Applications of Trigonometry & Pythagoras (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Bearings
What are bearings?
Bearings are a way of describing and using directions as angles
They are specifically defined for use in navigation because they give a precise location and/or direction
How are bearings defined?
There are three rules which must be followed every time a bearing is defined
They are measured from the North direction
An arrow showing the North line should be included on the diagram
They are measured clockwise
The angle is always written in 3 figures
If the angle is less than 100° the first digit will be a zero
What are bearings used for?
Bearings questions will normally involve the use of Pythagoras or trigonometry to find missing distances (lengths) and directions (angles) within navigation questions
You should always draw a diagram
There may be a scale given or you may need to consider using a scale
However normally in IB you will be using triangle calculations to find the distances
Some questions may also involve the use of angle facts to find the missing directions
To answer a question involving drawing bearings the following steps may help:
STEP 1: Draw a diagram adding in any points and distances you have been given
STEP 2: Draw a North line (arrow pointing vertically up) at the point you wish to measure the bearing from
If you are given the bearing from A to B draw the North line at A
STEP 3: Measure the angle of the bearing given from the North line in the clockwise direction
STEP 4: Draw a line and add the point B at the given distance
You will likely then need to use trigonometry to calculate the shortest distance or another given distance
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always draw a big, clear diagram and annotate it, be especially careful to label the angles in the correct places!
Worked Example
The point B is 7 km from A on a bearing of 105°. The distance from B to C is 5 km and the bearing from B to C is 230°. Find the distance from A to C.

Did this video help you?
Elevation & Depression
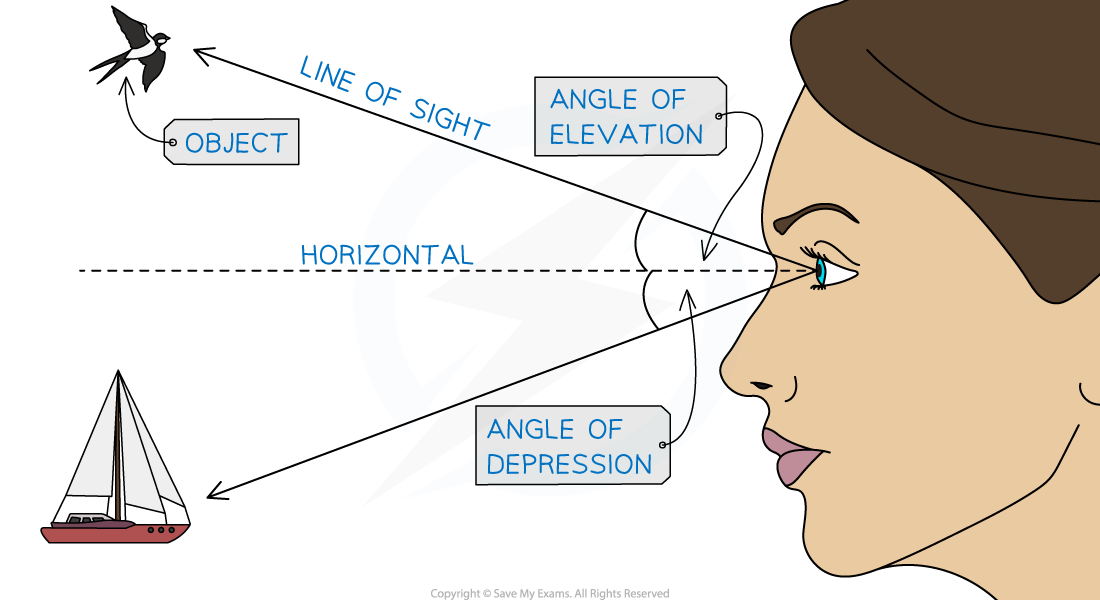
What are the angles of elevation and depression?
If a person looks at an object that is not on the same horizontal line as their eye-level they will be looking at either an angle of elevation or depression
If a person looks up at an object their line of sight will be at an angle of elevation with the horizontal
If a person looks down at an object their line of sight will be at an angle of depression with the horizontal
Angles of elevation and depression are measured from the horizontal
Right-angled trigonometry can be used to find an angle of elevation or depression or a missing distance
Tan is often used in real-life scenarios with angles of elevation and depression
For example if we know the distance we are standing from a tree and the angle of elevation of the top of the tree we can use Tan to find its height
Or if we are looking at a boat at to sea and we know our height above sea level and the angle of depression we can find how far away the boat is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It may be useful to draw more than one diagram if the triangles that you are interested in overlap one another
Worked Example
A cliff is perpendicular to the sea and the top of the cliff stands 24 m above the level of the sea. The angle of depression from the cliff to a boat at sea is 35°. At a point m up the cliff is a flag marker and the angle of elevation from the boat to the flag marker is 18°.
a) Draw and label a diagram to show the top of the cliff, T, the foot of the cliff, F, the flag marker, M, and the boat, B, labelling all the angles and distances given above.

b) Find the distance from the boat to the foot of the cliff.

c) Find the value of .

Did this video help you?
Constructing Diagrams
What diagrams will I need to construct?
In IB you will be expected to construct diagrams based on information given
The information will include compass directions, bearings, angles
Look out for the plane the diagram should be drawn in
It will either be horizontal (something occurring at sea or on the ground)
Or it will be vertical (Including height)
Work through the statements given in the instructions systematically
What do I need to know?
Your diagrams will be sketches, they do not need to be accurate or to scale
However the more accurate your diagram is the easier it is to work with
Read the full set of instructions once before beginning to draw the diagram so you have a rough idea of where each object is
Make sure you know your compass directions
Due east means on a bearing of 090°
Draw the line directly to the right
Due south means on a bearing of 180°
Draw the line vertically downwards
Due west means on a bearing of 270°
Draw the line directly to the left
Due north means on a bearing of 360° (or 000°)
Draw the line vertically upwards
Using the above bearings for compass directions will help you to estimate angles for other bearings on your diagram
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Draw your diagrams in pencil so that you can easily erase any errors
Worked Example
A city at B is due east of a city at A and A is due north of a city at E. A city at C is due south of B.
The bearing from A to D is 155° and the bearing from D to C is 30°.
The distance AB = 50 km, the distances BC = CD = 30 km and the distances DE = AE = 40 km.
Draw and label a diagram to show the cities A, B, C, D and E and clearly mark the bearings and distances given.


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
