The Purpose of Operations Management (DP IB Business Management) : Revision Note
What is Operations Management?
Operations management focuses on designing, controlling and improving the processes used in the production of goods and services
It involves overseeing the entire production process, from acquiring raw materials to delivering the final product/service to customers
The goal of operations management is to ensure that the production process is efficient, cost-effective and meets the desired quality standards
It involves making decisions related to production planning, stock management, resource allocation, scheduling and quality control
Diagram: operations management tasks
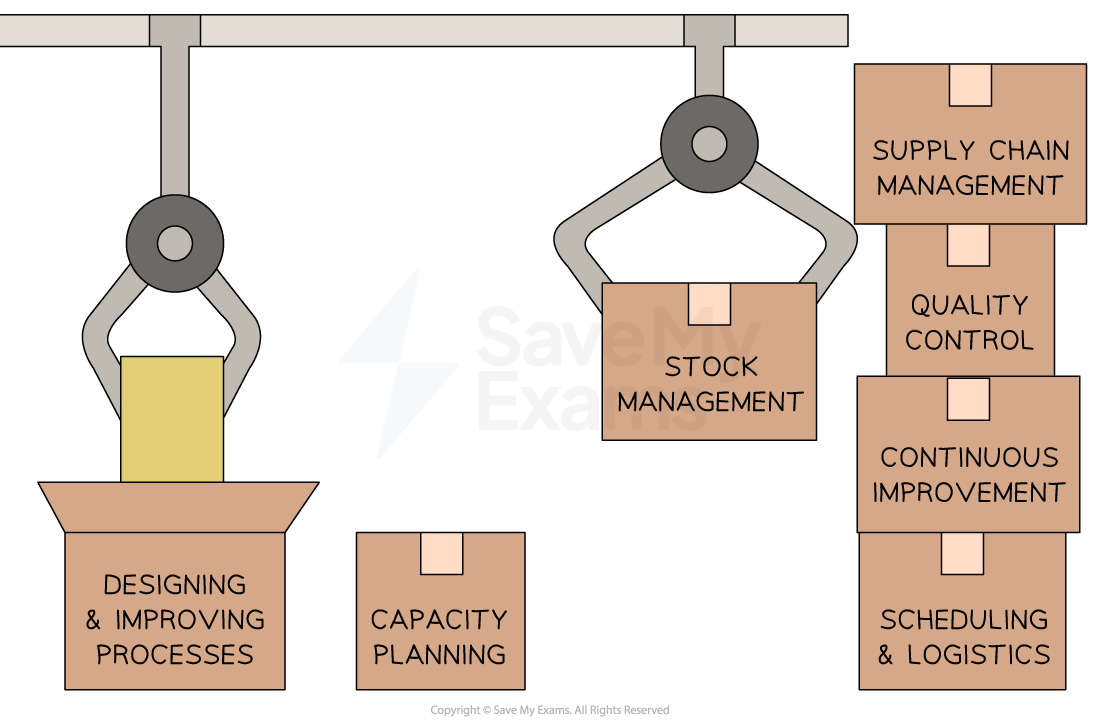
1. Designing and improving processes
Operations managers analyse existing processes and find ways to optimise them
They may use tools and techniques such as process mapping and lean production to identify inefficiencies and eliminate waste
2. Capacity planning
Operations managers determine the production capacity required to meet customer demand
They analyse historical data and market forecasts to ensure that the production resources are adequate to fulfil orders in a timely manner
3. Stock management
Operations managers are responsible for managing the stock levels of raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods
They aim to minimise costs while ensuring that enough stock is available to meet customer demand and allow the production process to continue without running out of resources
4. Supply chain management
Operations managers work closely with suppliers to ensure the timely delivery of raw materials and components
They establish relationships with suppliers, negotiate contracts and monitor supplier performance to ensure a reliable supply chain
5. Quality control
Operations managers implement quality control measures to ensure that the products/services meet the required quality standards
They develop and enforce quality assurance processes, conduct inspections and address any quality issues that arise
6. Continuous improvement
Operations managers strive for ongoing improvement in processes, productivity and efficiency
They identify opportunities for innovation, implement new technologies or techniques and encourage a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) among employees
7. Scheduling and logistics
Operations managers develop production schedules and coordinate the flow of materials, equipment and labour to ensure smooth operations
Operations & the Production of Goods/Services
Operations management does not only focus on the production of tangible goods/services in the secondary sector
It is equally applicable in the primary, tertiary and quaternary sectors
The input-output model is a simple explanation of the operations process
Diagram: the input-output model
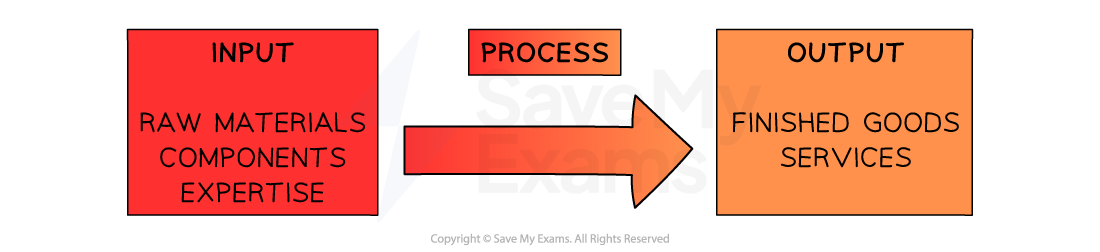
Examples of the Input-Output Model in Different Sectors
Sector & Example | Inputs | Process | Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
Primary (Fishing) |
|
|
|
Secondary (Car manufacture) |
|
|
|
Tertiary (Restaurant) |
|
|
|
Quaternary (Business consultancy) |
|
|
|
Operations & Sustainability
Sustainable operations management involves integrating sustainability practices into all aspects of the operations management process, from sourcing materials to delivering products
There are three elements to sustainable operations management
Diagram: sustainable operations management
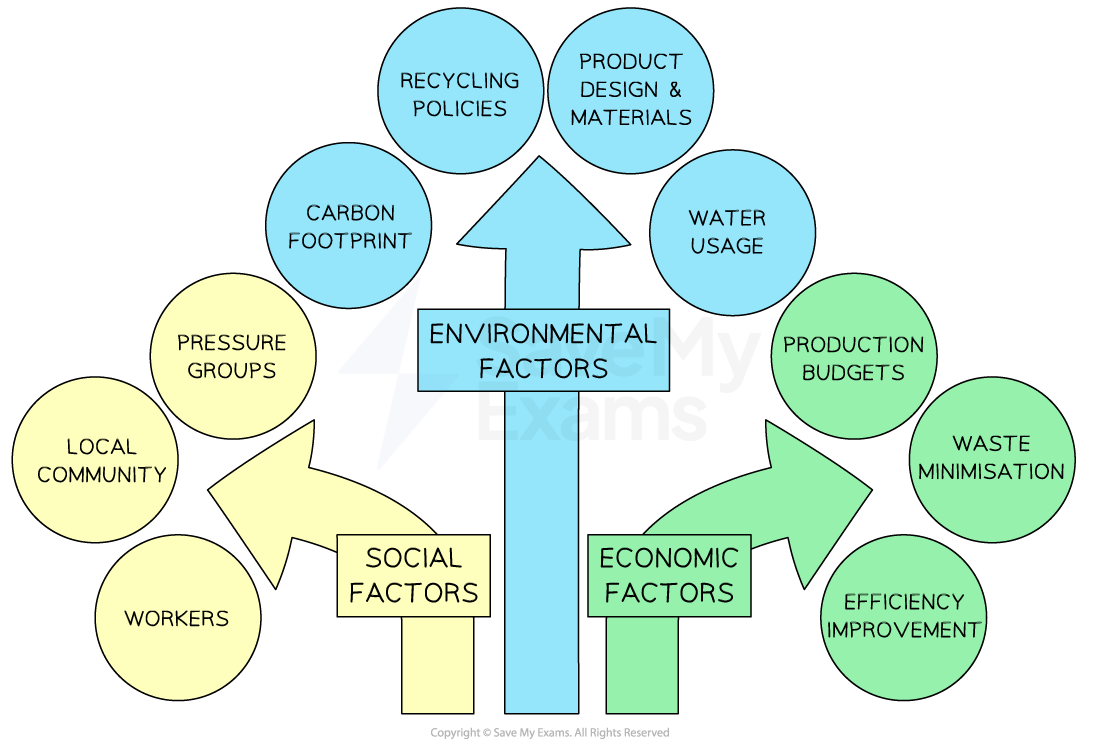
There are a range of ways to improve sustainability in operations management
Examples of Sustainability Practices in Operations Management
Method | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Green Supply Chain Management |
|
|
Energy Efficiency |
|
|
Waste Reduction and Recycling |
|
|
Promoting fair labour practices |
|
|

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

