The Ion Product of Water (DP IB Chemistry): Revision Note
The ion product of water
pH of water
An equilibrium exists in water, where a few water molecules dissociate into proton and hydroxide ions
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is:
Kc x [H2O] = [H+][OH–]
Since the concentration of the H+ and OH- ions is very small, the concentration of water is considered to be a constant
This means that the expression can be rewritten as:
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
Where Kw (ion product of water) = Kc x [H2O] = 1.00 10-14 at 298K
The product of the two ion concentrations is always 1.00 x 10–14
This makes it straightforward to see the relationship between the two concentrations and the nature of the solution:
[H+] & [OH–] Table
[H+] | [OH–] | Type of solution |
|---|---|---|
0.1 | 1 x 10–13 | acidic |
1 x 10–3 | 1 x 10–11 | acidic |
1 x 10–5 | 1 x 10–9 | acidic |
1 x 10–7 | 1 x 10–7 | neutral |
1 x 10–9 | 1 x 10–5 | alkaline |
1 x 10–11 | 1 x 10–3 | alkaline |
1 x 10–13 | 0.1 | alkaline |
Worked Example
What is the pH of a solution of potassium hydroxide, KOH (aq) of concentration 1.0 × 10−3 mol dm−3 ?
Kw = 1.0 × 10−14 at 298 K
A. 3
B. 4
C. 10
D. 11
Answer:
The correct option is D
Rearrange Kw = [H+] [OH-]
[H+] =
Calculate the concentration of [H+]
[H+] = = 1.0 × 10−11 mol dm−3
So the pH = 11
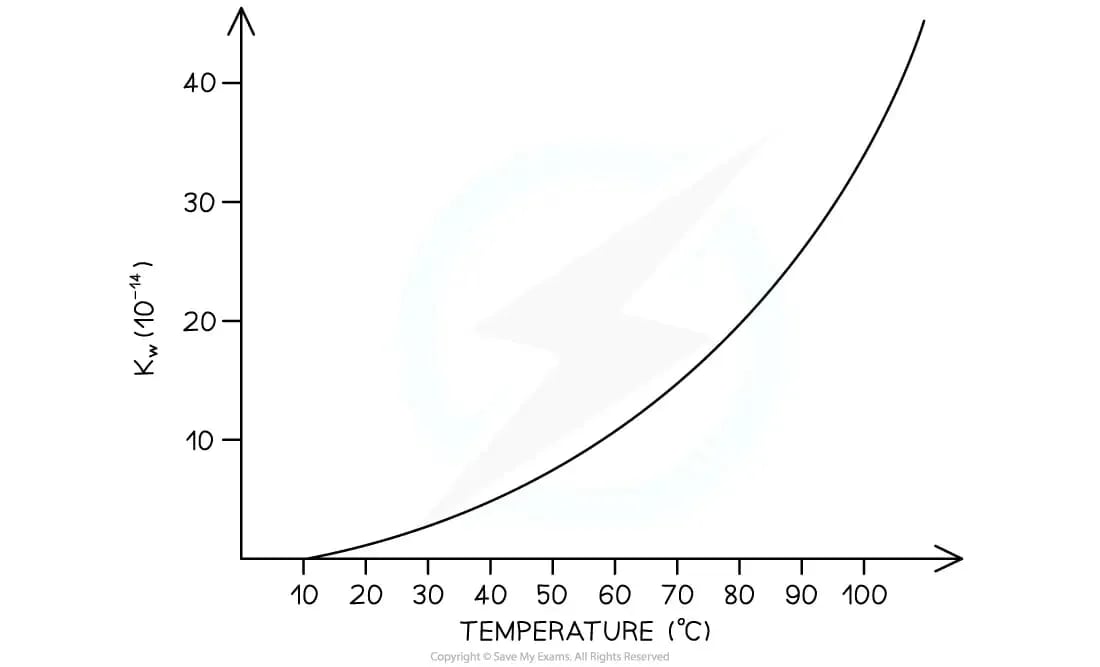
How does temperature affect the ion product of water, Kw?
The ionisation of water is an endothermic process
2H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
According to Le Châtelier's principle, if the temperature is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the right to absorb the added heat
This causes the concentrations of both H+ and OH- ions to increase
As a result, the values of Kw increases
The effect on pH
Since the concentration of H+ ions has increased, the pH of the water must decrease
pH = -log10[H+]
Due to the negative sign in the formula, as [H+] increases, pH decreases
Increasing the temperature decreases the pH of water (becomes more acidic)
Decreasing the temperature increases the pH of water (becomes more basic)
Graph to show how Kw changes with temperature
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Even though the pH of pure water is less than 7 at temperatures above 298 K, it is still neutral.
This is because the definition of neutrality is [H+] = [OH-], which remains true for pure water at any temperature.
The convention that "pH 7 is neutral" is only true at 298 K (25 °C).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?