Box & Whisker Diagrams (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Box plots
What is a box plot (box and whisker diagram)?
A box plot (or box and whisker diagram) is a graph that clearly shows key statistics from a data set
It shows the median, quartiles, minimum and maximum values and outliers
It does not show any other individual data items
The middle 50% of the data will be represented by the box section of the graph and the lower and upper 25% of the data will be represented by each of the whiskers
Any outliers are represented with a cross on the outside of the whiskers
If there is an outlier then the whisker will end at the value before the outlier
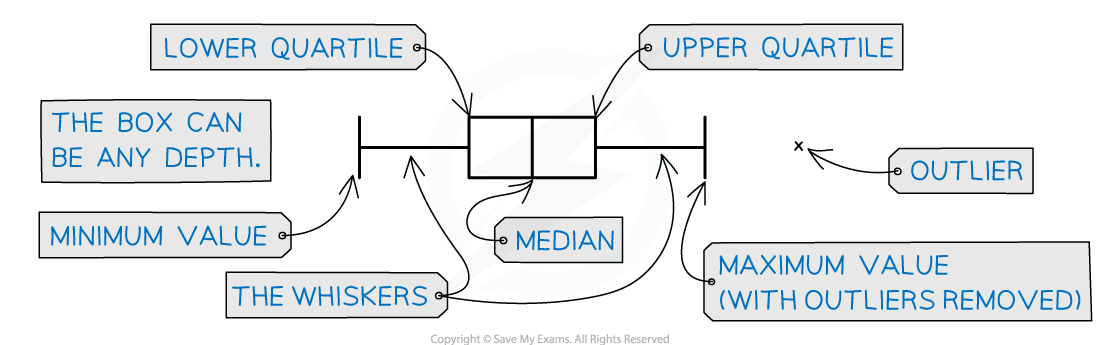
Only one axis is used when graphing a box plot
It is still important to make sure the axis has a clear, even scale and is labelled with units
What are box plots useful for?
Box plots can clearly show the shape of the distribution
If a box plot is symmetrical about the median then the data could be normally distributed
Box plots are often used for comparing two sets of data
Two box plots will be drawn next to each other using the same axis
They are useful for comparing data because it is easy to see the main shape of the distribution of the data from a box plot
You can easily compare the medians and interquartile ranges
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an exam you can use your GDC to draw a box plot if you have the raw data. Your calculator's box plot can also include outliers so this is a good way to check.
Worked Example
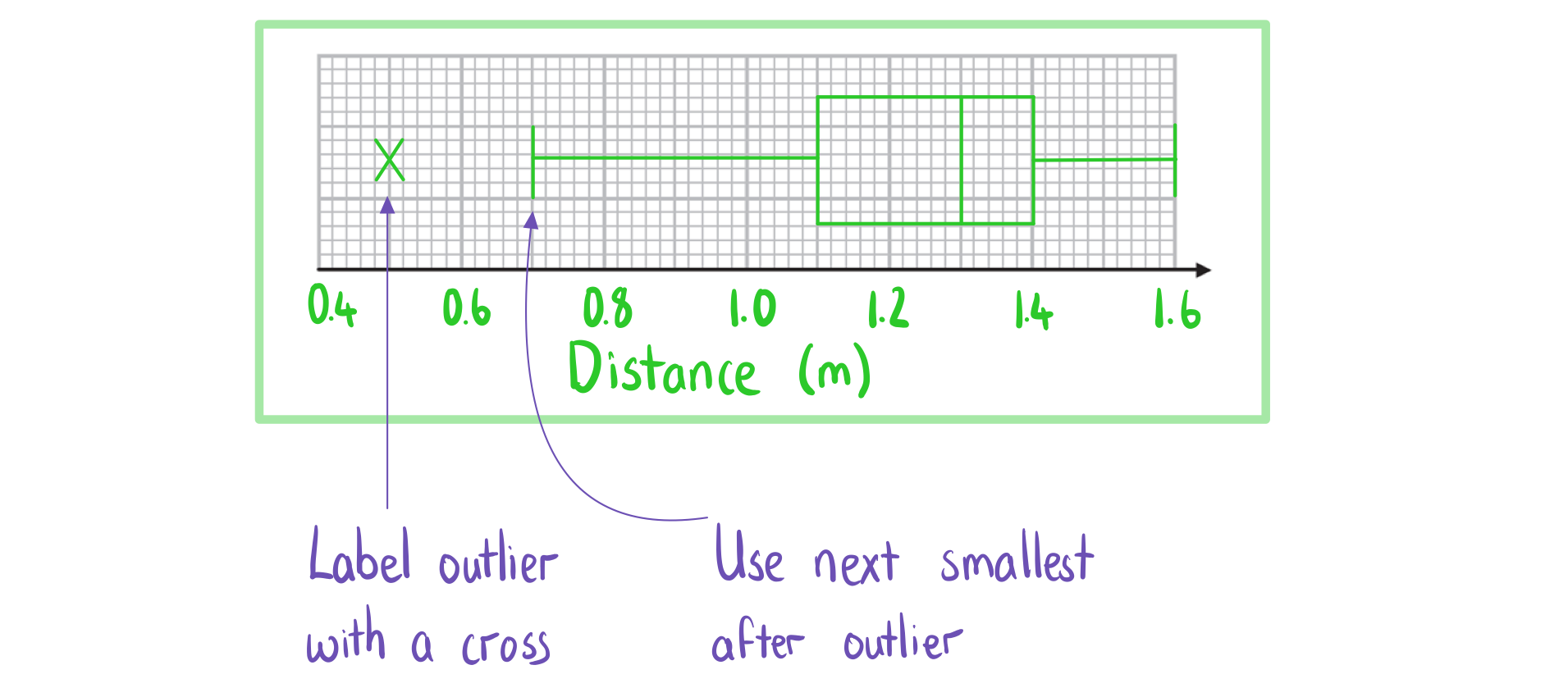
The distances, in metres, travelled by 15 snails in a one-minute period are recorded and shown below:
0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.2, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.4, 1.4, 1.4, 1.5, 1.5, 1.6
a) i) Find the values of and
.
ii) Find the interquartile range.
iii) Identify any outliers.
Answer:

b) Draw a box plot for the data.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
