The following diagram shows part of the blood clotting cascade.
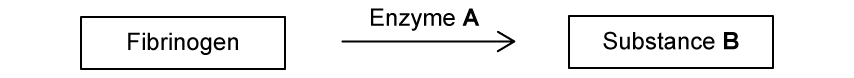
Enzyme A acts on fibrinogen.
Identify enzyme A.
Substance B is an insoluble protein formed by fibrinogen.
(i) Identify substance B.
[1]
(ii) State the purpose of substance B in the body.
[1]
Blood clotting is essential for the healing of wounds, but can be life-threatening if it occurs in the coronary arteries.
Define the term 'coronary arteries'.
Was this exam question helpful?


















