Biological Species Concept (DP IB Biology) : Revision Note
Variation Between Organisms
What is variation?
Differences exist between organisms; these differences are known as variation
There are multiple aspects of an organism that can vary, e.g.
Visual appearance, such as fur colour or body length
Behaviour, such as mating rituals and level of aggression
Biochemistry, such as antibiotic resistance or metabolic products
Causes of variation
Variation is the result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors
The genes determine which proteins an organism is capable of producing, so influencing an organism's characteristics
Genetic variation is generated when mutation occurs and when alleles are combined in different ways during sexual reproduction
The environment may determine whether or not an organism has the resources needed to produce a particular protein, so may affect gene expression
Factors in the environment that may generate variation include
Environmental temperatures
Nutrient availability
Oxygen concentration
Variation between and within species
Variation exists between organisms of different species
This variation can be used to classify organisms into different groups, e.g. morphological differences between species have historically been the main way of classifying organisms, and can still aid classification today
Variation exists between members of the same species
While members of a species will have a similar genetic makeup, different individuals have different combinations of alleles
No two individuals are identical when all characteristics are compared
Even identical twins, which have the same combination of alleles, will differ due to subtle environmental differences
Types of variation
Variation can be discontinuous, meaning that characteristics fall into distinct categories, e.g. black fur vs brown fur, or human blood type
Variation can be continuous, meaning that characteristics can be measured incrementally on a scale, e.g. height
Discontinuous and continuous variation graphs


Discontinuous and continuous variation have different features
Species: Linnaeus
Species classification using morphology
For biologists to make sense of the huge array of species on Earth, organising them into logical groups is essential
This process of putting organisms into groups is known as classification
The science of classification is known as taxonomy, and scientists working in the field of taxonomy are taxonomists
Classifying an organism involves deciding which biological group, or taxon (plural taxa), it fits into best, and then naming it according to its taxon
The smallest taxonomic group is the species
Historically an organism's species was determined on the basis of its observable characteristics; this is morphological classification
The morphological species concept states that:
A species is a group of organisms that are morphologically unique
While morphology can still be a useful guide for taxonomists, classification is no longer carried out using the morphological species concept alone
Linnaeus: the father of taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus was an 18th century Swedish botanist, famous today for his work on taxonomy
Linnaeus' developed the method of naming species that is used by scientists all over the world today
He is sometimes referred to as the 'father of taxonomy' for this reason
Linnaeus noticed that traditional methods of naming species were long and descriptive, for example the tomato plant was named Solanum caule inermi herbaceo, foliis pinnatis incises, racemis simplicibus, meaning ‘solanum with the smooth stem which is herbaceous and has incised pinnate leaves’
Under Linnaeus' new system, species were given two-part Latin names which would be the same everywhere in the world, e.g. the tomato became Solanum lycopersicum
Many species still have the same two-part Latin names that Linnaeus gave them
It is worth noting that while Linnaeus' work on taxonomic naming shaped modern taxonomy, he didn't always get his classification correct; many species named by him have since been reclassified and given new two-part Latin names
Linnaeus used the morphological species concept; classification based on morphology alone often leads to mistakes; species with a similar appearance are not always closely related

Linnaeus' binomial naming system allowed species to be given simplified names that scientists all over the world would recognise
Binomial System
The binomial naming system
The biological system of naming, used to name species according to their taxa, is known as the binomial system of nomenclature
This system is universal, ensuring that scientists around the world all use the same method of naming species
The system involves giving a species a two-part name, hence binomial
Both parts of the name are in Latin, or a latinised version of a non-Latin word
e.g. Eriovixia gryffindori is a species of orb spider named after a famous school house
The first part of the name is an organism's genus, and the second is its species name
E.g. the binomial name of a wolf is Canis lupus; wolves belong to the genus Canis, and the species lupus
Species that are grouped into the same genus will have similar characteristics
E.g. the genus Canis includes the wolf (Canis lupus), the coyote (Canis latrans), and the domestic dog (Canis familiaris)
Using binomial names
There are several conventions, or rules, that should be used when writing binomial names
The genus should begin with a capital letter, and the species with a lower-case letter, e.g. the honey bee is Apis mellifera
When typed, binomial names should appear in italics, and when written by hand, they should be underlined e.g. a limpet is Patella vulgata when typed, or Patella vulgata by hand
The first time a binomial name is used in a text it should appear in full, e.g. wheat is Triticum aestivum, but the genus name can from then on be abbreviated so that the name is given as T. aestivum
Biological Species Concept
Biological species concept
The morphological species concept relies on the observable features of a species, and often leads to mistakes in classification
Species with similar traits may not be closely related
Biologists now rely on other definitions of a species, one of which is the biological species concept
The biological species concept states that a species is:
A group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Limitations of the biological species concept
The biological species concept can be very useful to biologists, but there are some situations to which it can be difficult to apply:
Asexual reproduction
Organisms that reproduce by asexual reproduction cannot be classified using this method
E.g. bacteria reproduce asexually, so the question of whether or not they can breed together is irrelevant
Fertile hybrids
On rare occasions, animals of different species breed together and produce fertile offspring
E.g. the so-called 'wholphin' is the fertile offspring from a cross between a melon-headed whale and a common bottlenose dolphin
According to the biological species concept the wholphin would be a new species, but while scientists do believe that hybridisation can lead to new species, it needs to be a frequent event for this to occur, and wholphins are rare
Note that the melon-headed whale is actually a species of dolphin, so the name 'wholphin' is a bit inaccurate!
Extinction
Some species are extinct, so it is not possible to breed them together with members of an existing species to determine the fertility of their offspring
E.g. the woolly mammoth is quite similar in morphology to modern elephants, though it is classified as a different species; there is no way of checking this classification using the biological species concept
Asexual reproduction in bacteria diagram
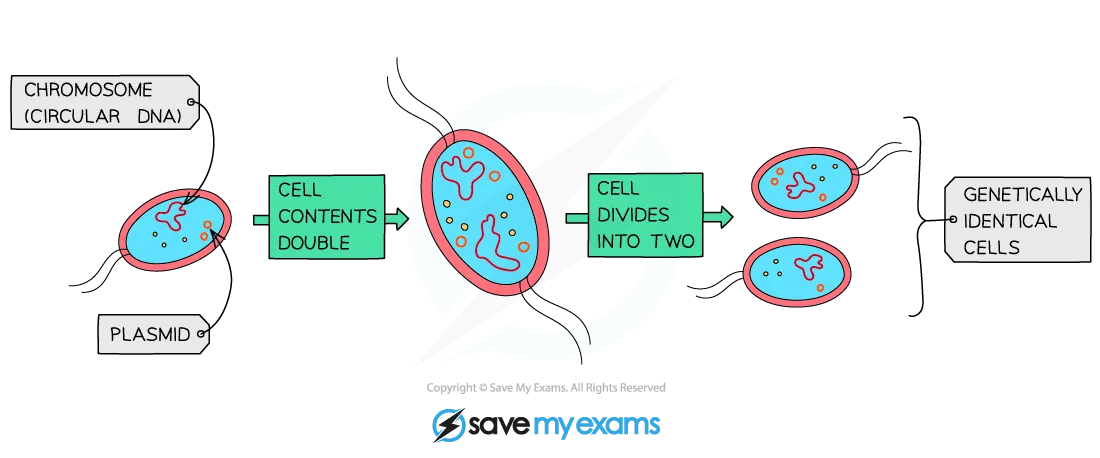
The biological species concept cannot be applied to bacteria because they reproduce asexually
The imperfect nature of the biological species concept means that other characteristics must sometimes be used to determine species
Morphology: organisms of the same species share similar morphology
DNA: sequences can be compared, with a certain level of similarity indicating that organisms are the same species
Biochemistry: species may produce different molecules as products of their metabolism
E.g. some bacteria produce carbon dioxide, while others may produce methane
Ecology: the precise ecological niche of a species is likely to be distinctive from other, similar species
Evolutionary lineage: fossilised remains of extinct species can be compared with morphologically similar existing species and classified within their evolutionary lineage
The characteristics used to aid classification will differ depending on the organism, e.g:
Bacteria may have very similar morphology, so may need to be classified on the basis of their biochemistry or their ecology
We might know very little about the biochemistry and ecology of a long-extinct species, but we can classify it according to its evolutionary lineage or morphology
Distinguishing Between Populations & Species
Speciation
Species do not stay the same over time; the species that we see around us today have developed over millions of years
This process of species change is known as evolution
The process by which one species gives rise to two or more new species is speciation
Speciation can occur when a population becomes isolated from other populations of the same species due to living in a different area
This isolation means that members of the separate populations cannot breed together and gene flow cannot take place between them
If the environmental conditions affecting each population are different, then natural selection could act differently on each population and eventually lead to speciation
Genetic drift can also lead to speciation
Once speciation has taken place, the two species can no longer breed to produce fertile offspring; they are reproductively isolated and are said to be separate species
Note that speciation is covered in more detail later in the course
Speciation diagram

Speciation can occur when gene flow does not occur between two populations of the same species
Distinguishing between populations and species
The process of speciation occurs over very long time periods, and the differences between isolated populations accumulate incrementally
In most cases it is likely that the ability of two populations to interbreed successfully declines gradually, rather than a sudden cut-off point occurring, meaning that it is difficult to pinpoint the stage at which two separate populations have become two new species
The decision as to when to assign separate species status to two populations can therefore seem arbitrary, and is often down to the opinions of scientists, i.e. it is subjective
E.g. killer whales (Orcinus orca) show significant variation between populations, and are currently said to consist of several 'ecotypes', but some scientists believe that there could in fact be more than one species of orca

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
