Higher Order Derivatives (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Second Order Derivatives
What is the second order derivative of a function?
If you differentiate the derivative of a function (i.e. differentiate the function a second time) you get the second order derivative of the function
There are two forms of notation for the second order derivative
(First order derivative)
(Second order derivative)
Note the position of the superscript 2’s
differentiating twice (so
) with respect to
twice (so
)
The second order derivative can be referred to simply as the second derivative
Similarly, the first order derivative can be just the first derivative
A first order derivative is the rate of change of a function
a second order derivative is the rate of change of the rate of change of a function
i.e. the rate of change of the function’s gradient
Second order derivatives can be used to
test for local minimum and maximum points
help determine the nature of stationary points
help determine the concavity of a function
graph derivatives
How do I find a second order derivative of a function?
By differentiating twice!
This may involve
rewriting fractions, roots, etc as negative and/or fractional powers
differentiating trigonometric functions, exponentials and logarithms
using chain rule
using product or quotient rule
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Negative and/or fractional powers can cause problems when finding second derivatives so work carefully through each term
Worked Example
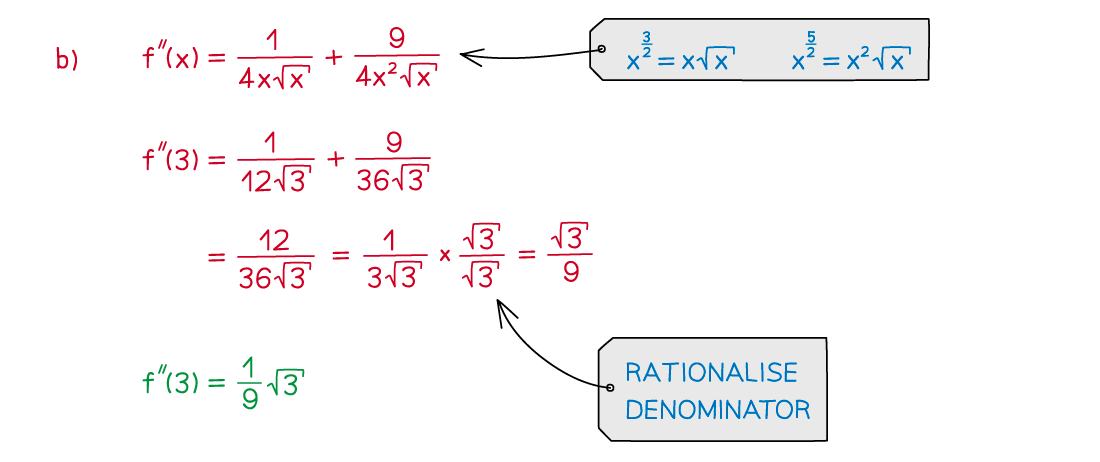
Given that
a) Find and
.

b) Evaluate .
Give your answer in the form , where
is an integer and
is a rational number.
Did this video help you?
Higher Order Derivatives
What is meant by higher order derivatives of a function?
Many functions can be differentiated numerous times
The third, fourth, fifth, etc derivatives of a function are generally called higher order derivatives
It may not be possible, or practical to (algebraically) differentiate complicated functions more than once or twice
Polynomials will, eventually, have higher order derivatives of zero
Since powers of x reduce by 1 each time
What is the notation for higher order derivatives?
The notation for higher order derivatives follows the logic from the first and second derivatives
or
except the ‘dash’ (prime) notation is replaced with numbers as this would become cumbersome after the first few
e.g. the fifth derivative would be
or
How do I find a higher order derivative of a function?
By differentiating as many times as required!
This may involve
rewriting fractions, roots, etc as negative and/or fractional powers
differentiating trigonometric functions, exponentials and logarithms
using chain rule
using product or quotient rule
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are required to evaluate a higher order derivative at a specific point your GDC can help
Typically a GDC will only work out the first and second derivative directly from the original function
But, if you wanted the fourth derivative, say, you only need differentiate twice algebraically, then call this the ‘original’ function on your GDC
Worked Example
It is given that .
a) Show that .

b) Without further working, write down an expression for .


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
