Resistance (OCR AS Physics) : Revision Note
Resistance
Resistance is defined as the opposition to current
For a given potential difference: The higher the resistance the lower the current
Wires are often made from copper because copper has a low electrical resistance
Materials with low resistance are known as good conductors
The resistance R of a conductor is defined as the ratio of the potential difference V across to the current I in it

Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω)
Ω is the Greek capital letter 'Omega'
An Ohm is defined as one volt per ampere (1 V A-1)
The resistance controls the size of the current in a circuit
A higher resistance means a smaller current
A lower resistance means a larger current
All electrical components, including wires, have some value of resistance
Worked Example
Calculate the potential difference through a resistor of resistance 10 Ω if there is a current of 0.3 A through it.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Resistance, R = 10 Ω
Current, I = 0.3 A
Step 2: Write the resistance equation
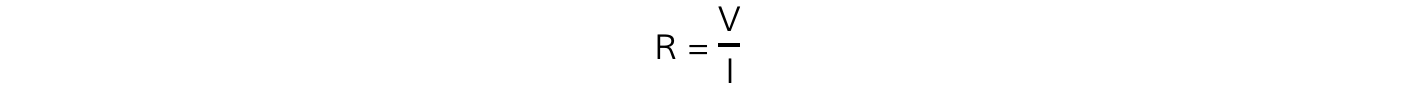
Step 3: Rearrange for V
V = IR
Step 4: Substitute in the values
V = 0.3 × 10 = 3 V
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although all electrical components have resistance, the resistance of wires is taken to be 0 in exam questions.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
