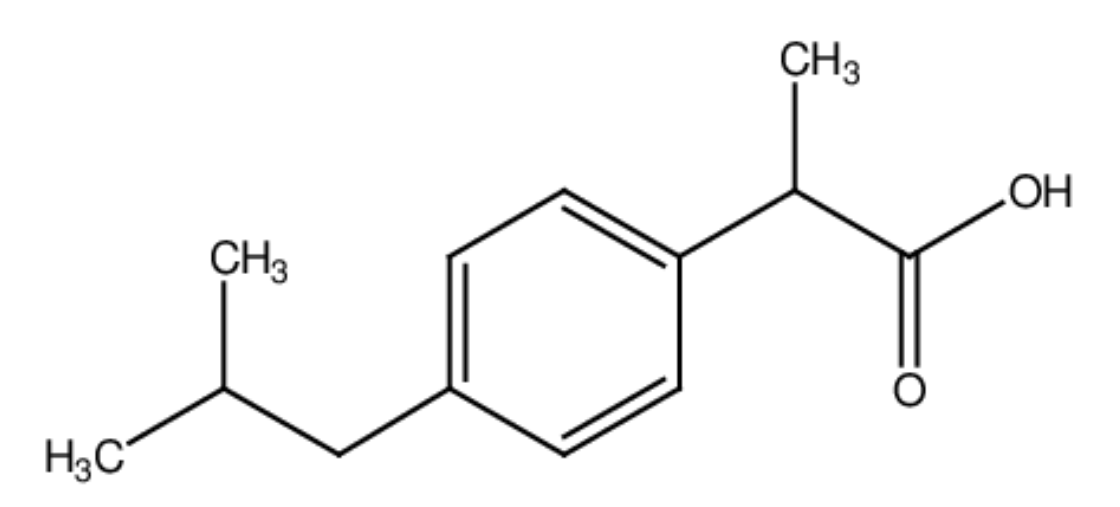
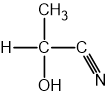
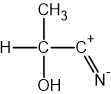
Using section 9 of the data booklet, state which of the following single covalent bonds is the most polar: C-O, C-H, or O-H.
Using section 11 of the data booklet, state the molecules C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6 in order of increasing carbon-carbon bond length.
Using section 12 of the data booklet, state the molecules C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6 in order of decreasing carbon-carbon bond strength.
A coordinate bond is one of the three covalent bonds in a molecule of carbon monoxide, CO.
State how a coordinate bond is formed.
Was this exam question helpful?