Quality Management (DP IB Business Management) : Revision Note
An Introduction to Quality Management
Quality management involves a business carefully considering the characteristics and features of a product that satisfy the needs of customers and ensuring that it has effective systems and procedures to meet these
Businesses need to maintain a level of quality that continues to attract and retain customers if they want to remain successful
Customer perceptions of quality are related to a range of product or business features
Diagram: factors that influence quality perception
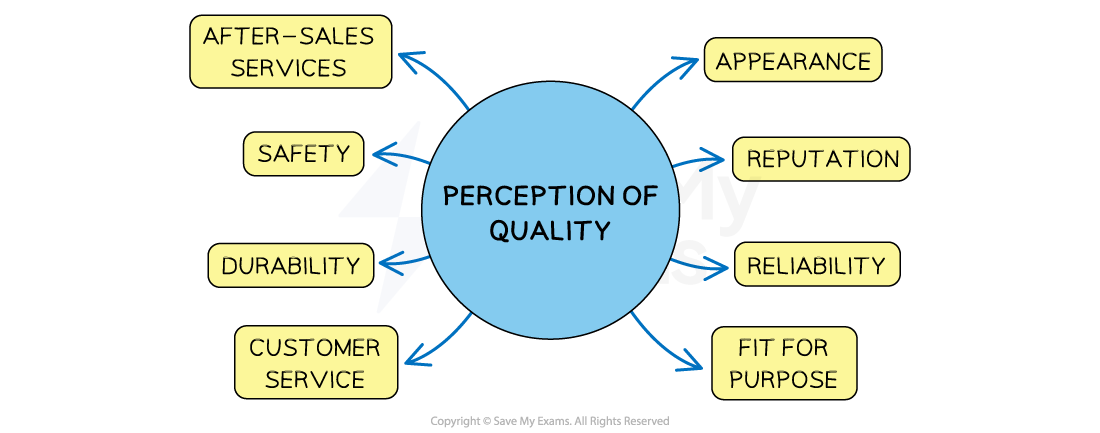
Customers may consider products or services to be of good quality if they
Look good and are sold by a reputable business or brand
Are reliable and durable
Are safe and fit for purpose
Receive good customer service, including after-sales service
Examiner Tips and Tricks
High quality may provide justification to charge a premium price for products
However, it is not always the case that good quality leads to increased sales
For many customers as long as a product's quality is 'good enough' they will be reluctant to upgrade to a more prestigious brand, especially when their incomes are squeezed
Measuring Quality
Businesses can measure the quality of their output in a range of ways
Reject Rates | Product Returns | Product Recalls |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
In addition factors such as customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and market share can provide useful indications of customer experiences and perceptions of quality
Customers satisfied with quality are less likely to make complaints and are likely to give positive feedback in surveys
High quality can drive repeat purchases
Increased market share may demonstrate satisfaction with quality over that offered by rival products/services
Categories of Quality Management
A businesses approach to quality management falls into one of two categories
Quality control involves inspecting the quality of output at the end of the production process
Workers focus on maximising output
Products that do not meet standards are rejected before they are released for sale
Quality assurance involves inspecting the quality of production throughout the process
Workers check their own work and, sometimes, the work of others at various stages of production
Some business take a whole business approach to quality assurance with systems such as quality circles, benchmarking and Total Quality Management (TQM)
An Evaluation of Approaches to Quality Management
Method | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
Quality Control |
|
|
Quality Assurance |
|
|
Quality Assurance Using Quality Circles
Quality circles involve groups of workers meeting regularly to identify and solve quality problems in the production process
Groups are made up of volunteers from different departments
Meetings are typically chaired by a senior leader
Members work together to execute and manage solutions
An Evaluation of Quality Circles
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Quality Assurance Using Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves a business comparing its quality and performance with market leaders within the same industry
Benchmarking can be internal or external
Internal benchmarking
Comparison of different functions within a business such as finance and marketing
Performance
Comparison of key performance indicators such as labour productivity or labour turnover rates
Process
Comparison of business operations and processes such as call centre queue times or delivery times
External benchmarking
Comparison of key performance indicators (such as product recalls) against those of market leaders in an industry
International benchmarking compares key performance indicators against those of market leaders overseas
An Evaluation of Benchmarking
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Quality Assurance Using Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) places quality at its core and makes every worker responsible for quality throughout the business
Quality is considered from the customer's perspective
Inefficiency and wastage is removed from every business activity or function - including those that are not directly related to production
An Evaluation of TQM
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
The Benefits of Lean Production & TQM
Implementing lean production and TQM can have a positive impact on various aspects of a business
It can lead to higher profits as a result of greater efficiency, less waste and lower costs
Fewer errors can lead to improved customer satisfaction and greater customer loyalty
Positive Impacts of Lean Production and TQM
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Waste reduction |
|
Streamlined processes |
|
Improved quality |
|
Employee empowerment |
|
Environmental Impact |
|
However, successful implementation of lean production is likely to require a cultural shift and ongoing efforts to sustain improvements
Commitment to careful recruitment, training and engagement of employees
'Getting it right first time' should be at the heart of all processes
It also needs strong relationships with suppliers
Defect-free components must be delivered on-time, in the right quantities
Trust needs to be developed with a small number of suppliers, emphasising quality rather than cost alone
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When developing a longer response that requires a justified decision, make sure that you consider the advantages and disadvantages of both options
This analysis should be wide ranging - that is, you should consider the impact on a variety of business functions, stakeholders, aims and objectives. Try to avoid focusing too much on financial aspects - though these should be covered.
National & international Quality Standards
Quality standards include national and international benchmarks that demonstrate a businesses commitment to quality
They are administered by independent bodies that carry out stringent tests to ensure standards are met or exceeded
Businesses awarded these standards are revisited regularly to ensure that standards are maintained
Diagram with a Selection of Quality Standard Accreditations

The Importance of Quality Standards
Achieving accreditation reassures customers of their commitment to quality
Accreditation also provides a range of further benefits
Having quality accreditation can set a business apart from competitors
Obtaining quality accreditation can allow a business to enter these markets
They reduce the risk of legal issues and penalties
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will not need to write about specific quality standards - it is enough to demonstrate an understanding of the types of protection they provide to consumers

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

