Changes to & Limitations of Break-even (DP IB Business Management) : Revision Note
Changes to Break Even
Changing any of the variables of break-even (selling price, variable cost per unit or total fixed costs) changes the break-even point and level of profit it can expect to achieve
Changes in Variables and the Break Even Point
Increased Selling Price
An increase in the selling price reduces the break-even point

An increase in the selling price increases revenue at each level of output from R1 to R2
The break-even point falls from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is increased
Decreased Selling Price
A decrease in the selling price increases the break-even point

A decrease in the selling price reduces revenue at each level of output from R1 to R2
The break-even point rises from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is decreased
Increased Variable Costs
An increase in variable costs increases the break-even point

An increase in variable costs increases total costs at each level of output from TC1 to TC2
The break-even point increases from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is decreased
Decreased Variable Costs
A decrease in variable costs decreases the break-even point

A decrease in variable costs decreases total costs at each level of output from TC1 to TC2
The break-even point falls from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is increased
Increased Fixed Costs
An increase in fixed costs increases the break-even point

An increase in fixed costs increases total costs at each level of output from TC1 to TC2
The break-even point increases from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is decreased
Decreased Fixed Costs
A decrease in fixed costs decreases the break-even point

A decrease in fixed costs reduces total costs at each level of output from TC1 to TC2
The break-even point falls from BEP1 to BEP2
Profit on each unit of output greater than the break-even point is increased
Benefits & Limitations of Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis provides valuable insights into the financial viability and performance of a business
It is particularly useful for communicating with stakeholders, including investors or lenders
It demonstrates the financial viability of the business and gives an insight into potential returns on investment
The Benefits of Break-even Analysis
Use of Break Even | Explanation |
|---|---|
Profitability assessment |
|
Cost control |
|
Pricing decisions |
|
Financial planning |
|
Sensitivity analysis |
|
Performance monitoring |
|
Decision making |
|
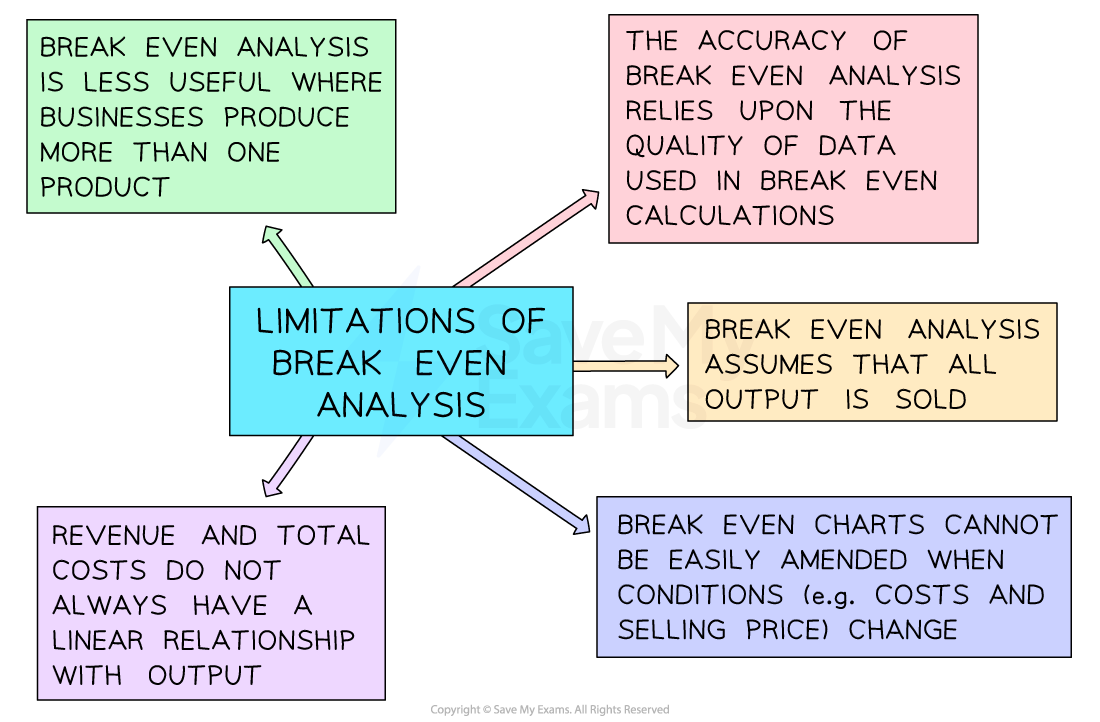
In common with other quantitative analysis tools, break even analysis has some limitations
Diagram: limitations of break even analysis
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When evaluating break-even analysis, ensure that you explain why it has an important internal planning role, but don’t forget that it has a significant external role too.
Break-even analysis should be included in a business plan when a business is trying to secure external finance. Businesses looking to borrow money or attract investors seeking to manage their risk should take care to model the break-even point, margin of safety and level of profit (or loss) at different levels of output and be prepared to be scrutinised on the figures.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

