Macromolecules (DP IB Biology): Revision Note
Formation of Macromolecules
Carbon compounds can be large molecules made from many small, repeating subunits
Monomers are the smaller units from which larger molecules are made
Polymers are molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together in a chain
The process by which monomers join to form polymers is polymerisation
Macromolecules are very large molecules
They contain 1000 or more atoms and so have a high molecular mass
Polymers can be macromolecules, however, not all macromolecules are polymers; polymers must consist of many repeating subunits
E.g. lipids are not polymers, as they do not consist of repeating monomers
Key biological macromolecules table
Macromolecule | Monomer |
|---|---|
Carbohydrates (polysaccharides) | Monosaccharides |
Lipids | Fatty acids, glycerol, phosphate groups |
Proteins (polypeptides) | Amino acids |
Nucleic acids | Nucleotides |
Formation of macromolecules
Macromolecules are formed during condensation reactions
A condensation reaction occurs when molecules combine together, forming covalent bonds and resulting in polymers (polymerisation) or macromolecules
Water is removed as part of the reaction
Examples of condensation reactions
Polysaccharides
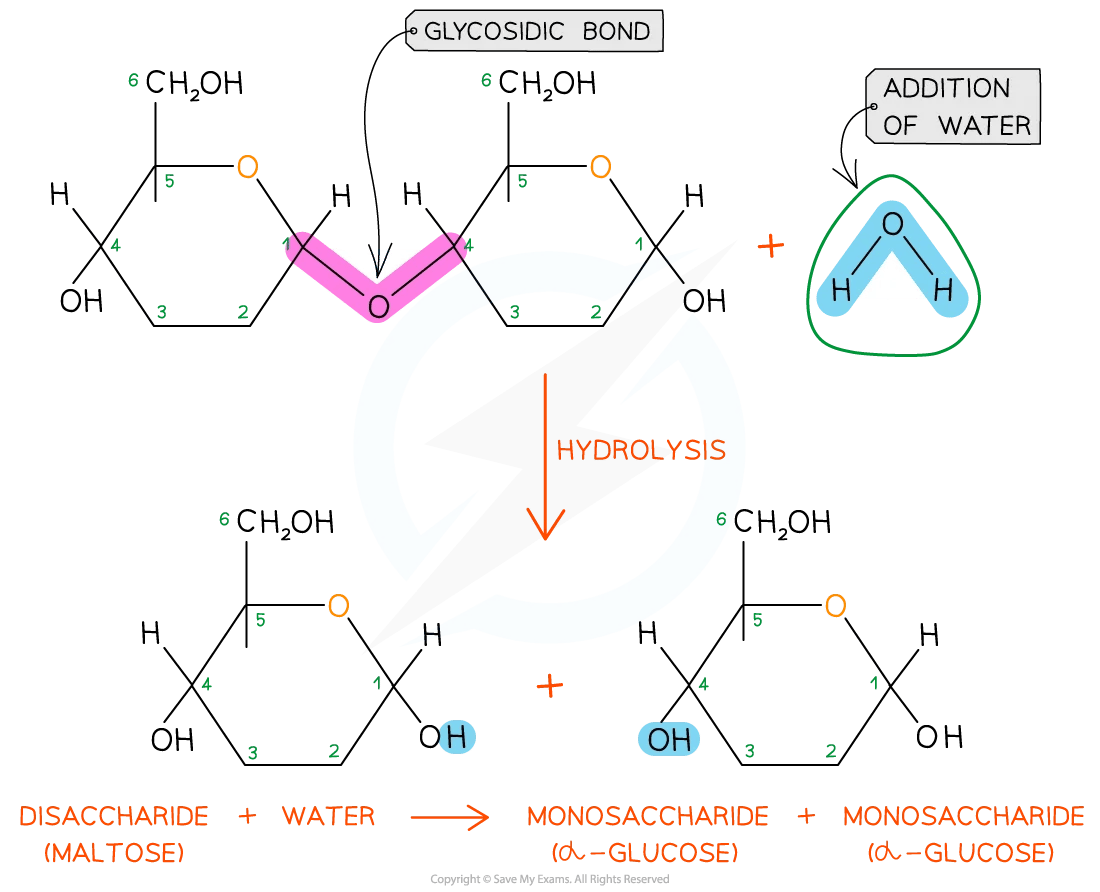
Polysaccharides are formed when two hydroxyl (OH) groups on different monosaccharides interact to form a strong covalent bond called a glycosidic bond
Glycosidic bond formation diagram

Polypeptides
Polypeptides are formed by condensation reactions
Two amino acid monomers interact to form a strong covalent bond called a peptide bond
Peptide bond formation diagram

Nucleic acids
Separate nucleotides are joined together via condensation reactions to form a phosphodiester bond
These condensation reactions occur between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of the next nucleotide
It is called a phosphodiester bond because it consists of a phosphate group and two ester bonds
Phosphodiester bond formation diagram

Digestion of Polymers
Macromolecules often need to be broken down into their monomers, e.g. this happens in digestion
The reaction that allows this to occur is a hydrolysis reaction
Hydrolysis means ‘lyse’ (to break) and ‘hydro’ (with water)
In the hydrolysis of macromolecules, covalent bonds are broken when water is added
The -O and -OH from the water molecule are used to form the functional groups of the products
Examples of hydrolysis reactions include:
The hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in poly- or disaccharides to produce monosaccharides
The hydrolysis of peptide bonds in polypeptides to produce amino acids
Hydrolysis of ester bonds in triglycerides to produce three fatty acids and glycerol
Hydrolysis of a disaccharide diagram

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?