Hormones in Pregnancy (DP IB Biology): Revision Note
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Shortly after the developing embryo implants into the endometrium it begins secretion of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG is secreted during the first 8-10 weeks of pregnancy
The role of this hormone is to:
Stimulate the corpus luteum in the ovary to maintain secretion of oestrogen and progesterone (in order to continue the development of the endometrium)
Stimulate the growth of the placenta and uterine enlargement
Inhibit menstruation
During the second trimester (after 12 weeks) hCG declines and the placenta takes over the role of stimulating the secretion of oestrogen and progesterone
Pregnancy tests detect the presence of hCG in the mother's urine and can be used to confirm a positive pregnancy
Hormone changes during pregnancy graph

hCG increases during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy to stimulate the release of oestrogen and progesterone; after 12 weeks hCG declines as the placenta takes over
Pregnancy tests
The confirmation of a pregnancy during the early stages can be through the presence of hCG
This is detected in the the mother's blood and urine
A pregnancy test kit makes use of a specific type of antibody called a monoclonal antibody (mAb) which is used to detect the presence of hCG
Monoclonal antibody is a single antibody that can be used outside of the body and will react to a specific antigen, in this hCG
When using a pregnancy test the mother will urinate onto the test strip, the urine will contain higher levels of hCG if the mother is pregnant
The urine, containing the hCG will travel along the test strip of the pregnancy test; the test strip contains the monoclonal antibodies which bind to the hCG (if present) and lead to a colour change within the pregnancy test which can be seen and inform the mother that she is pregnant
If there is no colour change it means that hCG is not present (in high enough concentrations) to bind to the monoclonal antibodies and give the colour change
Pregnancy test diagram


Monoclonal antibodies are used to detect the presence of the hormone hCG in the urine of pregnant women
Hormonal Control of Pregnancy & Birth
The role of progesterone
The hormone progesterone is secreted by the placenta throughout pregnancy
Progesterone inhibits the production of another hormone, oxytocin, by the pituitary gland
Progesterone inhibits contractions of the muscles of the uterus wall (the myometrium), which could induce birth if not inhibited
At the end of pregnancy, the foetus produces the hormone oestrogen, which signals to the placenta to stop producing progesterone, thereby initiating the production of oxytocin by the pituitary gland and the start of labour (and the start of the muscular contractions that eventually lead to the birth of the baby)
The role of oestrogen
At the end of pregnancy, the hormone oestrogen is produced by the foetus and the placenta
Oestrogen makes the uterine wall more sensitive to oxytocin
Progesterone is also inhibited by oestrogen
Labour
Oxytocin now stimulates contractions of the muscles in the myometrium
Oxytocin is released by the pituitary gland in the brain
Stretch receptors in the cervix detect the contractions and signal the pituitary gland to increase oxytocin secretion
More oxytocin creates further contractions, which in turn signal for further release of oxytocin in this positive feedback loop
This process increases the contractions slowly and rhythmically
Positive feedback loop diagram
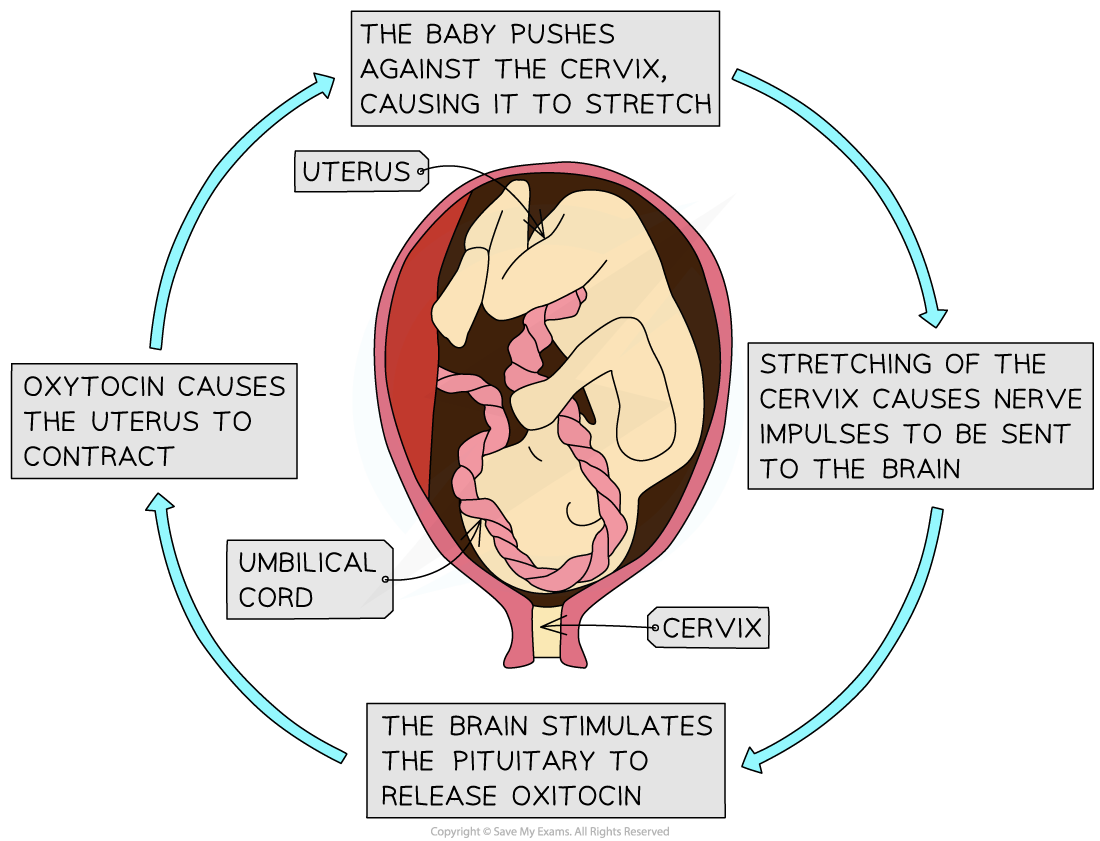
The positive feedback loop stimulates the release of oxytocin and causes the contraction of the uterus wall
Birth
Relaxation of the cervix muscles causes the cervix to dilate and widen
Uterine contractions continue and cause the amniotic sac to burst, releasing the amniotic fluid through the open cervix
The baby is pushed out through the cervix and vagina as contractions continue
As the umbilical cord is cut, the baby is physiologically separated from the mother
Afterbirth
After the baby has been delivered, uterine contractions continue and the placenta will separate from the uterine wall
The mother will then birth the placenta and remains of the umbilical cord
Stages of birth diagram

The stages of birth, which are initiated by the hormone oxytocin

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?