Modulus & Argument (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Modulus & Argument
How do I find the modulus of a complex number?
The modulus of a complex number is its distance from the origin when plotted on an Argand diagram
The modulus of
is written
If
, then we can use Pythagoras to show…
A modulus is never negative
What features should I know about the modulus of a complex number?
the modulus is related to the complex conjugate by…
This is because
In general,
e.g. both
and
have a modulus of 5, but
simplifies to 8i which has a modulus of 8
How do I find the argument of a complex number?
The argument of a complex number is the angle that it makes on an Argand diagram
The angle must be taken from the positive real axis
The angle must be in a counter-clockwise direction
Arguments are measured in radians
They can be given exact in terms of
The argument of
is written
Arguments can be calculated using right-angled trigonometry
This involves using the tan ratio plus a sketch to decide whether it is positive/negative and acute/obtuse
What features should I know about the argument of a complex number?
Arguments are usually given in the range
Negative arguments are for complex numbers in the third and fourth quadrants
Occasionally you could be asked to give arguments in the range
The question will make it clear which range to use
The argument of zero,
is undefined (no angle can be drawn)
What are the rules for moduli and arguments under multiplication and division?
When two complex numbers,
and
, are multiplied to give
, their moduli are also multiplied
When two complex numbers,
and
, are divided to give
, their moduli are also divided
When two complex numbers,
and
, are multiplied to give
, their arguments are added
When two complex numbers,
and
, are divided to give
, their arguments are subtracted
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always draw a quick sketch to help you see what quadrant the complex number lies in when working out an argument
Look for the range of values within which you should give your argument
If it is
then you may need to measure it in the negative direction
If it is
then you will always measure in the positive direction (counter - clockwise)
Worked Example
a) Find the modulus and argument of
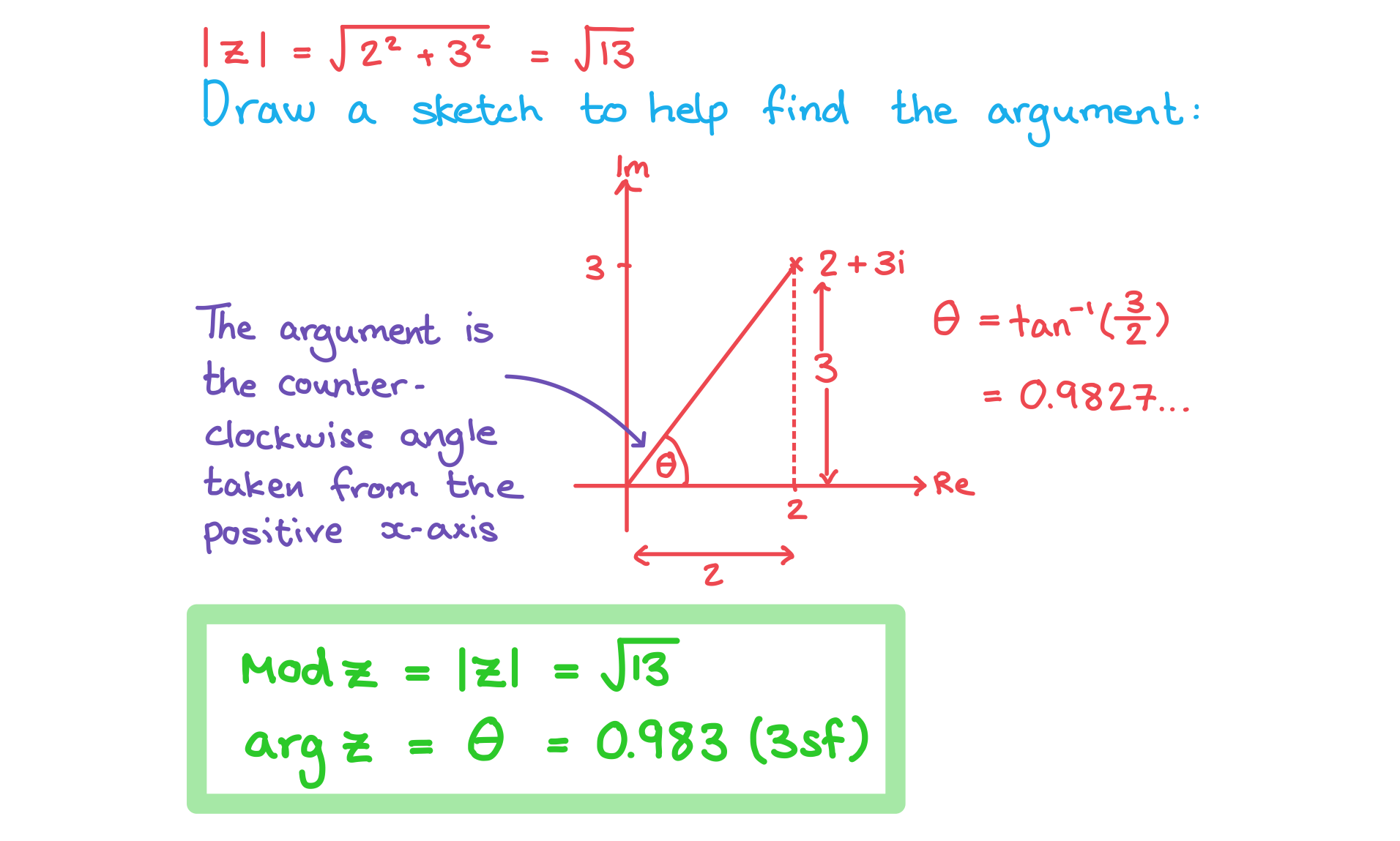
b) Find the modulus and argument of
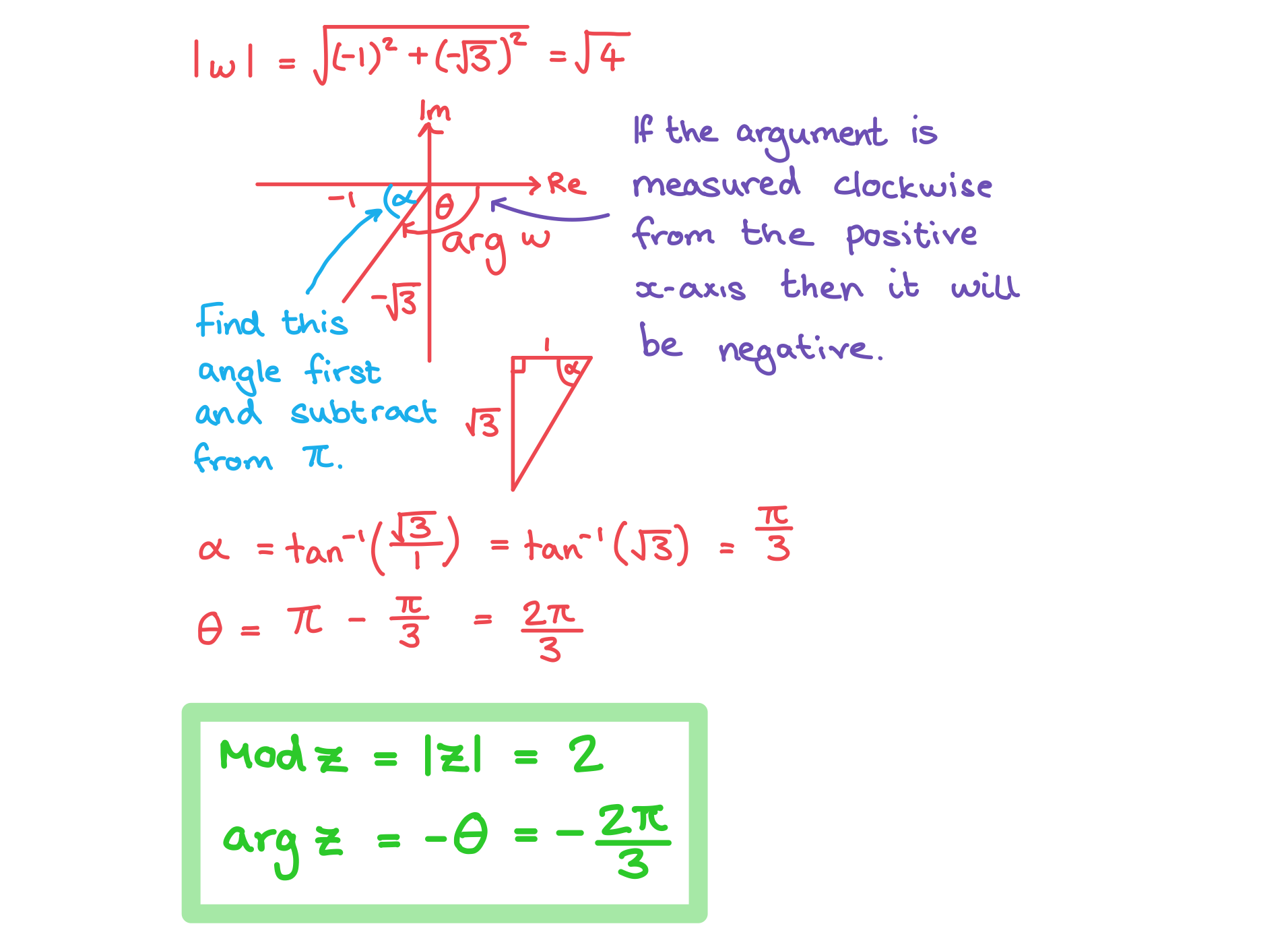

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
