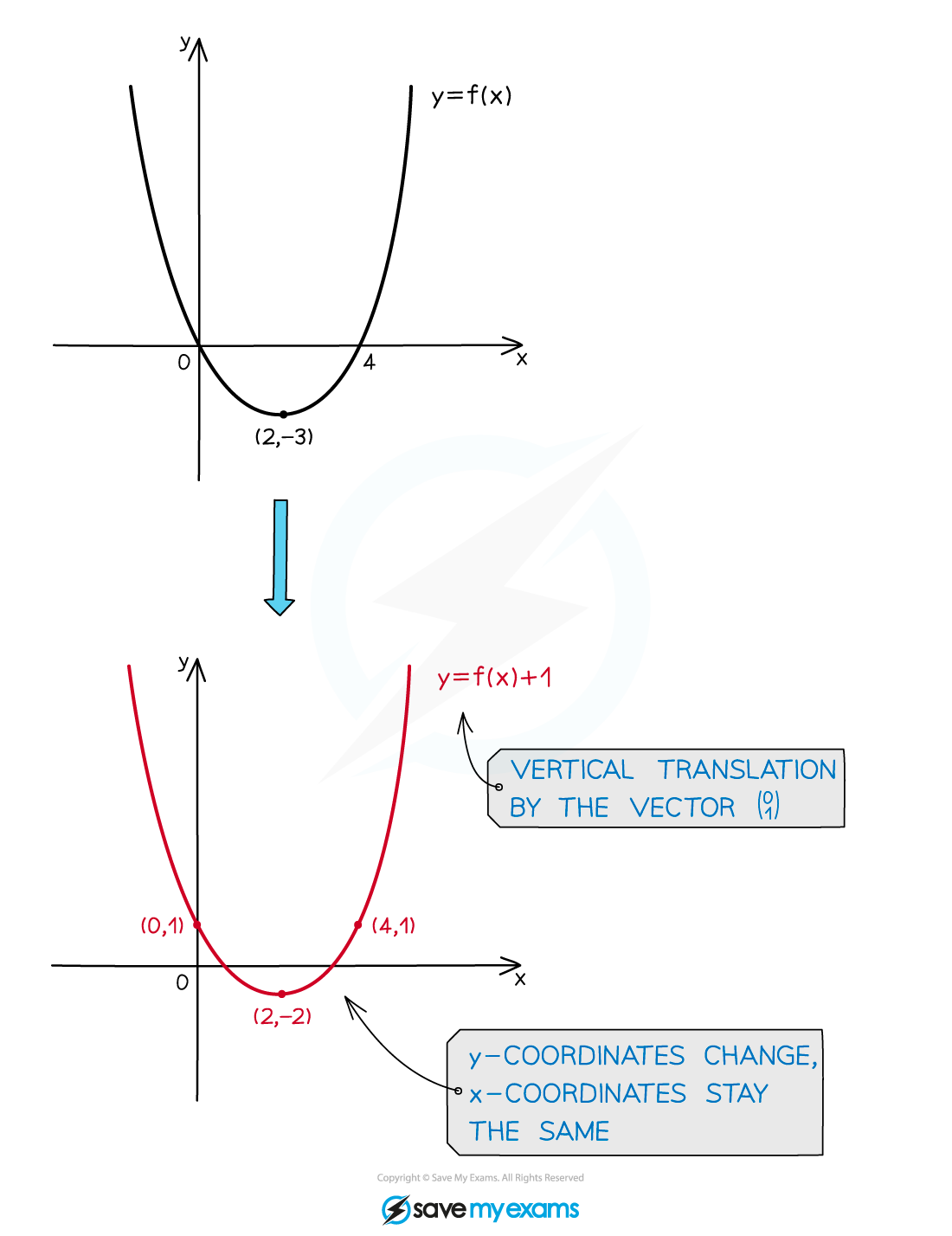
What effects do vertical translations have on the graphs and functions?
A vertical translation of the graph
by the vector
is represented by
This is often rearranged to
The x-coordinates stay the same
The y-coordinates change
The value b is added to them
The coordinates
become
Horizontal asymptotes change
becomes
Vertical asymptotes stay the same
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To get full marks in an exam make sure you use correct mathematical terminology
For example: Translate by the vector
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the graph of .
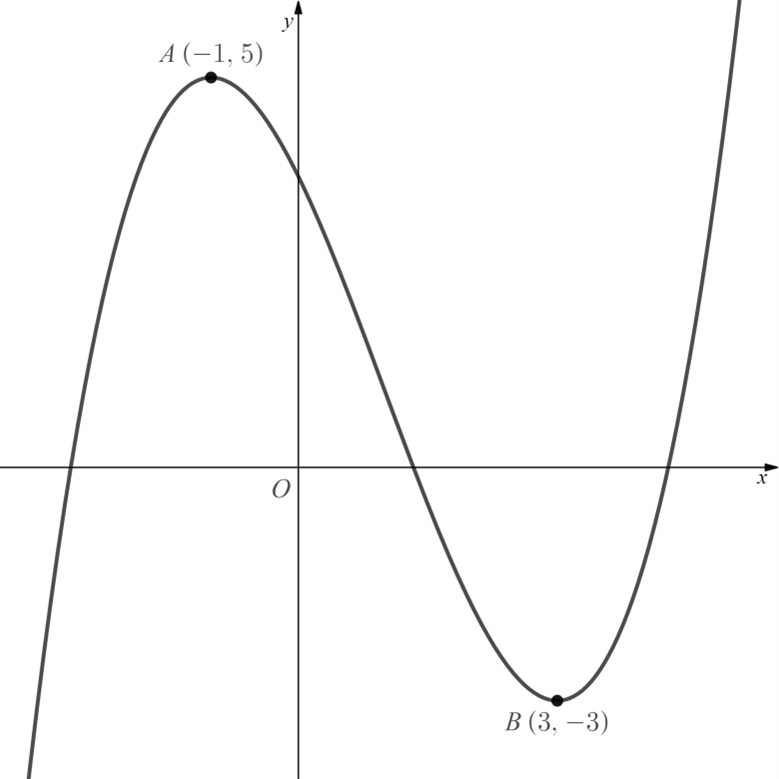
a) Sketch the graph of .

b) Sketch the graph of .


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
