Inheritance: Terminology (DP IB Biology): Revision Note
Written by: Emma Archbold
Updated on
Genotype
A gene is a short length of DNA found on a chromosome that codes for a particular characteristic (by coding for the production of a specific protein)
Alleles are variations of the same gene
As we have two copies of each chromosome, we have two copies of each gene and therefore every individual will have two alleles of each gene
One of the alleles is inherited from the mother and the other from the father
The alleles may be the same as each other, or they might be different. e.g. an individual has two copies of the gene for eye colour but one allele could code for brown eyes and one allele could code for blue eyes
The combination of alleles that an individual organism inherits is its genotype
When the two alleles at a locus are the same/identical, an individual is said to have a homozygous genotype
When the two alleles at a locus are different the genotype is said to be heterozygous
Chromosome diagram

Chromosomes showing genes, loci and alleles
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure to not use the words allele and gene interchangeably. They both have different definitions and need to be used correctly in your exams in order to gain marks.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an organism (seen just by looking - like eye colour, or found – like blood type) is called the phenotype
The phenotype of all characteristics is determined by the following factors:
The genotype only - the combination of the two alleles for the gene for the characteristic, for example blood group is determined this way
The environment only - surroundings such as chemical or radiation exposure, diet or exercise can affect physical characteristics, for example scars and accent are determined this way
Interaction between both the genotype and the environment, for example height and skin colour are determined this way
Dominant & Recessive Alleles
Alleles can be dominant or recessive
A dominant allele only needs to be inherited from one parent in order for the characteristic to be expressed in the phenotype
A recessive allele needs to be inherited from both parents in order for the characteristic to be expressed in the phenotype.
If there is only one recessive allele, it will remain hidden and the dominant characteristic will show
If the two alleles of a gene are the same, we describe the individual as being homozygous (homo = same)
An individual could be homozygous dominant (having two copies of the dominant allele), or homozygous recessive (having two copies of the recessive allele)
If the two alleles of a gene are different, we describe the individual as being heterozygous (hetero = different)
Different forms of allele pairs diagram
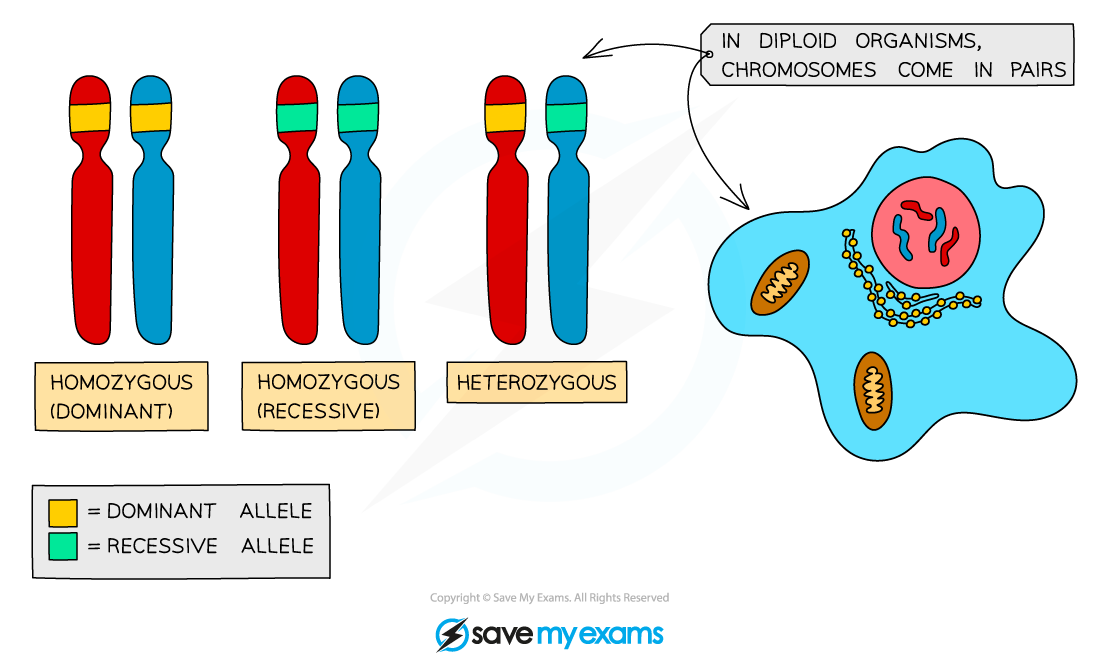
Alleles are different forms of the same gene. You can only inherit two alleles for each gene, and they can be the same (homozygous) or different (heterozygous). Alleles can be dominant or recessive.
Incomplete & Codominance
Co-dominant alleles have a combined effect on the phenotype
The alleles are both expressed to an equal extent in the phenotype
An example of codominance is in speckled chickens
Chickens can have different alleles for gene that determines the colour of their feathers
We can denote the gene for colour using the capital letter C
The two alleles for this gene are white for white feather colour, and black for black feather colour
We denote the two alleles using superscript letters, CW and CB
A chicken with the genotype CWCW has white feathers as their phenotype
A chicken with the genotype CBCB has black feathers as their phenotype
A chicken with the genotype CWCB has a combination of both feather colours, they are called speckled colour chickens
Because both alleles are expressed in the phenotype this is called codominance
Example of codominance in chickens diagram

Diagram showing the phenotypes and genotypes of white, black and speckled chickens, which is an example of codominance
Incomplete dominance is similar to codominance because two alleles are expressed together instead of just one dominant allele being expressed
However, instead of both alleles being expressed, both alleles are partially expressed leading to a phenotype which is a blend of both phenotypes or an intermediate phenotype between the two
An example is incomplete dominance can be found in the four o'clock flower or marvel of Peru (Mirabilis jalapa)
Marvel of Peru can have different alleles for gene that determines the colour of their flowers
We can denote the gene for colour using the capital letter C
The two alleles for this gene are white for white flower colour, and red for red flower colour
We denote the two alleles using superscript letters, CW and CR
A plant with the genotype CWCW has white flowers as their phenotype
A plant with the genotype CRCR has red flowers as their phenotype
A plant with the genotype CWCR has a blend of both colours, which is expressed in the phenotype as a pink flower colour
Because the flowers are neither white or red, but an intermediate between this two, this is incomplete dominance
Example of incomplete dominance in marvel of Peru diagram

Diagram showing the phenotypes and genotypes of white, red and pink flowers of the marvel of Peru, which is an example of incomplete dominance
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When referring to different species examples in an exam you can use either the common name or the scientific name to gain marks. For example you could say 'four o'clock flower' or 'marvel of Peru' or 'Mirabilis jalapa' to be awarded the mark.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
