Interference & Coherence (Cambridge (CIE) AS Physics) : Revision Note
Interference & coherence
Interference
Interference occurs when waves overlap and their resultant displacement is the sum of the displacement of each wave
This result is based on the principle of superposition and the resultant waves may be smaller or larger than either of the two individual waves
Interference of two waves can either be:
In phase, causing constructive interference. The peaks and troughs line up on both waves. The resultant wave has double the amplitude
In anti-phase, causing destructive interference. The peaks on one wave line up with the troughs of the other. The resultant wave has no amplitude
Constructive and destructive interference
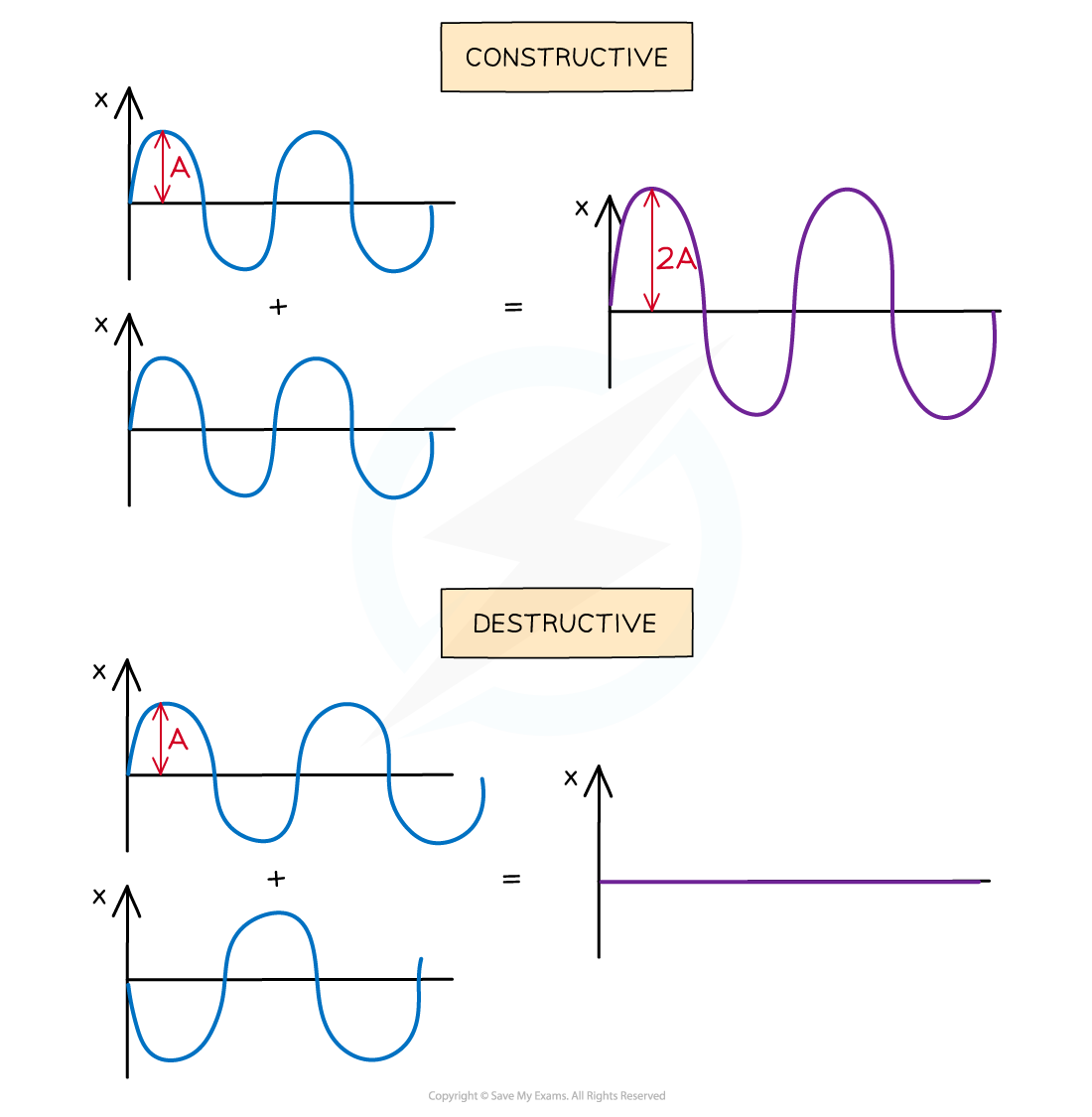
Waves in superposition can undergo constructive or destructive interference
Conditions for constructive and destructive interference
In general, for waves emitted by two coherent sources very close together:
The condition for constructive interference is:
path difference =
The condition for destructive interference is:
path difference =
Where:
λ = wavelength of the waves in metres (m)
n = 0, 1, 2, 3... (any other integer)
Coherence
At points where the two waves are neither in phase nor in antiphase, the resultant amplitude is somewhere in between the two extremes
Waves are coherent if they have the same frequency and constant phase difference
Coherent vs. incoherent waves
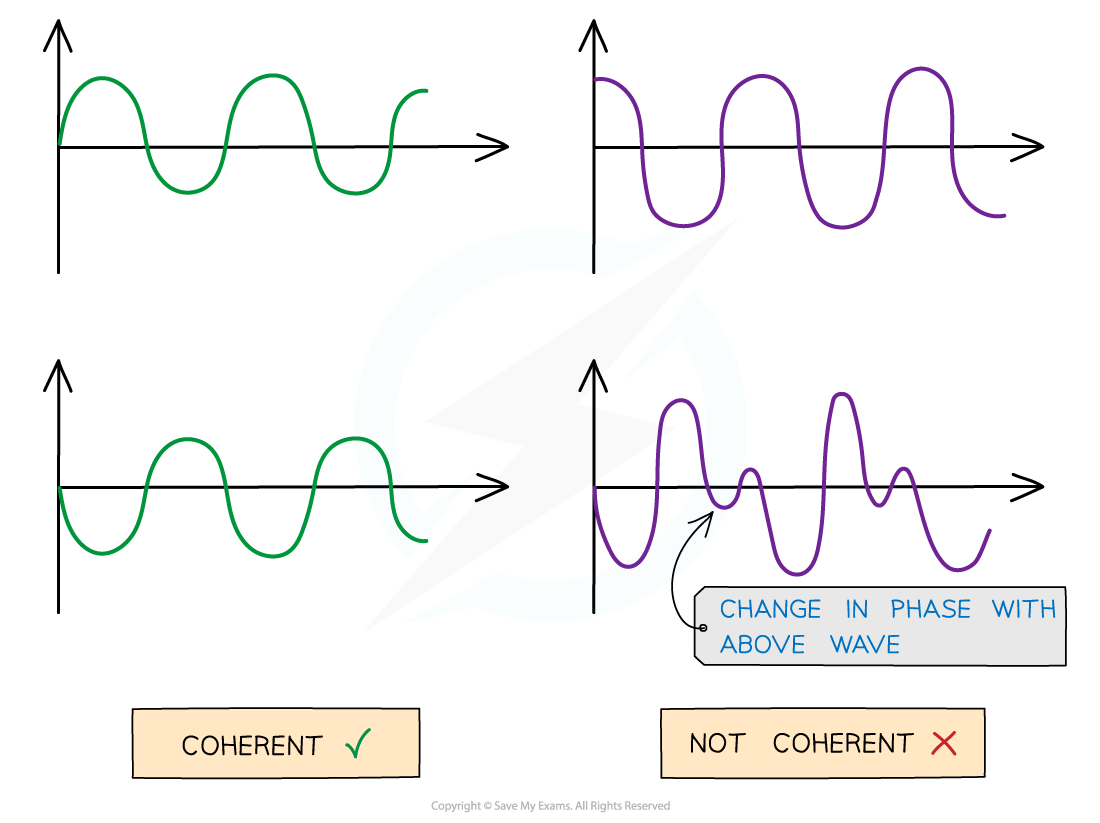
Coherent v non-coherent wave. The abrupt change in phase creates an inconsistent phase difference
Coherence is vital in order to produce an observable interference pattern
Laser light is an example of a coherent light source, whereas filament lamps produce incoherent light waves
Worked Example
The diagram shows the interferences of coherent waves from two point sources.
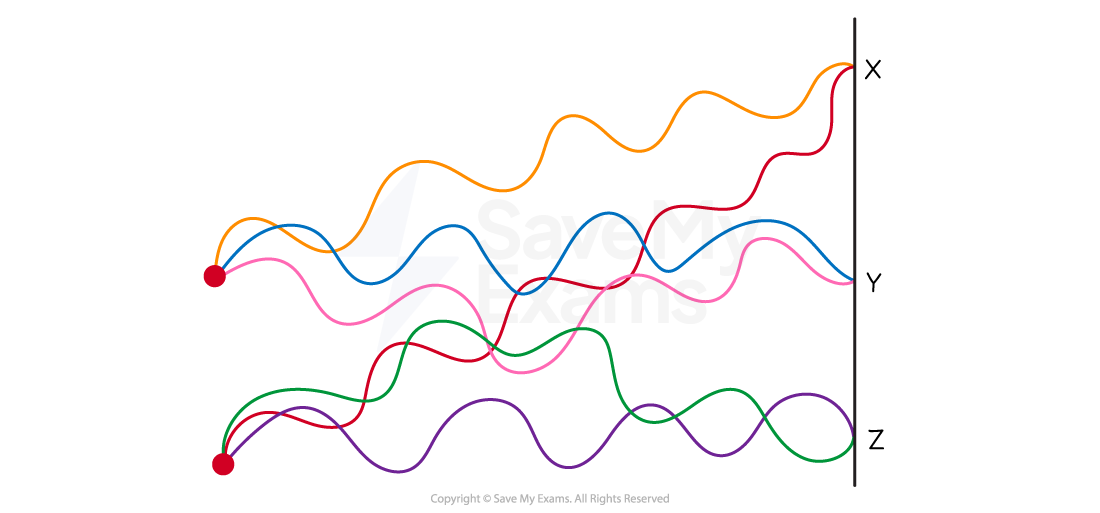

Which row in the table correctly identifies the type of interference at points X, Y and Z.
| X | Y | Z |
A | Constructive | Destructive | Constructive |
B | Constructive | Constructive | Destructive |
C | Destructive | Constructive | Destructive |
D | Destructive | Constructive | Constructive |
Answer: B
At point X:
Both peaks of the waves are overlapping. This is constructive interference and rules out options C and D
At point Y:
Both troughs are overlapping so constructive interference occurs there
At point Z:
A peak of one of the waves meets the trough of the other. This is destructive interference (Row B)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Think of ‘constructive’ interference as ‘building’ the wave and ‘destructive’ interference as ‘destroying’ the wave.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
