Calculating Electric Current & Charge (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Calculating electric charge
Current can also be defined as the charge passing through a circuit per unit time
Electric charge is measured in units of coulombs (C)
Charge, current and time are related by the following equation:
Q = It
Where:
Q = charge (C)
I = current (A)
t = time (s)
Worked Example
When will 8 mA of current pass through an electrical circuit?
A. When 1 J of energy is used by 1 C of charge
B. When a charge of 4 C passes in 500 s
C. When a charge of 8 C passes in 100 s
D. When a charge of 1 C passes in 8 s
Answer: B
Step 1: Write out the equation relating current, charge and time
Step 2: Rule out any obviously incorrect options
Option A does not contain time, so can be ruled out
Step 3: Try the rest of the options to determine the correct answer
Consider option B:
I = 4 ÷ 500 = 8 × 10–3 = 8 mA
Consider option C:
I = 8 ÷ 100 = 80 × 10–3 = 80 mA
Consider option D:
I = 1 ÷ 8 = 125 × 10–3 = 125 mA
Therefore, the correct answer is B
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although electric charge can be positive or negative, since the conventional direction of current is the flow of positive charge the current should always be a positive value for your exam answers.
Calculating current in a current carrying conductor
In a conductor, current is due to the movement of charge carriers
These charge carriers can be negative or positive; however, the conventional current is always taken to be the flow of positive charge from the positive terminal toward the negative terminal
In conductors, the charge carrier is usually free electrons
In the image below, the conventional current in each conductor flows from right to left but the charge carriers move in the opposite direction, as shown by the direction of the drift speed v
In diagram A, the drift speed refers to the speed of the positive charge as if it were flowing through the conductor
In diagram B, the drift speed refers to the speed of the negative charge carriers actually flowing through the conductor
The effect is the same, which is why the model of positive charge flow works, despite it not being accurate
Current in a current carrying conductor
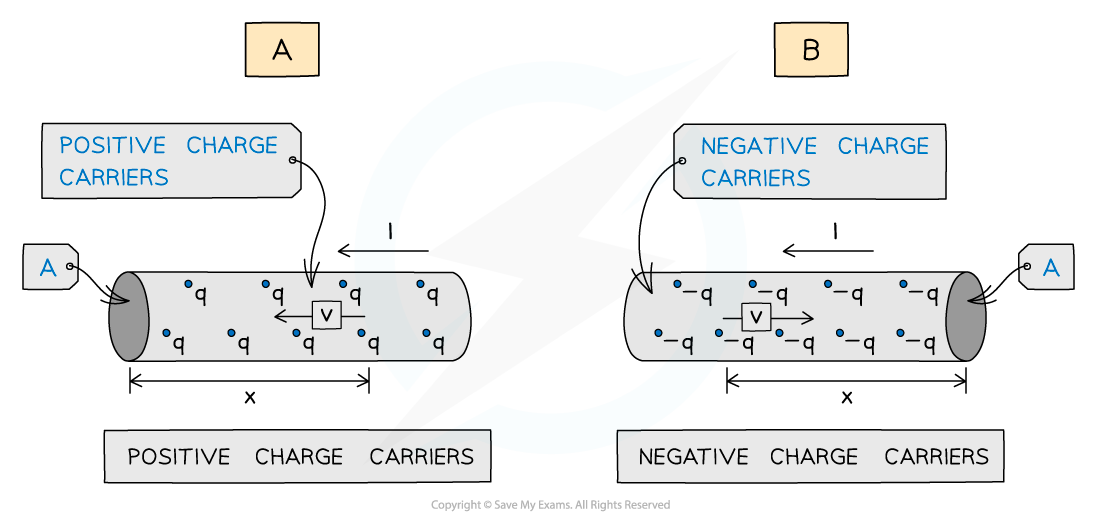
The charge carriers move in opposite directions, as shown by the direction of the drift speed v.
The drift speed is the average speed of the charge carriers travelling through the conductor
This value is quite slow (only about a cm per s)
However, since the number density of charge carriers is so large, current is seen to flow instantaneously
The current can be expressed in terms of the number density (number of charge carriers per unit volume) n, the cross-sectional area A, the drift speed v and the charge of the charge carriers q
I = Anvq
I = current (A)
A = cross-sectional area (m2)
n = number density of charge carriers (m-3)
v = average drift speed of charge carriers (ms-1)
q = charge of each charge carrier (C)
The same equation is used whether the charge carriers are positive or negative
Worked Example
A copper wire has 9.2 × 1028 free electrons m-3. The wire has a current of 3.5 A and a cross-sectional area of 1.5 mm2.
Calculate the average drift speed of the electrons.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Number density of charge carriers,
Current,
Cross-sectional area,
Charge on an electron,
Step 2: State the current in a conductor equation
Step 3: Rearrange for drift speed v
Step 4: Substitute in values

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?