Did this video help you?
Kinematics Toolkit (DP IB Maths: AA HL): Revision Note
Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration
What is kinematics?
- Kinematics is the branch of mathematics that models and analyses the motion of objects
- Common words such as distance, speed and acceleration are used in kinematics but are used according to their technical definition
What definitions do I need to be aware of?
- Firstly, only motion of an object in a straight line is considered
- this could be a horizontal straight line
- the positive direction would be to the right
- or this could be a vertical straight line
- the positive direction would be upwards
- this could be a horizontal straight line
Particle
- A particle is the general term for an object
- some questions may use a specific object such as a car or a ball
Time seconds
- Displacement, velocity and acceleration are all functions of time
- Initially time is zero
Displacement m
- The displacement of a particle is its distance relative to a fixed point
- the fixed point is often (but not always) the particle’s initial position
- Displacement will be zero
if the object is at or has returned to its initial position
- Displacement will be negative if its position relative to the fixed point is in the negative direction (left or down)
Distance m
- Use of the word distance needs to be considered carefully and could refer to
- the distance travelled by a particle
- the (straight line) distance the particle is from a particular point
- Be careful not to confuse displacement with distance
- if a bus route starts and ends at a bus depot, when the bus has returned to the depot, its displacement will be zero but the distance the bus has travelled will be the length of the route
- Distance is always positive
Velocity m s-1
- The velocity of a particle is the rate of change of its displacement at time
- Velocity will be negative if the particle is moving in the negative direction
- A velocity of zero means the particle is stationary
Speed m s-1
- Speed is the magnitude (a.k.a. absolute value or modulus) of velocity
- as the particle is moving in a straight line, speed is the velocity ignoring the direction
- if
- if
- if
- as the particle is moving in a straight line, speed is the velocity ignoring the direction
Acceleration m s-2
- The acceleration of a particle is the rate of change of its velocity at time
- Acceleration can be negative but this alone cannot fully describe the particle’s motion
- if velocity and acceleration have the same sign the particle is accelerating (speeding up)
- if velocity and acceleration have different signs then the particle is decelerating (slowing down)
- if acceleration is zero
the particle is moving with constant velocity
- in all cases the direction of motion is determined by the sign of velocity
Are there any other words or phrases in kinematics I should know?
- Certain words and phrases can imply values or directions in kinematics
- a particle described as “at rest” means that its velocity is zero,
- a particle described as moving “due east” or “right” or would be moving in the positive horizontal direction
- this also means that
- this also means that
- a particle “dropped from the top of a cliff” or “down” would be moving in the negative vertical direction
- this also means that
- this also means that
- a particle described as “at rest” means that its velocity is zero,
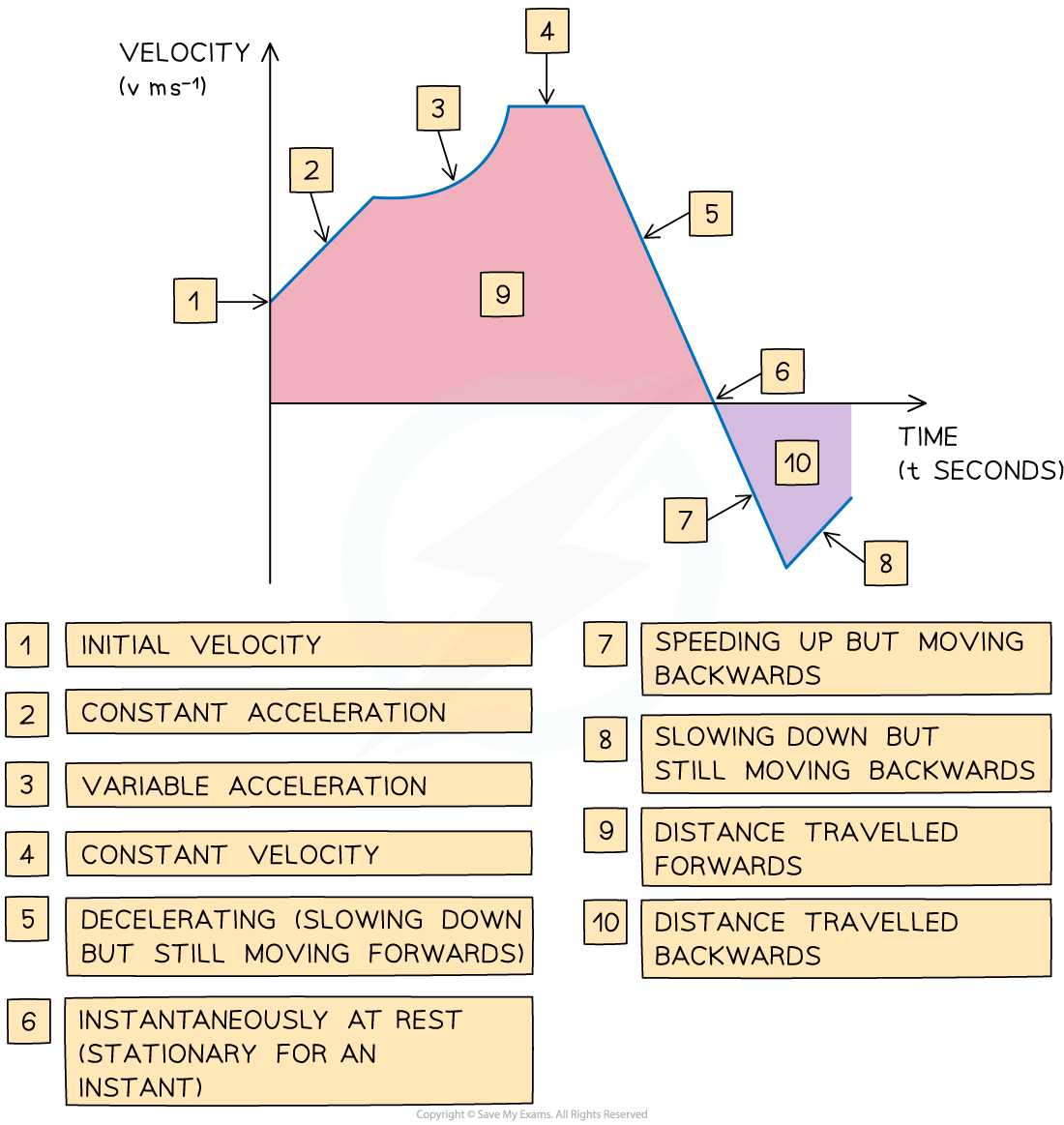
What are the key features of a velocity-time graph?
- The gradient of the graph equals the acceleration of an object
- A straight line shows that the object is accelerating at a constant rate
- A horizontal line shows that the object is moving at a constant velocity
- The area between graph and the x-axis tells us the change in displacement of the object
- Graph above the x-axis means the object is moving forwards
- Graph below the x-axis means the object is moving backwards
- The total displacement of the object from its starting point is the sum of the areas above the x-axis minus the sum of the areas below the x-axis
- The total distance travelled by the object is the sum of all the areas
- If the graph touches the x-axis then the object is stationary at that time
- If the graph is above the x-axis then the object has positive velocity and is travelling forwards
- If the graph is below the x-axis then the object has negative velocity and is travelling backwards
Examiner Tip
- In an exam if you are given an expression for the velocity then sketching a velocity-time graph can help visualise the problem
Worked example
A particle is projected vertically upwards from ground level, taking 8 seconds to return to the ground.
The velocity-time graph below illustrates the motion of the particle for these 8 seconds.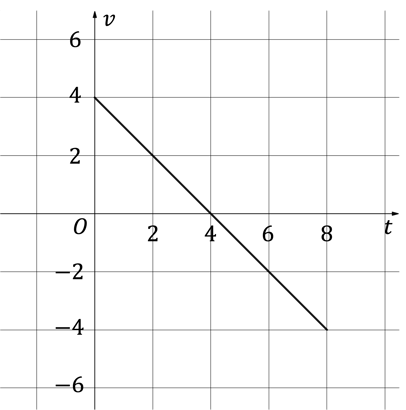
i)
How many seconds does the particle take to reach its maximum height?
Give a reason for your answer.
Give a reason for your answer.
ii)
State, with a reason, whether the particle is accelerating or decelerating at timeformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Et%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2218.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2231.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E3%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
