Break-Even Analysis (DP IB Business Management) : Revision Note
An Introduction to Break Even Analysis
Break Even analysis is a financial tool used to determine the point at which the business revenue equals its expenses, resulting in neither profit nor loss
It helps businesses understand the minimum level of sales or output they need to achieve in order to cover all costs
This helps business managers make informed decisions about pricing and production volumes
Break Even analysis takes into account three main components
Diagram: the components of break even analysis
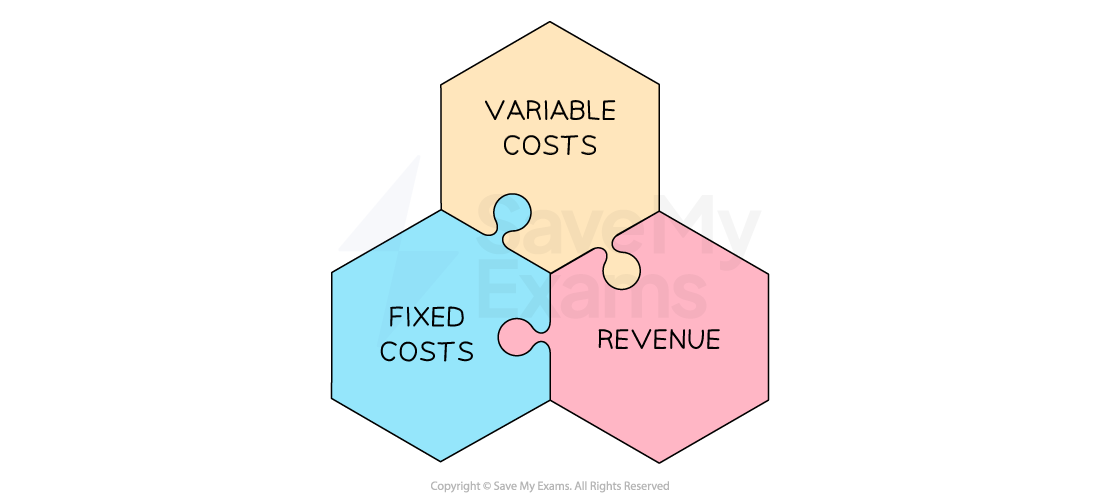
Fixed costs are costs that do not change regardless of the level of production or sales
E.g. rent, salaries and insurance
Variable costs are costs that vary with the level of production or sales
E.g. raw materials, direct labour costs, packaging and shipping costs
Sales revenue is the money gained from selling products/service and is calculated as follows
Sales revenue = number of items sold x selling price
Total Contribution Versus Contribution per unit
Contribution refers to the amount of money that the sale of a particular product contributes towards paying off the fixed costs of a business
Once the fixed costs are paid, the contribution becomes profit
Contribution can be calculated on a per unit basis or as an aggregate
Contribution per unit
Contribution per unit is a measure by which selling price of a unit exceeds the cost of making the unit
It is calculated using the formula:
E.g. If a product sells for $50 per unit and the variable cost of production is $30 per unit, the contribution per unit would be $20 ($50 - $30)
Total contribution
Total contribution is a measure of the combined profit per unit generated from the sale of each goods/services
It can be calculated in one of two ways
or
E.g if 1,000 units of a product are sold, and the contribution per unit is $20, the total contribution would be $20,000 ($20 × 1,000)
Total contribution is not the total profit made by the business because it does not take into account the fixed costs of the business
Interpreting Break Even Charts
A break even chart is a visual representation of the break even point and is used to identify the following:
Fixed costs, total costs and revenue over a range of output
The break even point - where total costs are equal to revenue
Profit or loss made at each level of output
The margin of safety
Diagram: break even chart

Diagram analysis
Fixed costs do not change as output increases
A2B's fixed costs are £8,000 and these do not change whether the business produces 0 units or 500 units
Total costs are made up of fixed and variable costs
At 0 units of output, they are made up exclusively of fixed costs
At 500 units the total variable costs equate to £11,800
This line slopes upwards because total variable costs increase as output increases
The revenue line also slopes upwards
At 0 units of output, the revenue is £0
At 500 units the total revenue equates to £11,800
Revenue will increase with the output
The line will slope more steeply than the total costs and will cross the total costs line at some point
The point at which the total costs and the revenue lines cross is the break even point
The break even level of output for A2B is 324 units
The margin of safety can be identified as the difference on the x-axis between the actual level of output (in this case 450 units) and the break even point
The profit made at a specific level of output can be identified as the space between the revenue and total costs lines
In this instance the profit made at 450 units of output is £14,400 - £11,250 = £3,150
Calculating the Break Even Point
The Break Even Point occurs where the total revenue earned for a product is exactly equal to its total costs
At the break even point the business is making neither a profit nor a loss
The contribution per unit value is used to calculate the Break Even Point
The break even point is expressed as units (e.g. the number of scented candles)
Identifying the break even point allows a business to understand how many items it needs to produce and sell to cover all costs before it starts to make a profit
Each subsequent unit sold past this point will generate profit for the business
Worked Example
Selected Cost and Revenue data for Montrose Glamping
| AUS$ |
Revenue per pod per night | 95 |
Variable costs per pod per night | 19 |
Annual fixed costs | 55,000 |
Using the information in the table, calculate how many pods need to be occupied each month for Montrose Glamping to break even. [4 marks]
Answer:
Step 1 - State the formula to calculate the break-even point
[1 mark]
Step 2 - Calculate the contribution
Selling price - variable cost per unit
= $95 - $19
= $76 [1 mark]
Step 3 - Apply the formula to calculate the break-even point
= 723.68 [1 mark]
Step 4 - Always round UP to the nearest whole number because only whole products can be sold
723.68
= 724 camping pods [1 mark]
The margin of safety
The margin of safety is the difference between the actual level of output of a business and its break even level of output
The margin of safety can be calculated using the following formula
Worked Example
The cost, sales and revenue for an electric bicycle manufacturer are presented in the table below
Annual fixed costs | £42,000 |
Selling price per unit | £750 |
Variable cost per unit | £350 |
Number of units sold | 240 |
Using the data, calculate the margin of safety. You are advised to show your workings. [4 marks]
Answer:
Step 1 - Calculate the contribution
£750 - £350
= £400 [1 mark]
Step 2 - Calculate the break even point
= 105 units [2 marks]
Step 3 - Calculate the margin of safety
240 units - 105 units
= 135 units [1 mark]
Calculating profit or loss
Profit or loss can be calculated in two ways
or
Worked Example
ForêtSaut is an outdoor treetop activity centre. In 2022 it earned revenue of €462,540 with fixed costs of €281,720 and total variable costs of €131,280.
Calculate the total profit made by ForêtSaut in 2022. [2 marks]
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the total contribution
[1 mark]
Step 2: Use the contribution figure to calculate profit
[1 mark]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be asked to use principles of break even to calculate
Target profit output
Target profit
Target price
Practice rearranging the formula for target profit output to find the other variables so that you don't have to remember all three formulas.
Calculating the target profit output
Break even analysis can also be used to calculate the level of output needed to earn a target level of profit
The target profit output can be calculated using the formula
This calculation helps a business plan the resources required, such as stock, machinery and workers
Worked Example
ForêtSaut is an outdoor treetop activity centre. In 2022 it attracted 38,545 customers and earned revenue of €462,540 with fixed costs of €281,720 and total variable costs of €131,280. In 2023 it has set a profit target of €84,000.
Calculate the target profit output if ForêtSaut is to achieve its target profit in 2023. [3 marks]
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the contribution per unit
= €8.60 [1 mark]
Step 2: Apply the formula to calculate target profit output
[1 mark]
= 42,526 customers (rounded up to next whole unit) [1 mark]
Calculating the target profit
The target profit output formula can be rearranged to calculate the target profit and the target price
The target profit is the profit a business should expect to achieve at the target profit output level
It is calculated using the formula
This calculation can help a business with financial planning including forecasting cash flow
Worked Example
ForêtSaut is an outdoor treetop activity centre. In 2022 it attracted 38,545 customers and earned revenue of €462,540 with fixed costs of €281,720 and total variable costs of €131,280. In 2023 it has set a target profit output of 42,526 customers.
Using 2022's costs and revenues data, calculate ForêtSaut's target profit if it is to achieve its total profit output of 42,526 customers in 2023. [3 marks]
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the contribution per unit
[1 mark]
Step 2: Apply the formula to calculate target profit
[2 marks]
Calculating the target price
The target price is the price at which a product should be sold in order to achieve the target profit
It is calculated using the formula
This calculation can help a business with its marketing planning, in particular its pricing strategy and sales promotions
Worked Example
ForêtSaut is an outdoor treetop activity centre. In 2022 it attracted 38,545 customers and earned revenue of €462,540 with fixed costs of €281,720 and total variable costs of €131,280. In 2023 it has set a target profit of €84,000 from 42,526 customers.
Using 2022's costs and revenues data, calculate ForêtSaut's target price if it is to achieve its target profit €84,000 in 2023. [4 marks]
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate variable costs per unit
[1 mark]
Step 2: Multiply target profit output by variable costs per unit
[1 mark]
Step 3 - Add fixed costs to target profit
[1 mark]
Step 4: Apply the formula to calculate the target price and round to two decimal places
[2 marks]

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

