Acid & Base Dissociation Constants (HL) (DP IB Chemistry): Revision Note
Acid & base dissociation constants
Weak acids
A weak acid is an acid that partially (or incompletely) dissociates in aqueous solutions
Examples; most carboxylic acids (e.g. ethanoic acid), HCN (hydrocyanic acid), H2S (hydrogen sulfide) and H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
In general, the following equilibrium is established:
HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
OR
HA (aq) ⇌ A- (aq) + H+ (aq)
At equilibrium:
Most HA molecules remain undissociated
The position lies to the left
An equilibrium constant can be written from this equation
This constant is called the acid dissociation constant, Ka
Carboxylic acids are weak acids
For example, propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH (aq), dissociates according to the following equation which leads to the Ka expression for propanoic acid:
CH3CH2COOH (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ CH3CH2COO– (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
OR
CH3CH2COOH (aq) ⇌ CH3CH2COO– (aq) + H+ (aq)
The acid dissociation constant expressions for propanoic acid:
Values of Ka are very small
The Ka for propanoic acid = 1.34 x 10-5
When writing the equilibrium expression for weak acids, we assume that the concentration of H+ (aq) due to the ionisation of water is negligible
Weak bases
A weak base only partially ionises in water.
This ionisation is described by the base dissociation constant Kb
In general, the equilibrium established is:
B (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ BH+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
The base dissociation constant expression is:
Amines are weak bases
For example, 1-phenylmethanamine, C6H5CH2NH2 (aq), dissociates according to the following equation which leads to the Ka expression for 1-phenylmethanamine:
C6H5CH2NH2 (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ C6H5CH2NH3+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
Base dissociation constant expression for 1-phenylmethanamine
pKa and pKb
The range of values of Ka and Kb is very wide
For weak acids, the values themselves are very small numbers
Table of Ka values
Acid | Ka | pKa |
|---|---|---|
Methanoic acid, HCOOH | 1.77 x 10–4 | 3.75 |
Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH | 1.74 x 10–5 | 4.75 |
Benzoic acid, C6H5COOH | 6.46 x 10–5 | 4.18 |
Carbonic acid, H2CO3 | 4.30 x 10-5 | 6.36 |
For this reason, it is easier to work with another term called pKa for acids or pKb for bases
In order to convert the values we need to apply the following calculations:
pKa = -logKa Ka= 10-pKa
pKb = -logKb Kb= 10-pKb
The range of pKa values for most weak acids lies between 3 and 7
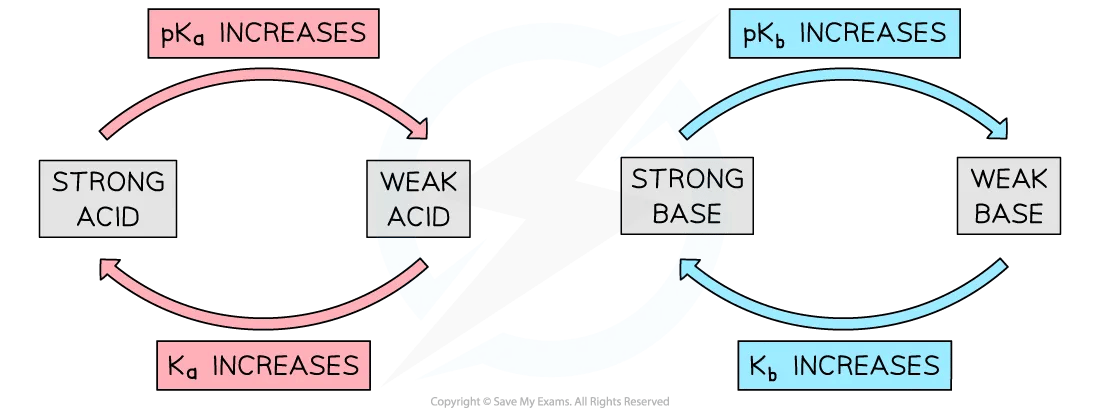
Relative strengths of acids and bases
A larger Ka value = stronger acid
A larger pKa = weaker acid
A larger Kb value = stronger base
A larger pKb value = weaker base
Diagram showing the relationship between strong and weak acids / bases
In all aqueous solutions, an equilibrium exists in water where a few water molecules dissociate into protons and hydroxide ions
We can derive an equilibrium constant for the reaction:
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
The concentration of water is constant, so the expression for Kw is:
Kw = [H+][OH-]
This is a specific equilibrium constant called the ion product for water
The product of the two ion concentrations is 1.00 x 10-14 at 298 K
For conjugate acid-base pairs, Ka and Kb are related to Kw
Ka x Kb = Kw
The conjugate base of ethanoic acid is the ethanoate ion, CH3COO– (aq)
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ CH3COO– (aq) + H+ (aq)
acid conjugate base
We can then put this into the Ka expression
The ethanoate ion will react with water according to the following equation
CH3COO– (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ CH3COOH (aq) + OH- (aq)
We can then put this into the Kb expression
Now, these two expressions can be combined, which corresponds to
Ka x Kb = Kw
Ka x Kb = 10-14
Or we could say that
pKa + pKb = pKw
pKa + pKb = 14
This makes the numbers much easier to deal with as using Ka Kb = 10-14 will give very small numbers
Combining the Ka and Kb expressions:
Or rearranging:

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?