Quadratic Functions (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Quadratic Functions & Graphs
What are the key features of quadratic graphs?
A quadratic graph can be written in the form
where
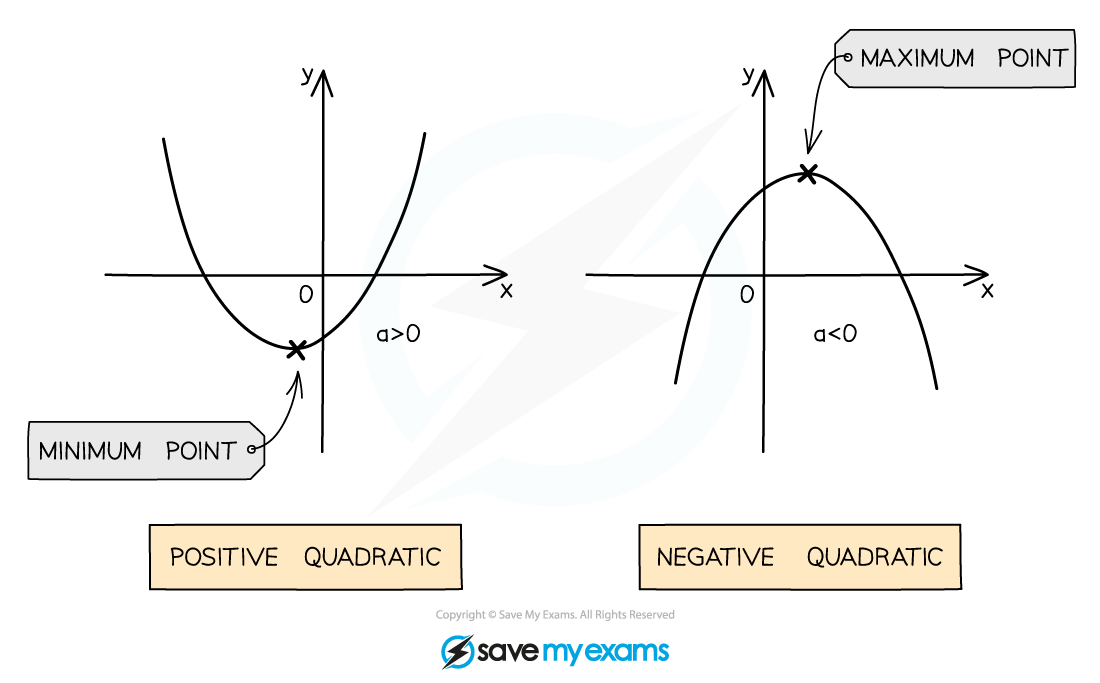
The value of a affects the shape of the curve
If a is positive the shape is concave up ∪
If a is negative the shape is concave down ∩
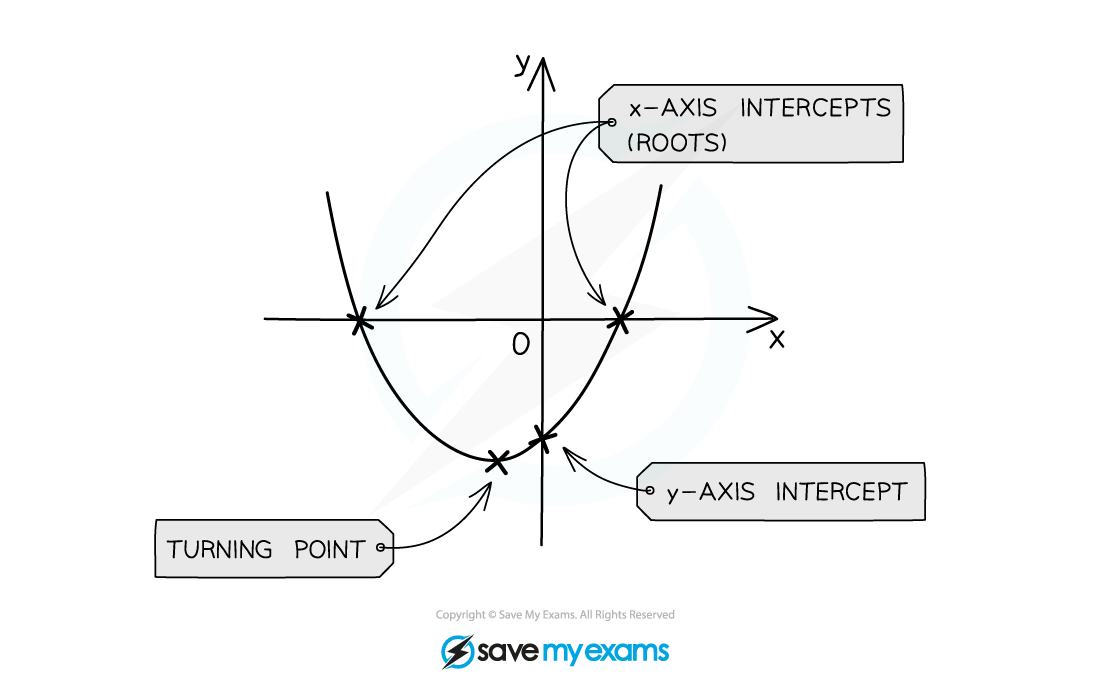
The y-intercept is at the point (0, c)
The zeros or roots are the solutions to
These can be found by
Factorising
Quadratic formula
Using your GDC
These are also called the x-intercepts
There can be 0, 1 or 2 x-intercepts
This is determined by the value of the discriminant
There is an axis of symmetry at
This is given in your formula booklet
If there are two x-intercepts then the axis of symmetry goes through the midpoint of them
The vertex lies on the axis of symmetry
It can be found by completing the square
The x-coordinate is
The y-coordinate can be found using the GDC or by calculating y when
If a is positive then the vertex is the minimum point
If a is negative then the vertex is the maximum point
What are the equations of a quadratic function?
This is the general form
It clearly shows the y-intercept (0, c)
You can find the axis of symmetry by
This is given in the formula booklet
This is the factorised form
It clearly shows the roots (p, 0) & (q, 0)
You can find the axis of symmetry by
This is the vertex form
It clearly shows the vertex (h, k)
The axis of symmetry is therefore
It clearly shows how the function can be transformed from the graph
Vertical stretch by scale factor a
Translation by vector
How do I find an equation of a quadratic?
If you have the roots x = p and x = q...
Write in factorised form
You will need a third point to find the value of a
If you have the vertex (h, k) then...
Write in vertex form
You will need a second point to find the value of a
If you have three random points (x1, y1), (x2, y2) & (x3, y3) then...
Write in the general form
Substitute the three points into the equation
Form and solve a system of three linear equations to find the values of a, b & c
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Use your GDC to find the roots and the turning point of a quadratic function
You do not need to factorise or complete the square
It is good exam technique to sketch the graph from your GDC as part of your working
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the graph of , where
is a quadratic function.
The intercept with the -axis and the vertex have been labelled.
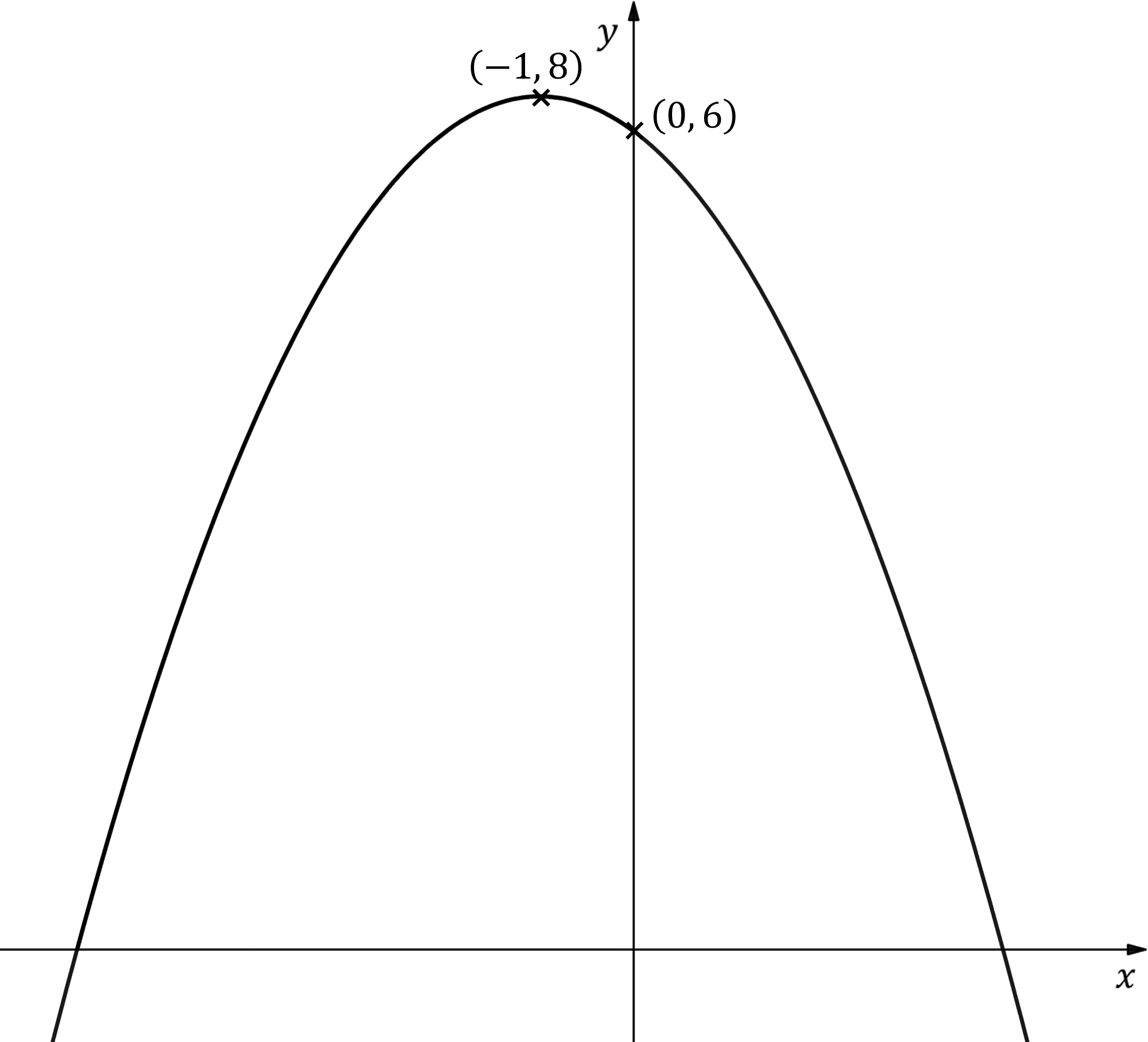
Write down an expression for .


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
