Examples of Specialised Cells (DP IB Biology): Revision Note
Pneumocyte Adaptations
There are millions of alveoli in the lungs which collectively provide maximum surface area for gas exchange by diffusion
In addition to this, the alveolar walls (also called alveolar epithelium) are only one cell thick which provides a short diffusion distance
Two different cell types make up the tissue of the alveolar epithelium
Type I Pneumocytes
Type I pneumocytes are extremely thin alveolar cells which make up the majority of the alveolar epithelium
They are adapted to maximise the rate of gas exchange by providing a short diffusion distance
The capillary walls are also only one cell thick which means there is usually less than 0.5μm between the air in the alveoli and the blood, this maximises the rate of diffusion
Structure and Adaptations of Type I Pneumocytes Diagram

The thin type I pneumocyte cells and the thin capillary walls provide a short diffusion distance to maximise gas exchange
Type II Pneumocytes
Type II pneumocytes are rounded cells which possess many secretory vesicles (lamellar bodies) which secrete a solution that coats the epithelium of the alveoli
They occupy a much smaller proportion of the alveolar epithelium than the type I pneumocytes, around 5%
The solution released by type II pneumocytes contains pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant has hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads
The molecules form a monolayer with the hydrophobic tails facing the alveolar air
Pulmonary surfactant reduces surface tension, maintaining alveolar shape and preventing the alveoli sacs sticking together
This prevents the alveoli, and therefore the lungs, from collapsing
The solution also aids gas exchange
The layer of moisture provided by the solution allows oxygen to dissolve before it diffuses into the blood
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the moist surface before it is removed in exhalation
Arrangement of Pulmonary Surfactant Produced by Type II Pneumocytes Diagram

The type II pneumocyte cells in the alveoli produce a solution containing pulmonary surfactant which reduces surface tension
Type I and Type II Pneumocytes Diagram
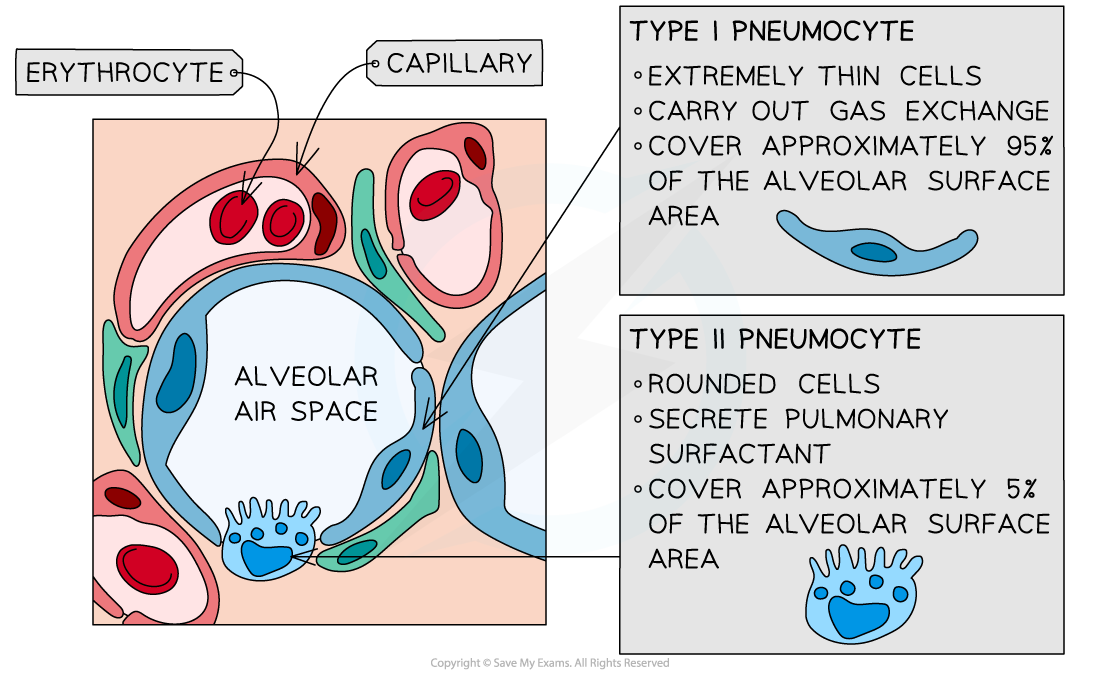
The alveolar epithelium is made up of type I and type II pneumocyte cells
Cardiac & Striated Muscle Adaptations
Muscles in the body that are attached to the skeleton and aid movement are called skeletal muscles
Other muscle types include:
Cardiac muscle which is found in the heart
Smooth muscle is found in the blood vessels and organs
Striated Muscle Fibres
Skeletal muscle is striated as it has a stripy appearance when viewed under a microscope
Striated muscle cells are bundled up into fibres which are surrounded by a single plasma membrane called the sarcolemma
The fibres are highly specialised cell-like units
Fibres are referred to as being cell-like due to features which distinguish their ultrastructure from that of other more traditional cells
Each muscle fibre contains:
An organised arrangement of contractile proteins in the cytoplasm
Many nuclei – this is why muscle fibres are not usually referred to as cells
Specialised endoplasmic reticulum called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) which stores calcium and conveys signals to all parts of the fibre at once using protein pumps in the membranes
Specialised cytoplasm called the sarcoplasm contains mitochondria and myofibrils
The mitochondria carry out aerobic respiration to generate the ATP required for muscle contraction
Myofibrils are bundles of actin and myosin filaments, which slide past each other during muscle contraction
The sarcolemma (muscle fibre membrane) has many deep tube-like projections that fold in from its outer surface
These are known as transverse system tubules or T-tubules
These run close to the SR
Diagram to show the Structure of Striated Muscle Fibres


The ultrastructure of striated muscle and of a section of muscle fibre
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is only present within the heart
It is a type of specialised striated muscle with the following properties:
It is myogenic, meaning that it can contract without external stimulation via nerves or hormones. This allows the heart to beat at its own regular intervals (the length of the intervals can be regulated by the nervous system and endocrine system)
It does not tire or fatigue so it can contract (beat) continuously throughout an individual's life
The cardiac muscle fibres form a network that spreads through the walls of the atria and ventricles
Cardiac muscle fibres are connected to each other via specialised branched connections called intercalated discs, this feature allows the contraction to spread more quickly across the chambers of the heart
There is a large number of mitochondria present in the muscle fibres. These are needed to provide the large quantity of ATP needed for continual contraction
Contractile myofibrils are present in cardiac muscle in the same way that they are in skeletal fibres
Diagram to show the Structure of Cardiac Muscle Cells

The structure of cardiac muscle. There is only one nucleus per cell.
Human Gamete Adaptations
Sperm Cells
Sperm and ova are examples of specialised cells, meaning that their structure aids their function
Special features of sperm cells that relate to function include
A haploid nucleus, contained within a streamlined head, that can fuse with an ovum nucleus to form a diploid zygote
An acrosome containing digestive, or hydrolytic, enzymes to aid entry into the ovum through the zona pellucida
Many mitochondria (within the middle piece) for the release of energy to aid movement
A flagellum made of protein microtubules to aid movement
Diagram to show the Structure of a Sperm Cell
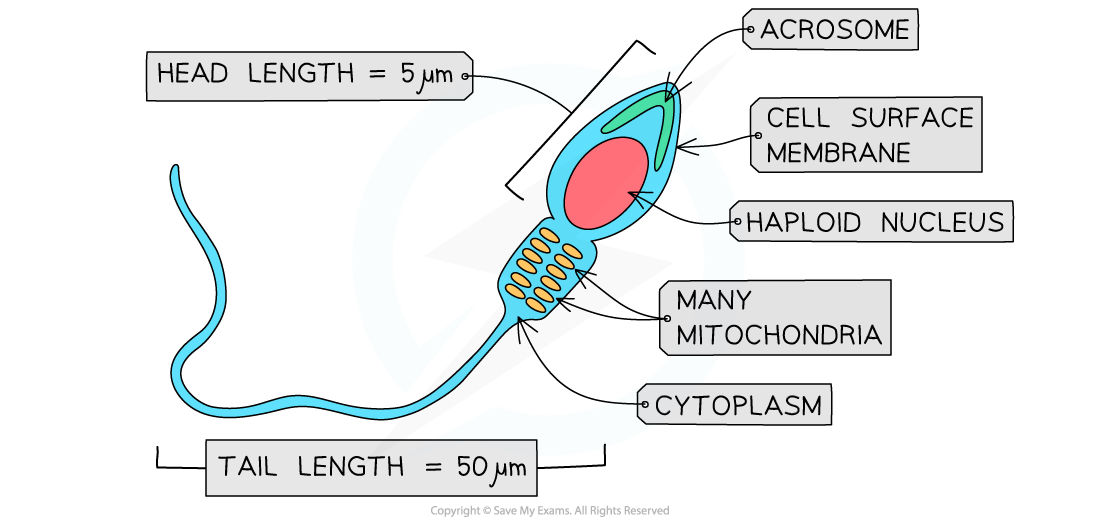
Sperm cells are specialised to enable movement towards and entry into the ovum
Egg Cells
Special features of ova that relate to function include
A haploid nucleus that can fuse with a sperm cell nucleus to form a diploid zygote
The final stage of meiosis is only completed after fertilisation
A surrounding jelly layer, or zona pellucida, that can harden to prevent polyspermy (when the ovum is penetrated by more than one sperm, this can affect embryo development)
Follicle cells which nourish and protect the ova
A series of vesicles, or cortical granules, containing digestive enzymes that are released into the zona pellucida to prevent polyspermy
A cytoplasm rich in nutrients for the developing embryo after fertilisation
Diagram to show the Structure of an Egg Cell

Ova are specialised to prevent polyspermy and aid development of the embryo

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?