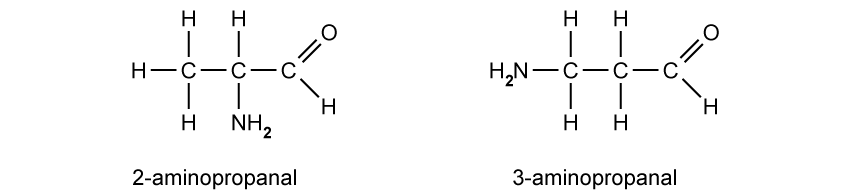Define the term hydrocarbon.
State the general formula for the following hydrocarbon families.
Alkanes …………………………
Alkenes …………………………
State the IUPAC name of the following hydrocarbon.

A student stated that as the number of carbon atoms increases in an alkane, the boiling point increases. State if the student is correct and justify your answer.
Did this page help you?