Active Transport & Bulk Transport (DP IB Biology): Revision Note
Bulk Transport
The processes of diffusion, osmosis and active transport are responsible for the transport of individual molecules or ions across cell membranes
However, the bulk transport of larger quantities of materials into or out of cells is also possible
Examples of these larger quantities of materials that might need to cross the membrane include:
Bulk transport into cells = endocytosis
Bulk transport out of cells = exocytosis
Bulk transport processes require energy and are therefore forms of active transport
They also require the formation of vesicles, which is dependent on the fluidity of membranes
Vesicles are small spherical sacs of plasma membrane that containing substances for transport, e.g. enzymes
The formation of vesicles is an active process and involves a small region of the plasma membrane being pinched off
Vesicles can also fuse with cell membranes, at which point they are re-incorporated into a larger membrane
In order to form from or fuse with membranes, vesicles need membranes to flex and bed, so fluidity is essential
Endocytosis
Endocytosis transports material into cells
During endocytosis the plasma membrane engulfs material, forming a small sac around it
There are two forms of endocytosis:
Phagocytosis:
This is the bulk intake of solid material by a cell
Cells that specialise in this process are called phagocytes
The vacuoles formed are called phagocytic vacuoles
An example is the engulfing of bacteria by phagocytic white blood cells
Pinocytosis:
This is the bulk intake of liquids
Endocytosis diagram

Phagocytosis is an example of endocytosis
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is the process by which materials are removed from, or transported out of, cells
It is the reverse of endocytosis
The substances to be released are packaged into secretory vesicles
These vesicles then travel to the cell surface membrane
Here they fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents outside the cell
An example is the secretion of digestive enzymes from pancreatic cells
Exocytosis diagram
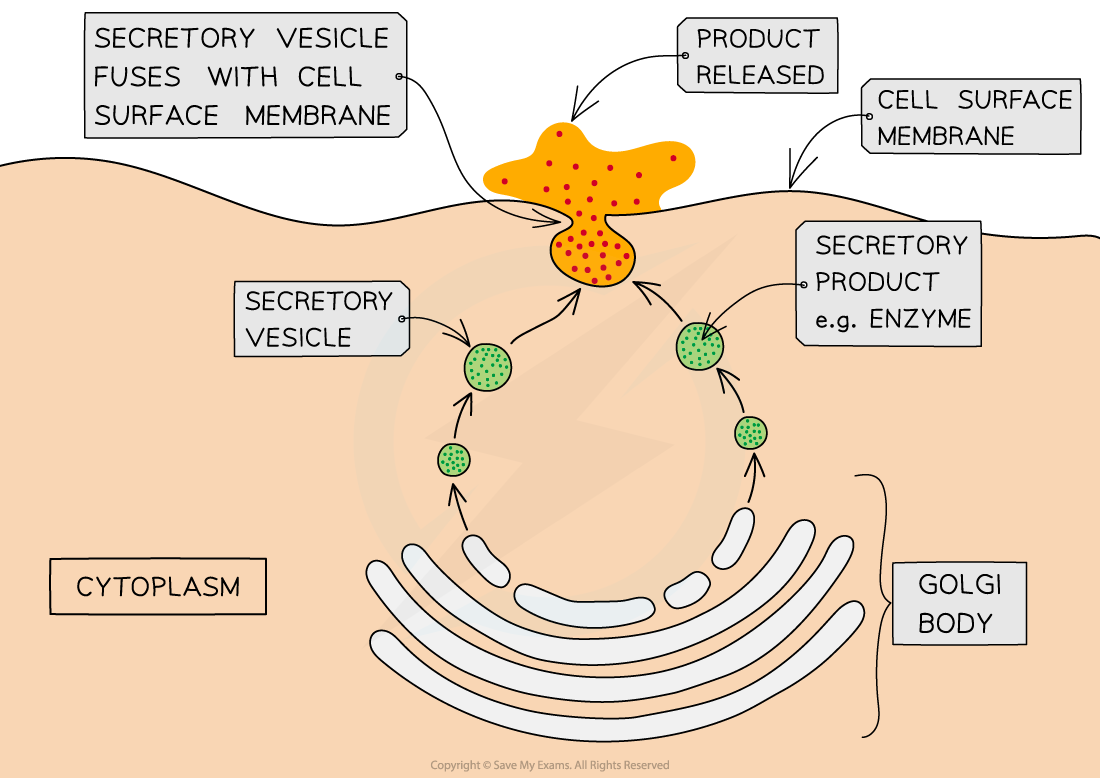
Exocytosis involves the fusion of a vesicle with the cell surface membrane
Gated Ion Channels
Specialised ion channels, called gated ion channels, are present in some cell membranes
These channels operate in response to chemical or electrical stimuli
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are an example of a gated ion channel, more specifically a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine can bind to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors which triggers the ion channel to open allowing certain ions, such as calcium (Ca2+) or sodium (Na+), to pass through
The influx of ions causes the membrane potential to change; this can generate an action potential in neurones
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are found specifically at the neuromuscular junction; the point at which nerve cells connect to muscles
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor diagram

Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are an example of a gated ion channel
Sodium-Potassium Pumps
Sodium-potassium pump proteins are integral proteins that generate an electrochemical gradient between the inside and outside of a nerve cell
Sodium-potassium pumps are an example of an exchange transporter
The sodium-potassium pumps move three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell using one ATP molecule
The pumps are always moving the ions against their concentration gradient via active transport
The steps that occur during the pumping process are:
Three sodium ions from the inside of the axon bind to the pump
ATP attaches to the pump and transfers a phosphate to the pump (phosphorylation), causing it to change shape and resulting in the pump opening to the outside of the axon
The three sodium ions are released out of the axon
Two potassium ions from outside the axon enter and bind to their sites
The attached phosphate is released altering the shape of the pump again
The change in shape causes the potassium ions to be released inside the axon
This process is essential to the function of nerve cells
The sodium-potassium pumps transport more positively charged sodium ions to the outside of the cell than positively charged potassium ions to the inside; the inside of the cell is therefore negatively charged in comparison to the outside
When nerve cells are stimulated, sodium ion channels open and sodium ions rush in down the electrochemical gradient, reversing the charge across the membrane
This can lead to the generation of a nerve impulse
Sodium-potassium pump diagram


Sodium-potassium pumps use ATP to transport sodium and potassium ions across cell membranes
Glucose Cotransporters
Cotransport & indirect active transport
Co-transport is the coupled movement of substances across a cell membrane via a carrier protein
Coupled processes occur at the same time and do not occur independently of each other
Cotransport involves a combination of facilitated diffusion and indirect active transport
Indirect active transport uses the energy released by the movement of one molecule down its concentration gradient to move another against its concentration gradient
ATP is used to set up the initial gradient
Sodium-dependent glucose co-transport
A well-known example of a co-transporter protein can be found on the cell surface membrane of the epithelial cells lining the mammalian ileum
This specific sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter protein is involved in the absorption of glucose into the blood
Sodium-potassium pumps actively transport sodium ions into the blood, reducing the concentration of sodium ions in the cell
Sodium ions move down their concentration gradient into the cell via a cotransporter protein
Glucose is drawn into the cell along with sodium ions via the same cotransporter protein
Glucose moves against its concentration gradient
Glucose then moves down its concentration gradient into the blood
The active part of the process is the generation of the initial sodium ion gradient; the transport of glucose itself does not require energy; this is why the process is described as indirect active transport
Co-transport in the small intestine diagram

Both facilitated diffusion and active transport occur during co-transport. Glucose molecules can only enter the epithelial cell when sodium ions are present.
This process also takes place in the kidney
Reabsorption of glucose back into the blood is under the control of sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter proteins
Glucose is co-transported with sodium ions in the way described above
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is worth being aware that the sequence of events in cotransport are sometimes given in a different order; the order above may seem a bit backwards, but it can be helpful to begin with the generation of the sodium gradient, as all the other steps then flow logically

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?