Language of Functions (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Language of functions
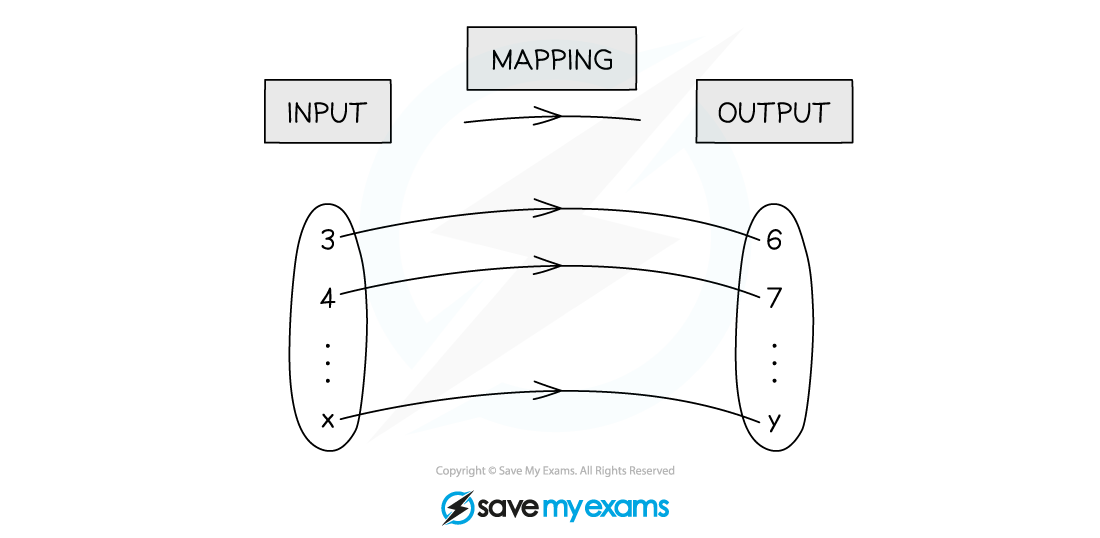
What is a mapping?
A mapping transforms one set of values (inputs) into another set of values (outputs)
Mappings can be:
One-to-one
Each input gets mapped to exactly one unique output
No two inputs are mapped to the same output
For example: A mapping that cubes the input
{1, 2, 3, ...} maps to {1, 8, 27, ...}
Many-to-one
Each input gets mapped to exactly one output
Multiple inputs can be mapped to the same output
For example: A mapping that squares the input
{±1, ±2, ±3, ...} map to {1, 4, 16, ...}
One-to-many
An input can be mapped to more than one output
No two inputs are mapped to the same output
For example: A mapping that gives the numbers which when squared equal the input
{1, 4, 16, ...} maps to {±1, ±2, ±3, ...}
Many-to-many
An input can be mapped to more than one output
Multiple inputs can be mapped to the same output
For example: A mapping that gives the factors of the input
e.g. the factors of {2, 3} are {1, 2, 3}
one input, e.g. {2}, has many outputs, e.g. {1, 2}
one output, e.g. {1}, has many inputs, e.g. {2, 3}
What is a function?
A function is a mapping between two sets of numbers where each input gets mapped to exactly one output
The output does not need to be unique
This means a function can be
one-to-one
or many-to-one

A sketch of the function must pass the vertical line test
Any vertical line will intersect with the graph at most once
e.g.
and any vertical line
pass the test
What notation is used for functions?
Functions are denoted using letters (such as
etc)
If
is the input
then
is the output of the function
e.g. if
when
, then
What are the domain and range of a function?
The domain of a function is the set of all inputs
A domain should be stated with a function
If a domain is not stated then it is assumed the domain is all the real values
Domains are expressed in terms of
e.g.
The range of a function is the set of all outputs
The range depends on the domain
Ranges are expressed in terms of
e.g.
To graph a function we use the inputs as the
-coordinates and the outputs as the
-coordinates
corresponds to the coordinates (2, 5)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are given the domain of a function, sketching a graph of the function often helps to find its range.
What sets of numbers do I need to know?
Common sets of numbers have special symbols:
represents all the real numbers that can be placed on a number line
means
is a real number
represents all the rational numbers
where
and
are integers and
represents all the integers (positive, negative and zero)
represents positive integers
represents the natural numbers (0,1,2,3...)

Examiner Tips and Tricks
If a question refers to the largest possible domain, it is usually all real numbers, , unless the function has a restriction, e.g. for
it is
or for
it is
.
What are piecewise functions?
Piecewise functions are defined by different functions depending on which interval the input is in
E.g.
so
whereas
The region for the individual functions cannot overlap
The function may or may not be continuous at the ends of the intervals
In the example above the function is
continuous at
as both sides match:
not continuous at
as
Worked Example
For the function :
(a) find the value of .
Answer:

(b) find the range of .
Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
